YouTube Ads are a versatile advertising solution on the world's largest video platform, allowing businesses to connect with billions of users. Here's a breakdown: 1. Types of YouTube Ads - TrueView Ads: Skippable video ads that appear before, during, or...
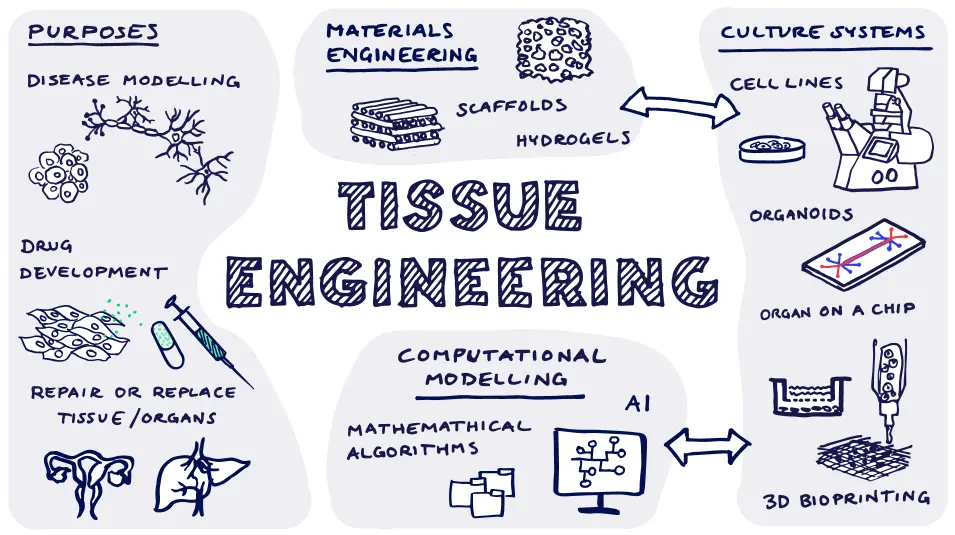
Tissue Engineering is a multidisciplinary field that combines principles of engineering, biology, and medicine to develop biological substitutes for repairing or replacing damaged tissues and organs. It emerged in the late 20th century, with key milestones including the first successful...
Sports Law is a specialized field that encompasses the legal principles, regulations, and frameworks governing the sports industry. It addresses the intersection of law with athletic activities, organizations, and events, drawing from contract law, labor law, intellectual property, and international...
Transportation Engineering is a branch of civil engineering focused on the planning, design, construction, operation, and maintenance of transportation systems. It encompasses various modes of transport, including roadways, railways, airways, waterways, and pipelines, aiming to ensure efficient, safe, and sustainable...
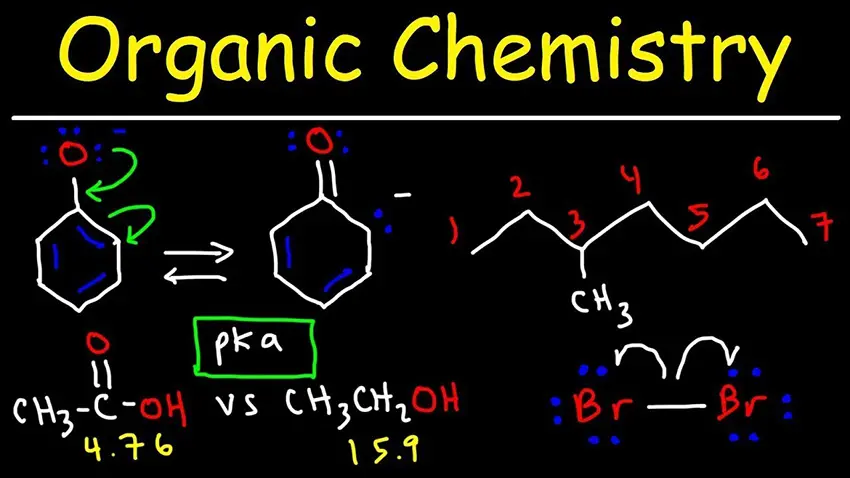
Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the study of carbon-based compounds, which are also known as organic compounds. Carbon is a unique element that can form stable covalent bonds with other carbon atoms and various other...
Chemical spill safety involves protocols to prevent, respond to, and mitigate the risks associated with accidental releases of hazardous substances. These incidents can occur in laboratories, industrial settings, or transportation, posing threats such as fires, explosions, toxic exposure, environmental contamination,...
Food safety plays a critical role in safeguarding public health. Contaminated or unsafe food can lead to foodborne illnesses, causing various health issues such as food poisoning, gastrointestinal infections, and even long-term health complications. By implementing food safety measures, the...
WooCommerce Variations is a powerful feature that enables online stores to offer customizable product options, such as different sizes, colors, materials, or any other attributes, all within a single product listing. This functionality helps streamline inventory management and enhances the...
Google Local Inventory Ads (LIAs) are a specialized advertising feature within Google Ads designed for brick-and-mortar retailers to showcase in-store product availability directly in Google search results. These ads highlight products that are physically available at nearby stores, helping to...
Earthquake engineering is a specialized branch of civil engineering focused on designing and constructing structures that can withstand the destructive forces of seismic events. It involves analyzing ground motion, seismic waves, and the dynamic behavior of buildings, bridges, dams, and...