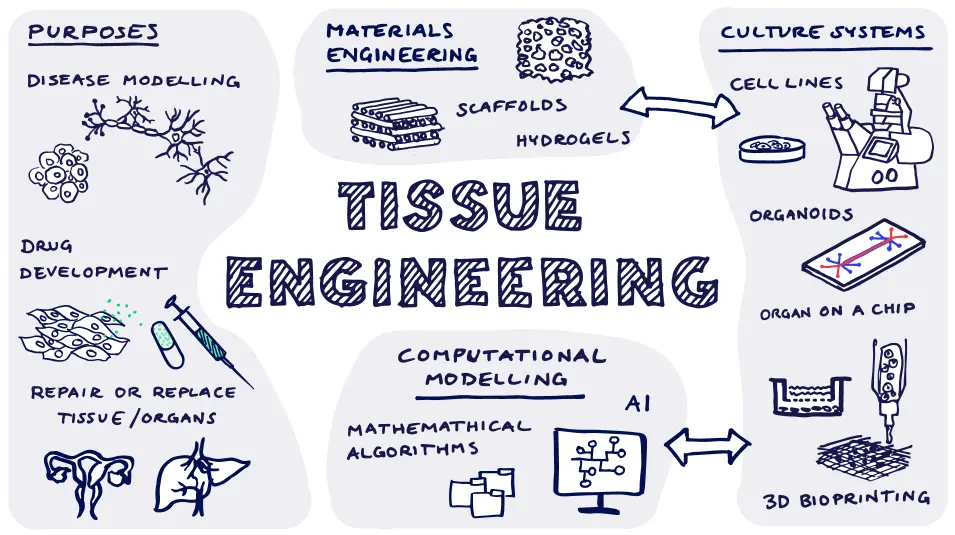
Tissue Engineering is a multidisciplinary field that combines principles of engineering, biology, and medicine to develop biological substitutes for repairing or replacing damaged tissues and organs. It emerged in the late 20th century, with key milestones including the first successful tissue-engineered skin grafts in the 1980s and the coining of the term by researchers like Robert Langer and Joseph Vacanti in 1993.
The core principles involve three main components: cells (such as stem cells or progenitor cells), scaffolds (biodegradable materials that provide a framework for cell growth), and bioactive molecules (like growth factors that stimulate tissue development). These elements work together to mimic the natural extracellular matrix, enabling cells to proliferate, differentiate, and form functional tissue.
Applications are vast and include regenerative medicine for skin, bone, cartilage, blood vessels, and organs like the liver or heart. For instance, tissue-engineered skin has been used for burn victims, while cartilage scaffolds help treat joint injuries. It also holds promise for personalized medicine, such as 3D-printed organs tailored to individual patients.
Challenges include achieving vascularization in thick tissues, ensuring biocompatibility, and scaling up for clinical use. Ongoing advancements, such as bioprinting and gene editing, are addressing these issues, paving the way for future innovations like fully functional bioartificial organs and reduced reliance on donor transplants.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and Share Tissue Engineering Quiz with AI Automatically
- Part 2: 20 Tissue Engineering Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: Try OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to Create Quiz Questions
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and Share Tissue Engineering Quiz with AI Automatically
OnlineExamMaker is a powerful AI-powered assessment platform to create auto-grading Tissue Engineering skills assessments. It’s designed for educators, trainers, businesses, and anyone looking to generate engaging quizzes without spending hours crafting questions manually. The AI Question Generator feature allows you to input a topic or specific details, and it generates a variety of question types automatically.
Top features for assessment organizers:
● Prevent cheating by randomizing questions or changing the order of questions, so learners don’t get the same set of questions each time.
● AI Exam Grader for efficiently grading quizzes and assignments, offering inline comments, automatic scoring, and “fudge points” for manual adjustments.
● Embed quizzes on websites, blogs, or share via email, social media (Facebook, Twitter), or direct links.
● Handles large-scale testing (thousands of exams/semester) without internet dependency, backed by cloud infrastructure.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Tissue Engineering Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. What is the primary goal of tissue engineering?
A) To replace damaged tissues with synthetic materials
B) To create functional tissues from cells, scaffolds, and bioactive molecules
C) To study the genetic makeup of tissues
D) To prevent tissue damage through vaccination
Answer: B
Explanation: Tissue engineering aims to regenerate or replace damaged tissues by combining cells, scaffolds, and signaling molecules to mimic natural tissue formation.
2. Which of the following is a key component in tissue engineering?
A) Antibiotics
B) Scaffolds
C) Vaccines
D) Hormones
Answer: B
Explanation: Scaffolds provide a structural framework for cells to attach, proliferate, and differentiate, which is essential for tissue development.
3. What role do stem cells play in tissue engineering?
A) They provide energy for cell growth
B) They can differentiate into various cell types to form tissues
C) They are used only for immune responses
D) They break down scaffolds
Answer: B
Explanation: Stem cells are versatile and can be directed to become specific cell types, making them crucial for regenerating diverse tissues.
4. Which biomaterial is commonly used as a scaffold in tissue engineering?
A) Glass
B) Polycaprolactone (PCL)
C) Steel
D) Rubber
Answer: B
Explanation: PCL is a biodegradable polymer that supports cell growth and degrades over time, allowing for natural tissue integration.
5. What is decellularization in tissue engineering?
A) Adding cells to a scaffold
B) Removing cells from a tissue while preserving the extracellular matrix
C) Freezing tissues for storage
D) Injecting growth factors
Answer: B
Explanation: Decellularization creates a natural scaffold by stripping away cells, reducing immunogenicity while maintaining the tissue’s architecture.
6. How do growth factors contribute to tissue engineering?
A) They provide structural support
B) They stimulate cell proliferation and differentiation
C) They replace scaffolds
D) They inhibit cell growth
Answer: B
Explanation: Growth factors are signaling proteins that guide cellular processes like division and specialization, essential for tissue formation.
7. What is a bioreactor in tissue engineering?
A) A device for storing tissues
B) A system that provides a controlled environment for tissue growth
C) A tool for genetic modification
D) A method for tissue disposal
Answer: B
Explanation: Bioreactors simulate physiological conditions, such as nutrient supply and mechanical forces, to promote effective tissue development.
8. Which technique is used to create 3D tissue structures?
A) 2D cell culturing
B) Bioprinting
C) Simple injection
D) Freezing
Answer: B
Explanation: Bioprinting layers cells and biomaterials precisely to form complex 3D structures, mimicking natural tissue organization.
9. What challenges are associated with vascularization in tissue engineering?
A) Overgrowth of cells
B) Ensuring adequate blood supply to thick tissues
C) Excessive scaffold degradation
D) High costs of materials
Answer: B
Explanation: Vascularization is critical for delivering oxygen and nutrients; poor vascularization can lead to tissue necrosis in larger engineered constructs.
10. Which type of tissue is most commonly engineered for skin repair?
A) Bone
B) Dermal substitutes
C) Muscle
D) Neural tissue
Answer: B
Explanation: Dermal substitutes, made from cells and scaffolds, are used to treat burns and wounds by promoting skin regeneration.
11. What is the function of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in tissue engineering?
A) To store nutrients
B) To provide a supportive environment for cells
C) To generate electricity
D) To block cell signals
Answer: B
Explanation: The ECM offers structural and biochemical support, influencing cell behavior and tissue organization in engineered constructs.
12. How does mechanical stimulation affect tissue engineering?
A) It has no effect
B) It can enhance cell alignment and tissue strength
C) It destroys scaffolds
D) It reduces cell viability
Answer: B
Explanation: Mechanical forces, like shear stress, mimic in vivo conditions and promote proper tissue maturation, such as in bone or muscle engineering.
13. What is immunomodulation in tissue engineering?
A) Controlling immune responses to prevent rejection
B) Increasing immune activity
C) Removing all immune cells
D) Adding foreign proteins
Answer: A
Explanation: Immunomodulation strategies, such as using anti-inflammatory materials, help integrate engineered tissues without triggering host rejection.
14. Which cell source is autologous in tissue engineering?
A) From a donor
B) From the patient’s own body
C) From animal sources
D) From synthetic origins
Answer: B
Explanation: Autologous cells, derived from the patient, minimize immune rejection and are ideal for personalized tissue engineering.
15. What is the significance of porosity in scaffolds?
A) It makes scaffolds heavier
B) It allows for nutrient diffusion and cell infiltration
C) It prevents cell attachment
D) It increases cost
Answer: B
Explanation: Porosity enables the exchange of gases, nutrients, and waste, which is vital for cell survival and tissue integration within scaffolds.
16. In tissue engineering, what is cartilage regeneration often achieved through?
A) Metal implants
B) Chondrocyte seeding on scaffolds
C) Electrical stimulation
D) Antibiotic treatment
Answer: B
Explanation: Chondrocytes, the cells in cartilage, are seeded onto scaffolds to form new cartilage tissue, addressing conditions like osteoarthritis.
17. How does gene therapy enhance tissue engineering?
A) By altering the scaffold material
B) By delivering genes to cells for improved function
C) By removing genes from tissues
D) By blocking protein synthesis
Answer: B
Explanation: Gene therapy introduces therapeutic genes into cells, enhancing their ability to produce necessary proteins for tissue repair.
18. What ethical concern is associated with embryonic stem cells in tissue engineering?
A) High cost of production
B) Potential for tumor formation
C) The use of human embryos
D) Material toxicity
Answer: C
Explanation: The derivation of embryonic stem cells involves destroying embryos, raising ethical issues about the beginning of human life.
19. Which application of tissue engineering involves organ printing?
A) Drug testing
B) Creating replacement organs like kidneys
C) Storing blood samples
D) Treating infections
Answer: B
Explanation: Organ printing uses bioprinting to fabricate functional organs, addressing the shortage of donor organs for transplantation.
20. What is the role of nanotechnology in tissue engineering?
A) To create large-scale tissues
B) To design nanomaterials for targeted drug delivery and enhanced scaffolds
C) To eliminate cells
D) To increase tissue rigidity
Answer: B
Explanation: Nanotechnology allows for the development of precise, nanoscale features in scaffolds and delivery systems, improving tissue regeneration outcomes.
or
Part 3: Try OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to Create Quiz Questions
Automatically generate questions using AI