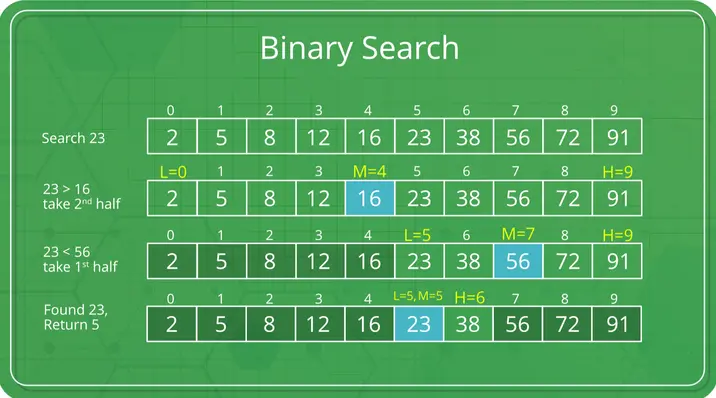
Binary Search is an efficient algorithm used to find the position of a target value within a sorted array. It works by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half, comparing the target value to the middle element of the array. If the target matches the middle element, the search is successful. If the target is less than the middle element, the algorithm continues searching in the lower half; if greater, it searches in the upper half. This process repeats until the target is found or the search interval is empty. The algorithm requires the array to be sorted and operates with a time complexity of O(log n), making it ideal for large datasets.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and Share Binary Search Quiz with AI Automatically
- Part 2: 20 Binary Search Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and Share Binary Search Quiz with AI Automatically
The quickest way to assess the Binary Search knowledge of candidates is using an AI assessment platform like OnlineExamMaker. With OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, you are able to input content—like text, documents, or topics—and then automatically generate questions in various formats (multiple-choice, true/false, short answer). Its AI Exam Grader can automatically grade the exam and generate insightful reports after your candidate submit the assessment.
What you will like:
● Create a question pool through the question bank and specify how many questions you want to be randomly selected among these questions.
● Allow the quiz taker to answer by uploading video or a Word document, adding an image, and recording an audio file.
● Display the feedback for correct or incorrect answers instantly after a question is answered.
● Create a lead generation form to collect an exam taker’s information, such as email, mobile phone, work title, company profile and so on.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Binary Search Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is the primary condition required for using Binary Search on an array?
A) The array must be unsorted
B) The array must be sorted
C) The array must contain duplicate elements
D) The array must be empty
Answer: B
Explanation: Binary Search requires a sorted array to efficiently divide the search space in half by comparing the target with the middle element.
2. Question: In Binary Search, what happens when the target element is equal to the middle element of the array?
A) The search continues on the left half
B) The search continues on the right half
C) The element is found and the search ends
D) The array is reshuffled
Answer: C
Explanation: If the target matches the middle element, Binary Search returns the index immediately, as the element has been located.
3. Question: What is the time complexity of Binary Search in the best case?
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(log n)
D) O(n^2)
Answer: A
Explanation: In the best case, if the target is the middle element, Binary Search finds it in constant time, O(1).
4. Question: For an array of 16 elements, how many comparisons does Binary Search make in the worst case to find an element?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
Answer: B
Explanation: Binary Search halves the array each time; for 16 elements, it takes 4 divisions (2^4 = 16), so up to 4 comparisons in the worst case.
5. Question: Which of the following is NOT a step in the Binary Search algorithm?
A) Compare the target with the middle element
B) Divide the array into two halves
C) Sort the array if it’s not already sorted
D) Repeat the process on the appropriate half
Answer: C
Explanation: Binary Search assumes the array is already sorted; sorting is not part of the algorithm itself.
6. Question: What is the space complexity of an iterative Binary Search?
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(log n)
D) O(n log n)
Answer: A
Explanation: Iterative Binary Search uses a constant amount of extra space, regardless of the input size, making its space complexity O(1).
7. Question: In a sorted array [1, 3, 5, 7, 9], what is the middle element when searching for 5?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 5
D) 7
Answer: C
Explanation: For an array of 5 elements, the middle index is 2 (0-based), which corresponds to the element 5.
8. Question: Binary Search can be implemented using which of the following methods?
A) Recursion only
B) Iteration only
C) Both recursion and iteration
D) Neither recursion nor iteration
Answer: C
Explanation: Binary Search can be implemented iteratively with a loop or recursively by calling the function on subarrays.
9. Question: What is the worst-case time complexity of Binary Search?
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(log n)
D) O(n log n)
Answer: C
Explanation: In the worst case, Binary Search requires logarithmic comparisons, resulting in O(log n) time complexity.
10. Question: If a sorted array has an even number of elements, how is the middle element selected in Binary Search?
A) The first of the two middle elements
B) The second of the two middle elements
C) The average of the two middle elements
D) It depends on the programming language
Answer: A or B (typically the lower middle)
Explanation: Most implementations choose the lower middle index (e.g., for indices 0-3, middle is 1), but consistency in calculation ensures correctness.
11. Question: Which searching algorithm is Binary Search generally faster than for large sorted arrays?
A) Linear Search
B) Depth-First Search
C) Breadth-First Search
D) Quick Sort
Answer: A
Explanation: Binary Search is faster than Linear Search on sorted arrays because it reduces the search space exponentially with each step.
12. Question: In Binary Search, if the target is less than the middle element, where does the search continue?
A) The right half of the array
B) The left half of the array
C) The entire array
D) A random half
Answer: B
Explanation: If the target is smaller than the middle element, it must be in the left subarray, so the search narrows to that half.
13. Question: What would happen if you apply Binary Search on an unsorted array?
A) It will still work correctly
B) It may return incorrect results
C) It will sort the array first
D) It will throw an error
Answer: B
Explanation: Binary Search assumes a sorted array; on an unsorted one, it might not find the element or return the wrong index.
14. Question: For a sorted array of 1 element, how many steps does Binary Search take to find the element if it exists?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) Depends on the element
Answer: B
Explanation: The array has only one element, so Binary Search will compare the target with it in one step.
15. Question: Binary Search divides the search interval in what manner?
A) By thirds
B) By halves
C) Randomly
D) Sequentially
Answer: B
Explanation: It repeatedly divides the sorted array into two halves until the target is found or the interval is empty.
16. Question: What is the average-case time complexity of Binary Search?
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(log n)
D) O(n^2)
Answer: C
Explanation: On average, Binary Search performs logarithmically fewer operations than linear search, resulting in O(log n) complexity.
17. Question: In a recursive implementation of Binary Search, what is passed to the recursive call?
A) The entire array
B) A subarray or its bounds
C) Only the target element
D) Nothing
Answer: B
Explanation: Recursive Binary Search passes the subarray (or low and high indices) to narrow down the search space.
18. Question: Why is Binary Search not suitable for unsorted data?
A) It requires extra memory
B) It assumes the data is ordered
C) It is too slow
D) It only works on strings
Answer: B
Explanation: Binary Search relies on the array being sorted to make accurate comparisons and decisions about which half to search.
19. Question: If Binary Search is applied to a sorted array with duplicates, what might happen?
A) It will always find the first occurrence
B) It may find any occurrence
C) It will throw an error
D) It will sort the array again
Answer: B
Explanation: Standard Binary Search will find one occurrence of the duplicate element, but not necessarily the first or last one.
20. Question: Compared to Linear Search, when is Binary Search most efficient?
A) For small arrays
B) For large sorted arrays
C) For unsorted arrays
D) When the array is partially sorted
Answer: B
Explanation: Binary Search excels with large, sorted datasets due to its logarithmic time complexity, making it more efficient than Linear Search.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI