Powder Metallurgy is a versatile manufacturing process that creates metal parts by compacting fine metal powders into a desired shape and then heating them to fuse the particles together. This technique, known as sintering, allows for the production of complex, high-precision components with minimal waste and excellent material properties. It is particularly advantageous for materials that are difficult to machine, such as tungsten, and is widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics to produce items like gears, bearings, and filters. By enabling cost-effective mass production and consistent quality, Powder Metallurgy offers an efficient alternative to traditional casting or forging methods.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: Best AI Quiz Making Software for Creating A Powder Metallurgy Quiz
- Part 2: 20 Powder Metallurgy Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: Save Time and Energy: Generate Quiz Questions with AI Technology
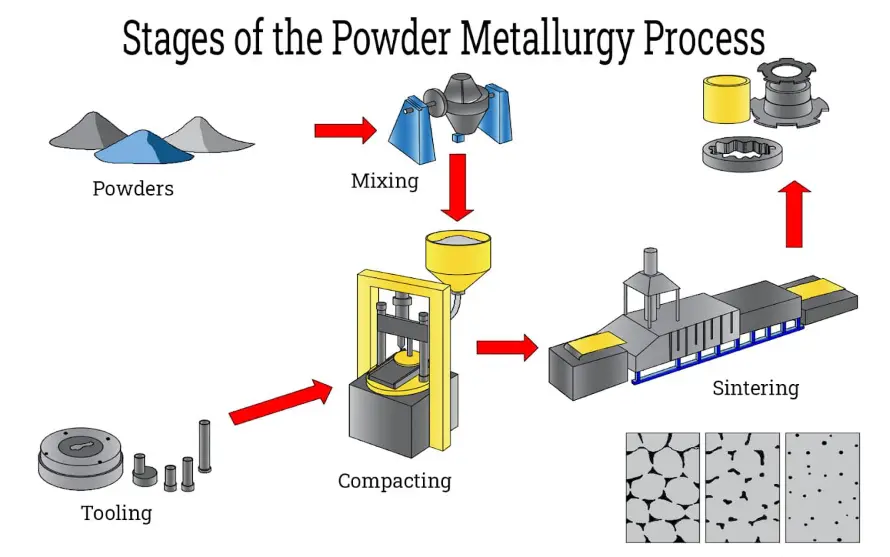
Part 1: Best AI Quiz Making Software for Creating A Powder Metallurgy Quiz
OnlineExamMaker is a powerful AI-powered assessment platform to create auto-grading Powder Metallurgy skills assessments. It’s designed for educators, trainers, businesses, and anyone looking to generate engaging quizzes without spending hours crafting questions manually. The AI Question Generator feature allows you to input a topic or specific details, and it generates a variety of question types automatically.
Top features for assessment organizers:
● Combines AI webcam monitoring to capture cheating activities during online exam.
● Enhances assessments with interactive experience by embedding video, audio, image into quizzes and multimedia feedback.
● Once the exam ends, the exam scores, question reports, ranking and other analytics data can be exported to your device in Excel file format.
● API and SSO help trainers integrate OnlineExamMaker with Google Classroom, Microsoft Teams, CRM and more.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Powder Metallurgy Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. What is the primary raw material used in powder metallurgy?
A) Liquid metal
B) Metal powders
C) Solid metal blocks
D) Metal alloys in molten form
Answer: B
Explanation: Powder metallurgy starts with metal powders as the raw material, which are compacted and sintered to form the final product.
2. Which process involves heating compacted metal powders below their melting point?
A) Forging
B) Sintering
C) Casting
D) Extrusion
Answer: B
Explanation: Sintering bonds the particles in the compacted powder by diffusion at high temperatures below the melting point, strengthening the material.
3. What is the main advantage of powder metallurgy in producing parts?
A) High production speed
B) Ability to produce complex shapes with minimal waste
C) Requirement for large machinery
D) Use of only ferrous metals
Answer: B
Explanation: Powder metallurgy allows for the creation of intricate designs and near-net shapes, reducing material waste compared to traditional methods.
4. Which method is commonly used for producing metal powders?
A) Atomization
B) Welding
C) Rolling
D) Tempering
Answer: A
Explanation: Atomization involves breaking molten metal into fine particles using a high-pressure gas or liquid stream, making it a standard powder production technique.
5. In powder metallurgy, what does compaction do?
A) Melts the powder
B) Increases the density by pressing the powder into a shape
C) Removes impurities
D) Adds lubricants
Answer: B
Explanation: Compaction applies pressure to the metal powder to form a green compact, which is then sintered to achieve the desired density and strength.
6. Which of the following is a disadvantage of powder metallurgy?
A) High dimensional accuracy
B) Porosity in the final product
C) Low cost of production
D) Versatility in materials
Answer: B
Explanation: Porosity can occur if sintering is not perfect, leading to reduced mechanical properties like strength and fatigue resistance.
7. What type of powders are used in powder metallurgy for automotive applications?
A) Ceramic powders
B) Iron-based powders
C) Plastic powders
D) Wooden powders
Answer: B
Explanation: Iron-based powders are widely used in automotive parts due to their strength, cost-effectiveness, and ability to be alloyed for specific properties.
8. Which stage follows compaction in the powder metallurgy process?
A) Machining
B) Sintering
C) Melting
D) Coating
Answer: B
Explanation: After compaction, sintering is performed to fuse the particles together, enhancing the material’s integrity and performance.
9. Powder metallurgy is particularly suitable for which industry?
A) Textile
B) Aerospace
C) Food processing
D) Agriculture
Answer: B
Explanation: The aerospace industry benefits from powder metallurgy for producing lightweight, high-strength components with precise tolerances.
10. What is the role of binders in powder metallurgy?
A) To provide color
B) To hold powders together during compaction
C) To increase melting point
D) To add weight
Answer: B
Explanation: Binders are added to the powder mix to improve flowability and cohesion during the compaction stage, ensuring uniform shaping.
11. Which factor affects the quality of sintered products?
A) Room temperature
B) Sintering atmosphere
C) Powder color
D) Powder size only
Answer: B
Explanation: The sintering atmosphere (e.g., vacuum or inert gas) prevents oxidation and controls the diffusion process, directly impacting the final product’s quality.
12. What is a common application of powder metallurgy?
A) Building bridges
B) Manufacturing porous bearings
C) Creating fabrics
D) Producing glass
Answer: B
Explanation: Powder metallurgy is ideal for making porous bearings, as it allows for controlled porosity to retain lubricants and reduce friction.
13. In powder metallurgy, what does “green compact” refer to?
A) A finished product
B) The compacted powder before sintering
C) Recycled material
D) Liquid metal form
Answer: B
Explanation: The green compact is the shape formed after compaction but before sintering, and it is fragile and not yet fully densified.
14. Which metal is most commonly processed via powder metallurgy?
A) Aluminum
B) Gold
C) Iron
D) Copper
Answer: C
Explanation: Iron is the most common metal used in powder metallurgy due to its abundance, versatility, and ability to form strong alloys.
15. What is the purpose of secondary operations in powder metallurgy?
A) To start the process
B) To enhance properties like surface finish or density
C) To create powders
D) To melt the material
Answer: B
Explanation: Secondary operations, such as sizing or heat treatment, are performed after sintering to improve the mechanical properties and precision of the part.
16. Which powder characteristic influences the final product’s density?
A) Particle shape and size
B) Particle color
C) Odor of the powder
D) Weight of the container
Answer: A
Explanation: The shape and size of powder particles affect how they pack during compaction, directly influencing the density and uniformity of the sintered product.
17. Powder metallurgy can produce parts with what unique feature?
A) High electrical conductivity only
B) Infiltrated structures for composites
C) Soft materials exclusively
D) Large-scale items
Answer: B
Explanation: It allows for the creation of infiltrated structures, where another material is added to fill pores, enhancing properties like strength in composites.
18. What environmental benefit does powder metallurgy offer?
A) High energy consumption
B) Reduced material waste
C) Increased pollution
D) Need for toxic chemicals
Answer: B
Explanation: Powder metallurgy minimizes waste by using precise amounts of material and recycling scraps, making it an environmentally friendly process.
19. Which technique is used to measure powder flowability?
A) Hall flowmeter
B) Thermometer
C) pH meter
D) Scale
Answer: A
Explanation: The Hall flowmeter tests how easily powder flows, which is crucial for ensuring uniform filling during the compaction process.
20. How does powder metallurgy compare to casting in terms of microstructure?
A) Similar grain structure
B) Finer grain structure in powder metallurgy
C) Larger grains in powder metallurgy
D) No grains at all
Answer: B
Explanation: Powder metallurgy often results in a finer grain structure due to the sintering process, leading to improved mechanical properties compared to casting.
or
Part 3: Save Time and Energy: Generate Quiz Questions with AI Technology
Automatically generate questions using AI