Kirchhoff’s laws are fundamental principles in electrical circuit analysis, named after Gustav Kirchhoff. They consist of two key laws:
1. Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL): At any node in a circuit, the total current entering the node equals the total current leaving the node. This is based on the principle of conservation of electric charge.
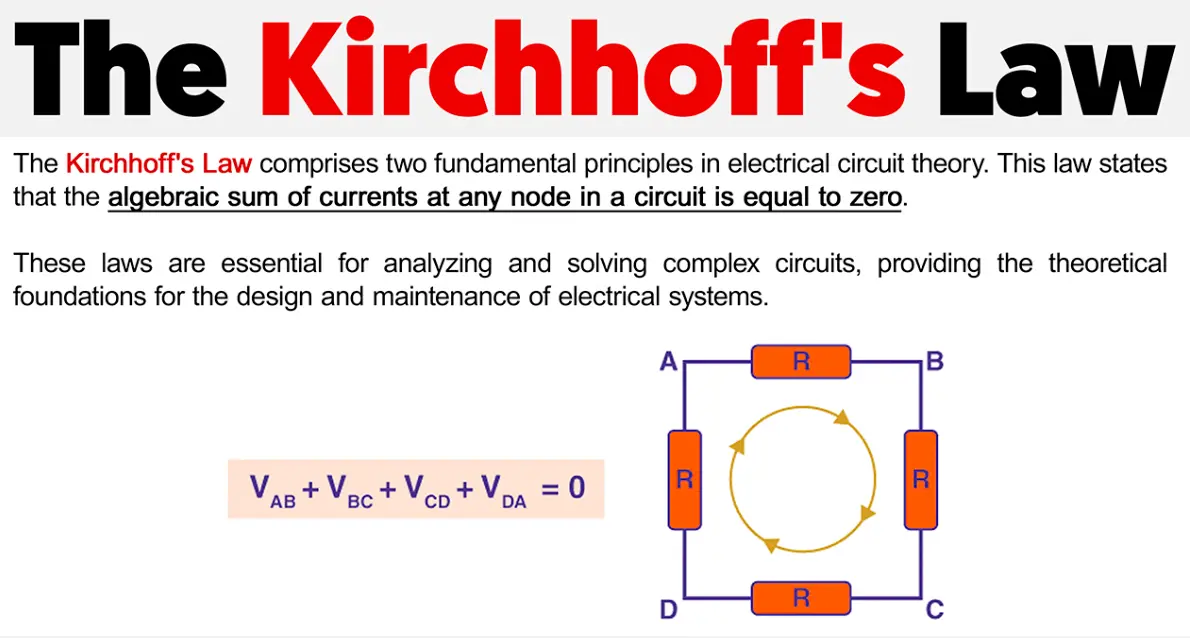
2. Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL): In any closed loop of a circuit, the sum of all voltages (electromotive forces and drops) equals zero. This reflects the conservation of energy around the loop.
These laws are essential for solving complex circuits, enabling the determination of currents and voltages in networks.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Best AI quiz making software for creating a Kirchhoff’s laws quiz
- Part 2: 20 Kirchhoff’s laws quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate questions for any topic
Part 1: Best AI quiz making software for creating a Kirchhoff’s laws quiz
OnlineExamMaker is a powerful AI-powered assessment platform to create auto-grading Kirchhoff’s laws assessments. It’s designed for educators, trainers, businesses, and anyone looking to generate engaging quizzes without spending hours crafting questions manually. The AI Question Generator feature allows you to input a topic or specific details, and it generates a variety of question types automatically.
Top features for assessment organizers:
● Combines AI webcam monitoring to capture cheating activities during online exam.
● Enhances assessments with interactive experience by embedding video, audio, image into quizzes and multimedia feedback.
● Once the exam ends, the exam scores, question reports, ranking and other analytics data can be exported to your device in Excel file format.
● API and SSO help trainers integrate OnlineExamMaker with Google Classroom, Microsoft Teams, CRM and more.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Kirchhoff’s laws quiz questions & answers
or
1. What does Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) state?
A. The sum of voltages in a loop is zero.
B. The total current entering a junction equals the total current leaving it.
C. The voltage drop across a resistor is proportional to the current.
D. The current is the same through all components in series.
Answer: B
Explanation: KCL is based on the conservation of charge, meaning that at any junction in a circuit, the incoming current must equal the outgoing current.
2. In a circuit junction, 5 A enters from one wire, 2 A enters from another, and 4 A leaves through one wire. What is the current leaving through the remaining wire?
A. 1 A
B. 3 A
C. 5 A
D. 7 A
Answer: B
Explanation: According to KCL, total incoming current (5 A + 2 A = 7 A) equals total outgoing current. If 4 A leaves through one wire, then 7 A – 4 A = 3 A leaves through the other.
3. For a closed loop in a circuit with a 10 V battery and a 5 V voltage drop across a resistor, what must be the net voltage if another 5 V drop occurs?
A. 0 V
B. 5 V
C. 10 V
D. 15 V
Answer: A
Explanation: Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law states that the sum of all voltages around a closed loop is zero, so 10 V – 5 V – 5 V = 0 V.
4. In a series circuit, if the voltage across the first resistor is 2 V and across the second is 3 V, what is the battery voltage if the loop is closed?
A. 1 V
B. 5 V
C. 6 V
D. 3 V
Answer: B
Explanation: KVL requires that the sum of voltage drops equals the source voltage in a loop, so 2 V + 3 V = 5 V.
5. A junction has currents of 10 A and 15 A entering, and 12 A leaving. What is the current in the fourth branch?
A. 3 A entering
B. 13 A leaving
C. 5 A entering
D. 7 A leaving
Answer: B
Explanation: KCL states that total incoming current (10 A + 15 A = 25 A) equals total outgoing current. If 12 A leaves through one branch, then 25 A – 12 A = 13 A leaves through the fourth branch.
6. In a loop with two batteries (6 V and 4 V) and a 2 V voltage drop, what is the net voltage?
A. 8 V
B. 0 V
C. 10 V
D. -2 V
Answer: B
Explanation: KVL dictates that the algebraic sum of voltages is zero, so 6 V + 4 V – 2 V – (another voltage to balance) = 0 V, assuming the loop is complete.
7. If 8 A flows into a node and 3 A leaves through one path, how much current must leave through the other two paths combined?
A. 5 A
B. 8 A
C. 11 A
D. 3 A
Answer: A
Explanation: By KCL, total outgoing current must equal incoming current, so if 8 A enters and 3 A leaves through one path, the remaining outgoing current is 8 A – 3 A = 5 A.
8. For a circuit loop with a 12 V source and voltage drops of 4 V and 8 V, what does KVL confirm?
A. The drops exceed the source.
B. The net voltage is zero.
C. There is infinite current.
D. The source is insufficient.
Answer: B
Explanation: KVL ensures that 12 V – 4 V – 8 V = 0 V around the loop.
9. At a junction, currents of 2 A, 4 A, and 1 A are leaving. What must be the incoming current?
A. 7 A
B. 3 A
C. 1 A
D. 5 A
Answer: A
Explanation: KCL requires that total incoming current equals total outgoing current, so the incoming current must be 2 A + 4 A + 1 A = 7 A.
10. In a loop with a 9 V battery and two 3 V drops across resistors, what is the voltage at the end of the loop?
A. 9 V
B. 0 V relative to start
C. 3 V
D. 6 V
Answer: B
Explanation: KVL states that returning to the starting point, the total voltage sum is zero, so 9 V – 3 V – 3 V = 3 V, but the loop closes at zero net.
11. If a node has 6 A entering and currents of 2 A and 1 A leaving, what is the current in the third branch?
A. 3 A entering
B. 5 A leaving
C. 3 A leaving
D. 1 A entering
Answer: C
Explanation: KCL: Total outgoing = incoming, so 2 A + 1 A + x = 6 A, thus x = 6 A – 3 A = 3 A leaving.
12. For a circuit with a 15 V source and 5 V and 10 V drops, what does KVL indicate?
A. Overvoltage
B. Balanced loop
C. Short circuit
D. Open circuit
Answer: B
Explanation: 15 V – 5 V – 10 V = 0 V, confirming the loop is balanced as per KVL.
13. At a junction, 10 A enters, 4 A leaves, and 3 A leaves. What is the current in the fourth wire?
A. 3 A entering
B. 7 A entering
C. 3 A leaving
D. 13 A leaving
Answer: A
Explanation: KCL: 10 A incoming = 4 A outgoing + 3 A outgoing + x, so x = 10 A – 7 A = 3 A entering (as it must balance).
14. In a loop with batteries of 10 V and 5 V (opposing), and a 3 V drop, what is the net?
A. 12 V
B. 0 V
C. 2 V
D. -2 V
Answer: B
Explanation: KVL: 10 V – 5 V – 3 V + (adjustment) = 0 V for a closed loop.
15. A junction sees 7 A entering from one wire and 2 A entering from another. If 4 A leaves, what leaves the third?
A. 5 A
B. 3 A
C. 9 A
D. 1 A
Answer: A
Explanation: Total incoming = 7 A + 2 A = 9 A; total outgoing = 4 A + x = 9 A, so x = 5 A.
16. For a loop with 20 V source and drops of 10 V and 10 V, KVL shows:
A. Net gain of 20 V
B. Zero net voltage
C. Loss of 20 V
D. Infinite voltage
Answer: B
Explanation: 20 V – 10 V – 10 V = 0 V, as required by KVL.
17. If 9 A enters a node and 2 A leaves one path, with 3 A leaving another, what is the third path’s current?
A. 4 A leaving
B. 6 A entering
C. 4 A entering
D. 14 A leaving
Answer: C
Explanation: KCL: 9 A incoming = 2 A outgoing + 3 A outgoing + x; x = 9 A – 5 A = 4 A entering (to balance).
18. In a circuit loop, a 7 V battery and 2 V drop with another 5 V drop result in:
A. 14 V total
B. 0 V net
C. 7 V drop
D. 5 V gain
Answer: B
Explanation: KVL ensures 7 V – 2 V – 5 V = 0 V.
19. At a junction, currents of 5 A and 6 A enter, while 8 A leaves. What is the other leaving current?
A. 3 A
B. 1 A
C. 11 A
D. 3 A entering
Answer: A
Explanation: Total incoming = 5 A + 6 A = 11 A; if 8 A leaves, then 11 A – 8 A = 3 A leaves the other path.
20. For a loop with 8 V source and 4 V drop, plus 4 V drop, KVL confirms:
A. 8 V excess
B. Zero sum
C. Negative voltage
D. Open loop
Answer: B
Explanation: 8 V – 4 V – 4 V = 0 V, satisfying KVL.
or
Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate questions for any topic
Automatically generate questions using AI