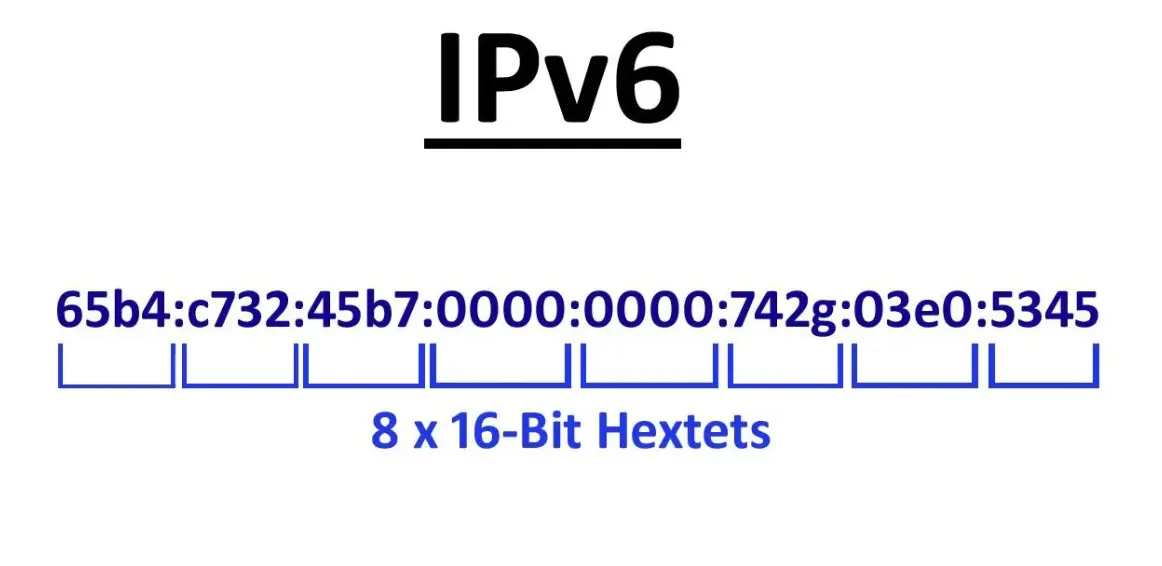
IPv6, or Internet Protocol version 6, is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol, designed to replace IPv4 and address the limitations of its predecessor. It features a 128-bit address space, enabling approximately 3.4 x 10^38 unique addresses, which vastly expands the capacity for connecting devices to the internet and supports the growing number of global users and IoT devices. Unlike IPv4, IPv6 includes built-in security through IPsec, improved header efficiency for faster routing, and enhanced support for multicast and anycast communications. This protocol ensures better network autoconfiguration, reduces the need for Network Address Translation (NAT), and facilitates seamless end-to-end connectivity, making it essential for modern networking infrastructure.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Create an amazing IPv6 quiz using AI instantly in OnlineExamMaker
- Part 2: 20 IPv6 quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Part 1: Create an amazing IPv6 quiz using AI instantly in OnlineExamMaker
The quickest way to assess the IPv6 knowledge of candidates is using an AI assessment platform like OnlineExamMaker. With OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, you are able to input content—like text, documents, or topics—and then automatically generate questions in various formats (multiple-choice, true/false, short answer). Its AI Exam Grader can automatically grade the exam and generate insightful reports after your candidate submit the assessment.
Overview of its key assessment-related features:
● Create up to 10 question types, including multiple-choice, true/false, fill-in-the-blank, matching, short answer, and essay questions.
● Automatically generates detailed reports—individual scores, question report, and group performance.
● Instantly scores objective questions and subjective answers use rubric-based scoring for consistency.
● API and SSO help trainers integrate OnlineExamMaker with Google Classroom, Microsoft Teams, CRM and more.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 IPv6 quiz questions & answers
or
Question 1: What is the length of an IPv6 address?
A) 32 bits
B) 64 bits
C) 128 bits
D) 256 bits
Answer: C
Explanation: An IPv6 address is 128 bits long, allowing for a vastly larger number of unique addresses compared to IPv4.
Question 2: How many hexadecimal digits are typically used to represent an IPv6 address?
A) 16
B) 32
C) 64
D) 128
Answer: B
Explanation: An IPv6 address is represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, totaling 32 characters.
Question 3: What is the IPv6 loopback address?
A) 127.0.0.1
B) ::1
C) 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1
D) FF00::
Answer: B
Explanation: The loopback address in IPv6 is ::1, which is equivalent to 127.0.0.1 in IPv4 and is used for local testing.
Question 4: Which of the following is a valid IPv6 address?
A) 192.168.1.1
B) 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
C) 255.255.255.0
D) 10.0.0.1
Answer: B
Explanation: IPv6 addresses use hexadecimal notation with colons, as in 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334, while the others are IPv4 addresses.
Question 5: What does the “::” notation represent in IPv6?
A) A range of addresses
B) Compression of zeros
C) A multicast address
D) An anycast address
Answer: B
Explanation: The “::” notation is used to compress consecutive zeros in an IPv6 address for brevity.
Question 6: How many bits are allocated for the interface identifier in a standard IPv6 address?
A) 32 bits
B) 64 bits
C) 96 bits
D) 128 bits
Answer: B
Explanation: In IPv6, the interface identifier is typically 64 bits, while the first 64 bits are used for the network prefix.
Question 7: What type of IPv6 address is used for communication on the same local network segment?
A) Global unicast
B) Link-local
C) Unique local
D) Multicast
Answer: B
Explanation: Link-local addresses, starting with FE80::/10, are used for communication within the same local network link.
Question 8: Which IPv6 address type is similar to private IPv4 addresses like 192.168.x.x?
A) Global unicast
B) Unique local
C) Anycast
D) Multicast
Answer: B
Explanation: Unique local addresses (FC00::/7) are designed for private networks, much like IPv4 private addresses.
Question 9: What is the purpose of the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) in IPv6?
A) To route packets between networks
B) To discover neighboring devices and manage addresses
C) To encrypt data packets
D) To assign IP addresses dynamically
Answer: B
Explanation: NDP replaces ARP in IPv6 and is used for functions like address resolution and duplicate address detection.
Question 10: How does IPv6 handle IP address autoconfiguration?
A) Only through DHCPv6
B) Through stateless autoconfiguration using router advertisements
C) Manually by network administrators
D) Via IPv4 compatibility mode
Answer: B
Explanation: Stateless autoconfiguration allows devices to automatically configure their IPv6 addresses based on router advertisements.
Question 11: What is the size of the IPv6 header compared to IPv4?
A) Smaller
B) Larger
C) The same
D) Variable
Answer: A
Explanation: The IPv6 header is fixed at 40 bytes, which is larger than the typical IPv4 header but more efficient due to its streamlined design.
Question 12: Which of the following is an example of an IPv6 multicast address?
A) 2001:db8::1
B) FF02::1
C) FE80::1
D) FC00::1
Answer: B
Explanation: Multicast addresses in IPv6 start with FF00::/8, such as FF02::1, which is used for all nodes on a local network.
Question 13: What is an anycast address in IPv6?
A) An address assigned to a single device
B) An address that can be shared by multiple devices, with packets routed to the nearest one
C) A broadcast address
D) A loopback address
Answer: B
Explanation: Anycast addresses allow multiple interfaces to share the same address, and packets are delivered to the closest instance.
Question 14: Which transition mechanism allows both IPv4 and IPv6 to run on the same network device?
A) Tunneling
B) Dual stack
C) NAT64
D) 6to4
Answer: B
Explanation: Dual stack enables devices to support both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols simultaneously on the same interface.
Question 15: What does ICMPv6 provide that is not in ICMP for IPv4?
A) Only error messaging
B) Neighbor Discovery and Multicast Listener Discovery
C) Routing protocols
D) Address resolution
Answer: B
Explanation: ICMPv6 includes enhanced features like Neighbor Discovery Protocol, which handles tasks previously managed by separate protocols in IPv4.
Question 16: In IPv6, what is the role of the “prefix” in an address?
A) It identifies the device on the network
B) It specifies the network portion of the address
C) It denotes a multicast group
D) It is used for encryption
Answer: B
Explanation: The prefix in an IPv6 address defines the network segment, similar to the network part in an IPv4 address.
Question 17: How many addresses are available in the IPv6 global unicast range?
A) Approximately 2^32
B) Approximately 2^64
C) Approximately 2^128
D) Approximately 2^256
Answer: C
Explanation: The full IPv6 address space is 2^128, and global unicast addresses occupy a significant portion of this vast space.
Question 18: What security feature is built into IPv6 that was optional in IPv4?
A) IPsec
B) Firewalls
C) SSL
D) VPNs
Answer: A
Explanation: IPsec is mandatory in IPv6 for end-to-end encryption and authentication, whereas it was optional in IPv4.
Question 19: Which command is used to test connectivity in IPv6, similar to ping in IPv4?
A) ping6
B) tracert6
C) ipconfig
D) netstat
Answer: A
Explanation: The ping6 command is used in IPv6 to send ICMPv6 echo requests and test if a host is reachable.
Question 20: What is the main advantage of IPv6 over IPv4?
A) Shorter address length
B) Built-in support for mobile devices
C) Larger address space and improved efficiency
D) Faster routing
Answer: C
Explanation: IPv6 provides a much larger address space (128 bits vs. 32 bits) and includes features like simplified header processing for better efficiency.
or
Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Automatically generate questions using AI