A data warehouse is a centralized repository designed for storing, analyzing, and reporting integrated data from multiple sources. It supports business intelligence (BI) activities by enabling efficient querying, decision-making, and data-driven insights.
Key Components
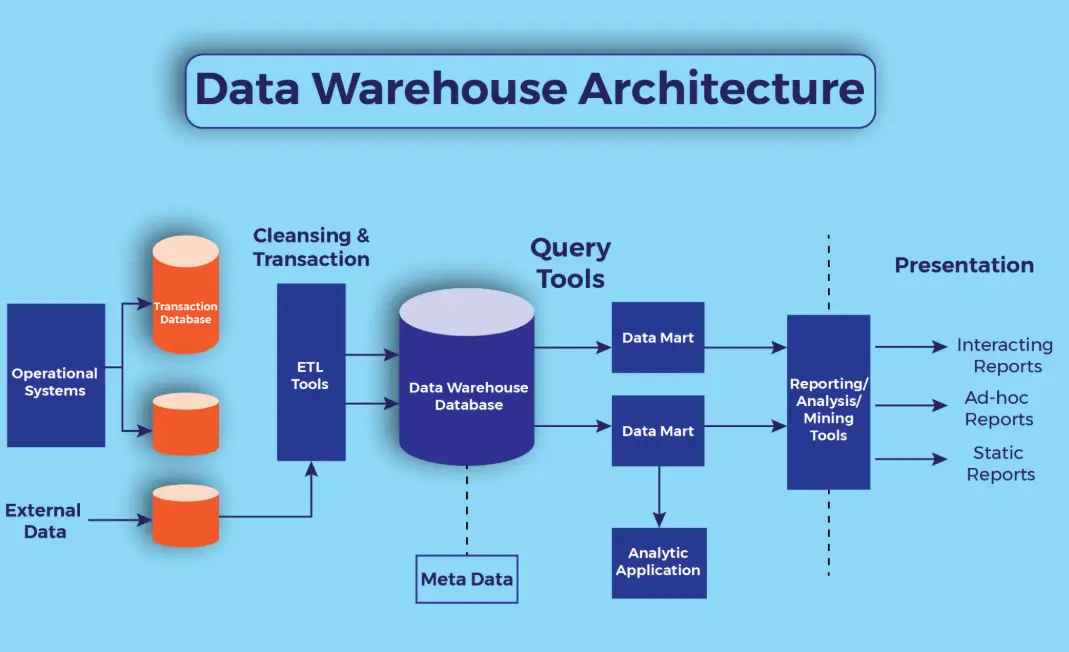
Data Sources: Includes operational databases, external feeds, and other systems that provide raw data.
ETL Processes: Extract, Transform, and Load mechanisms that clean, integrate, and organize data for storage.
Data Storage: Uses structures like star schemas or snowflake schemas to optimize for analytical queries.
OLAP Tools: Online Analytical Processing for multidimensional data analysis, such as slicing, dicing, and drilling down into data.
Reporting and Visualization Tools: Software for generating reports, dashboards, and visualizations to interpret data trends.
Differences from Traditional Databases
Unlike operational databases (e.g., OLTP systems) that handle real-time transactions, data warehouses are optimized for read-heavy operations, supporting complex queries on large datasets without affecting day-to-day business processes.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Best AI quiz making software for creating a data warehouse quiz
- Part 2: 20 data warehouse quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically create questions for your next assessment
Part 1: Best AI quiz making software for creating a data warehouse quiz
Nowadays more and more people create data warehouse quizzes using AI technologies, OnlineExamMaker a powerful AI-based quiz making tool that can save you time and efforts. The software makes it simple to design and launch interactive quizzes, assessments, and surveys. With the Question Editor, you can create multiple-choice, open-ended, matching, sequencing and many other types of questions for your tests, exams and inventories. You are allowed to enhance quizzes with multimedia elements like images, audio, and video to make them more interactive and visually appealing.
Take a product tour of OnlineExamMaker:
● Create a question pool through the question bank and specify how many questions you want to be randomly selected among these questions.
● Build and store questions in a centralized portal, tagged by categories and keywords for easy reuse and organization.
● Simply copy a few lines of codes, and add them to a web page, you can present your online quiz in your website, blog, or landing page.
● Randomize questions or change the order of questions to ensure exam takers don’t get the same set of questions each time.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 data warehouse quiz questions & answers
or
1. What is a data warehouse?
A. A database used for online transaction processing
B. A subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant, and non-volatile collection of data
C. A tool for real-time data entry
D. A system for managing unstructured data
Answer: B
Explanation: A data warehouse is designed for query and analysis rather than transaction processing, focusing on historical data to support decision-making.
2. Which of the following is a key characteristic of a data warehouse?
A. High volatility of data
B. Focus on current operational data only
C. Time-variant nature, storing historical data
D. Real-time updates for every transaction
Answer: C
Explanation: Data warehouses maintain historical data over time, allowing users to analyze trends and patterns, unlike operational systems that focus on current data.
3. What does ETL stand for in the context of data warehousing?
A. Extract, Transform, Load
B. Enter, Transfer, Log
C. Evaluate, Test, Launch
D. Export, Track, Link
Answer: A
Explanation: ETL is the process used to extract data from various sources, transform it into a suitable format, and load it into the data warehouse for analysis.
4. In data warehousing, what is a fact table?
A. A table that stores descriptive attributes
B. A table that contains measures and keys linking to dimension tables
C. A table used for transaction logging
D. A table that holds metadata
Answer: B
Explanation: Fact tables store quantitative data (measures) and foreign keys that connect to dimension tables, enabling detailed analysis.
5. What is a star schema in data warehousing?
A. A schema where dimension tables are normalized
B. A schema with a central fact table connected directly to dimension tables
C. A schema designed for operational databases
D. A schema without any relationships between tables
Answer: B
Explanation: The star schema simplifies queries by having a fact table at the center surrounded by dimension tables, reducing the number of joins needed.
6. Which schema is an extension of the star schema with normalized dimension tables?
A. Snowflaked schema
B. Galaxy schema
C. Snowflake schema
D. Constellation schema
Answer: C
Explanation: The snowflake schema normalizes dimension tables to reduce redundancy, making it more flexible but potentially increasing query complexity.
7. What is OLAP in data warehousing?
A. Online Analytical Processing for multidimensional analysis
B. Online Transaction Processing for daily operations
C. A method for data extraction
D. A type of database schema
Answer: A
Explanation: OLAP enables users to perform complex queries and analyses on multidimensional data, such as slicing, dicing, and drilling down.
8. How does a data mart differ from a data warehouse?
A. A data mart is for the entire organization, while a data warehouse is for a specific department
B. A data mart is subsetted for a particular business line, while a data warehouse serves the whole enterprise
C. They are the same thing
D. A data mart handles real-time data only
Answer: B
Explanation: A data mart is a smaller, focused version of a data warehouse, typically designed for a specific department or business function.
9. What is the primary purpose of data warehousing?
A. To speed up daily transactions
B. To support business intelligence and decision-making through data analysis
C. To store raw, unprocessed data
D. To replace operational databases
Answer: B
Explanation: Data warehouses consolidate data from various sources to provide insights that aid in strategic decision-making.
10. Which methodology advocates for a dimensional approach to data warehousing?
A. Inmon methodology
B. Kimball methodology
C. Agile methodology
D. Waterfall methodology
Answer: B
Explanation: The Kimball methodology focuses on building data marts using dimensional modeling, emphasizing user needs and rapid implementation.
11. What are Slowly Changing Dimensions (SCD) in data warehousing?
A. Dimensions that change rapidly in real-time
B. Techniques to handle changes in dimensional data over time
C. Fast-updating fact tables
D. Methods for loading data quickly
Answer: B
Explanation: SCD manages how historical data is preserved when attributes in dimension tables change, such as Type 1, 2, or 3 changes.
12. In data warehousing, what does denormalization aim to achieve?
A. Reduce data redundancy and improve storage efficiency
B. Improve query performance by adding redundancy
C. Eliminate all joins in queries
D. Normalize data for operational use
Answer: B
Explanation: Denormalization intentionally introduces redundancy to speed up read operations and simplify queries in analytical environments.
13. What is a dimension table in a data warehouse?
A. A table that stores numerical metrics
B. A table that provides descriptive attributes for analysis
C. A table used for ETL processes
D. A table that logs errors
Answer: B
Explanation: Dimension tables contain the textual attributes that provide context to the numerical data in fact tables, such as time, location, or product details.
14. Which of the following is a common OLAP operation?
A. Inserting new records
B. Drilling down to more detailed data
C. Updating transactions in real-time
D. Deleting obsolete data
Answer: B
Explanation: Drilling down allows users to navigate from summary data to more granular levels, a key feature of OLAP for exploratory analysis.
15. What is the main difference between OLTP and OLAP systems?
A. OLTP is for analysis, and OLAP is for transactions
B. OLTP handles day-to-day operations with quick transactions, while OLAP is for complex queries on historical data
C. They are interchangeable terms
D. OLAP focuses on real-time data entry
Answer: B
Explanation: OLTP systems are optimized for speed in processing transactions, whereas OLAP systems are designed for analytical processing of large datasets.
16. In data warehousing, what is data granularity?
A. The level of detail in the data stored
B. The size of the data warehouse
C. The speed of data loading
D. The number of users accessing the system
Answer: A
Explanation: Data granularity refers to the fineness of data, such as storing data at the daily level versus monthly, which affects analysis depth.
17. Which architecture involves a centralized data warehouse with dependent data marts?
A. Federated architecture
B. Hub-and-spoke architecture
C. Independent data marts
D. Virtual architecture
Answer: B
Explanation: In a hub-and-spoke architecture, the central data warehouse (hub) feeds data to surrounding data marts (spokes), ensuring consistency.
18. What role does metadata play in a data warehouse?
A. It stores the actual business data
B. It provides information about the data, such as definitions and structures
C. It handles user authentication
D. It performs data transformations
Answer: B
Explanation: Metadata acts as a roadmap for the data warehouse, helping users understand the data’s meaning, origin, and usage.
19. Why is data cleansing important in data warehousing?
A. To increase data volume
B. To ensure data accuracy and consistency before loading
C. To speed up ETL processes
D. To add new data sources
Answer: B
Explanation: Data cleansing corrects errors and inconsistencies in source data, ensuring the data warehouse contains reliable information for analysis.
20. What is the primary benefit of using a data warehouse for business intelligence?
A. Faster transaction processing
B. Integration of data from multiple sources for comprehensive reporting
C. Real-time operational control
D. Reduced storage costs
Answer: B
Explanation: A data warehouse consolidates disparate data sources, enabling businesses to generate accurate reports and gain actionable insights.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically create questions for your next assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI