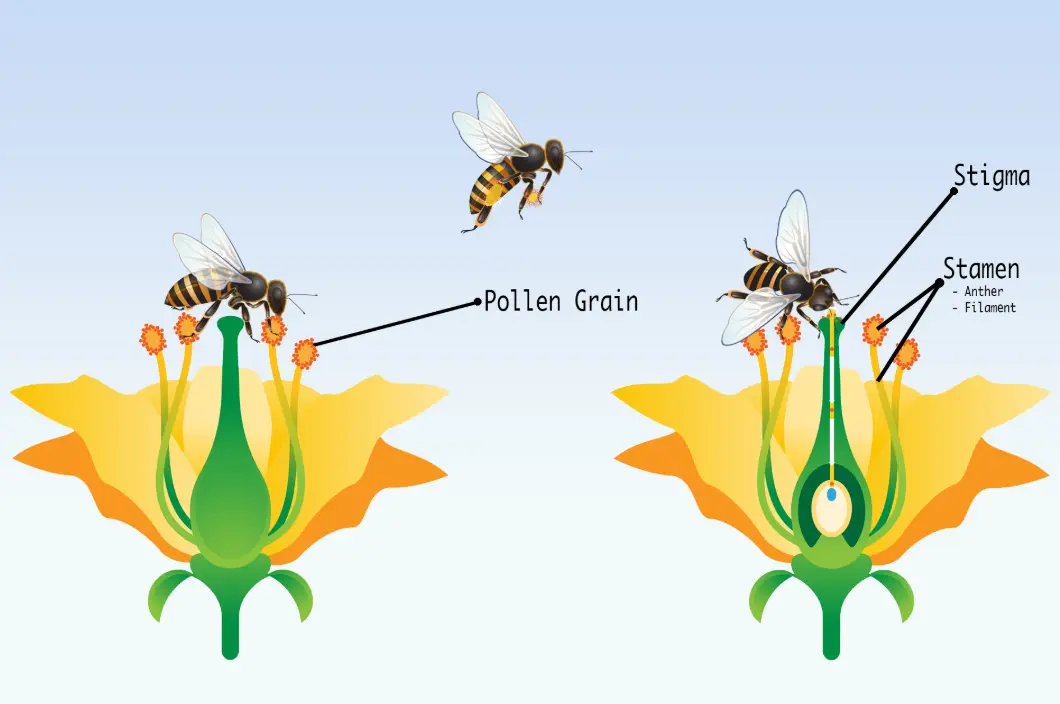
Pollination is the essential process in plant reproduction where pollen grains are transferred from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma, enabling fertilization and the production of seeds and fruits. This mechanism is crucial for the diversity and survival of plant species and ecosystems worldwide.
There are two primary types: self-pollination, where pollen from a flower fertilizes its own ovules, often seen in plants like peas and tomatoes; and cross-pollination, which involves pollen transfer between different flowers of the same species, promoting genetic diversity and typically requiring external agents.
Agents of pollination include wind, which disperses lightweight pollen over long distances in plants like grasses; insects such as bees and butterflies, attracted by nectar and pollen in flowers like sunflowers; birds, like hummingbirds aiding tropical species; and other animals, including bats and mammals.
Pollination plays a vital role in agriculture, contributing to the production of about one-third of the world’s food supply, including fruits, vegetables, and nuts. Human activities, such as habitat destruction and pesticide use, threaten pollinators, underscoring the need for conservation efforts to maintain biodiversity and food security.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Create a pollination quiz in minutes using AI with OnlineExamMaker
- Part 2: 20 pollination quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Part 1: Create a pollination quiz in minutes using AI with OnlineExamMaker
Are you looking for an online assessment to test the pollination knowledge of your learners? OnlineExamMaker uses artificial intelligence to help quiz organizers to create, manage, and analyze exams or tests automatically. Apart from AI features, OnlineExamMaker advanced security features such as full-screen lockdown browser, online webcam proctoring, and face ID recognition.
Recommended features for you:
● Includes a safe exam browser (lockdown mode), webcam and screen recording, live monitoring, and chat oversight to prevent cheating.
● Enhances assessments with interactive experience by embedding video, audio, image into quizzes and multimedia feedback.
● Once the exam ends, the exam scores, question reports, ranking and other analytics data can be exported to your device in Excel file format.
● Offers question analysis to evaluate question performance and reliability, helping instructors optimize their training plan.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 pollination quiz questions & answers
or
Question 1:
What is pollination?
A. The process by which pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma.
B. The fusion of gametes to form a zygote.
C. The growth of roots in plants.
D. The dispersal of seeds by wind.
Answer: A
Explanation: Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma, which is essential for fertilization in flowering plants.
Question 2:
Which of the following is an example of an insect pollinator?
A. Wind
B. Bee
C. Water currents
D. Gravity
Answer: B
Explanation: Bees are insects that transfer pollen while collecting nectar, making them a key agent in pollination.
Question 3:
In self-pollination, pollen is transferred from:
A. The anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower.
B. The stigma of one flower to the anther of another flower.
C. The anther to the stigma of the same flower.
D. Different plants of the same species.
Answer: C
Explanation: Self-pollination occurs when pollen from the anther lands on the stigma of the same flower, reducing genetic diversity.
Question 4:
What type of pollination occurs when pollen is carried by wind?
A. Insect pollination
B. Animal pollination
C. Anemophily
D. Hydrophily
Answer: C
Explanation: Anemophily is wind-mediated pollination, common in plants like grasses that produce lightweight pollen.
Question 5:
Which plant adaptation aids in bird pollination?
A. Brightly colored flowers
B. Dull-colored flowers
C. Flowers that open at night
D. Flowers with no nectar
Answer: A
Explanation: Brightly colored flowers attract birds, which feed on nectar and inadvertently transfer pollen during visits.
Question 6:
Pollination by water is known as:
A. Anemophily
B. Zoophily
C. Hydrophily
D. Entomophily
Answer: C
Explanation: Hydrophily involves water as the pollinating agent, as seen in aquatic plants like seagrasses.
Question 7:
What is the main difference between pollination and fertilization?
A. Pollination involves seed dispersal.
B. Fertilization is the transfer of pollen.
C. Pollination is the transfer of pollen, while fertilization is the fusion of gametes.
D. Both occur simultaneously in plants.
Answer: C
Explanation: Pollination precedes fertilization; it transfers pollen, enabling the sperm to fuse with the egg in fertilization.
Question 8:
Which of the following flowers is typically pollinated by butterflies?
A. Small, inconspicuous flowers
B. Flowers with long tubes and bright colors
C. Wind-dispersed flowers
D. Flowers that close during the day
Answer: B
Explanation: Butterflies are attracted to flowers with long tubes and bright colors, from which they extract nectar and carry pollen.
Question 9:
In cross-pollination, pollen is transferred between:
A. Different flowers on the same plant.
B. Flowers of different species.
C. The anther and stigma of the same flower.
D. Flowers of the same species but different plants.
Answer: D
Explanation: Cross-pollination involves pollen transfer between flowers of the same species on different plants, promoting genetic variation.
Question 10:
What role do bees play in pollination?
A. They eat the pollen without transferring it.
B. They transfer pollen while foraging for nectar.
C. They only pollinate water plants.
D. They prevent pollination in flowers.
Answer: B
Explanation: Bees collect nectar and pollen, and in the process, they transfer pollen grains between flowers.
Question 11:
Which of the following is not an agent of pollination?
A. Wind
B. Insects
C. Soil
D. Birds
Answer: C
Explanation: Soil does not act as a pollinating agent; pollination typically involves wind, insects, birds, or water.
Question 12:
Orchids often use which method for pollination?
A. Self-pollination only
B. Mimicking the appearance of female insects
C. Wind dispersal exclusively
D. Water currents
Answer: B
Explanation: Some orchids mimic female insects to attract males, which then carry pollen while attempting to mate.
Question 13:
What happens after successful pollination in a flower?
A. Immediate seed dispersal
B. Fertilization of the ovule
C. The flower wilts instantly
D. Pollen production stops
Answer: B
Explanation: Successful pollination leads to fertilization, where the pollen tube grows to deliver sperm to the ovule.
Question 14:
Which pollination type is most common in flowering plants?
A. Hydrophily
B. Anemophily
C. Entomophily
D. Zoophily
Answer: C
Explanation: Entomophily, or insect-mediated pollination, is the most common method due to the abundance of insects like bees and butterflies.
Question 15:
Why are some plants adapted for night-time pollination?
A. To avoid daytime heat
B. To attract nocturnal pollinators like moths
C. To conserve water
D. To prevent insect damage
Answer: B
Explanation: Plants with night-blooming flowers attract nocturnal pollinators such as moths, which are active at night.
Question 16:
In which scenario is cross-pollination more likely?
A. In plants with perfect flowers that self-pollinate easily
B. When pollinators are scarce
C. In plants that produce large amounts of pollen
D. When flowers are isolated from other plants
Answer: C
Explanation: Plants producing large amounts of pollen often rely on cross-pollination agents like wind or insects for effective transfer.
Question 17:
What is the primary advantage of cross-pollination?
A. It requires less energy from the plant.
B. It increases genetic diversity in offspring.
C. It always results in larger fruits.
D. It prevents fertilization.
Answer: B
Explanation: Cross-pollination introduces genetic variation, making offspring more adaptable to environmental changes.
Question 18:
Which flower structure directly receives pollen during pollination?
A. Ovary
B. Stigma
C. Sepal
D. Petal
Answer: B
Explanation: The stigma is the receptive part of the female reproductive organ where pollen grains land and germinate.
Question 19:
Bats are examples of which type of pollinators?
A. Anemophilous
B. Hydrophilous
C. Chiropterophilous
D. Entomophilous
Answer: C
Explanation: Chiropterophily refers to bat pollination, where bats visit flowers for nectar and transfer pollen in the process.
Question 20:
How does pollination contribute to ecosystems?
A. By increasing soil erosion
B. By supporting plant reproduction and food chains
C. By reducing biodiversity
D. By causing plant diseases
Answer: B
Explanation: Pollination enables plant reproduction, which provides food and habitat for animals, maintaining ecosystem balance.
or
Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Automatically generate questions using AI