Physics knowledge assessments play a pivotal role in education, helping educators gauge students’ understanding of fundamental concepts and their ability to apply them. These assessments provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of teaching methods and curriculum. Whether you’re a teacher crafting a physics exam or an institution designing standardized tests, these five tips will help you create physics knowledge assessments that are effective and aligned with your educational goals.
- Part 1: 6 Creative Tips for Physics Knowledge Assessments
- Part 2: OnlineExamMaker: Free Auto-Grading Physics Testing Platform for Teachers
- Part 3: 4 Steps Create A Physics Assessment with OnlineExamMaker
6 Creative Tips for Physics Knowledge Assessments
Defining Your Assessment Goals
A. Identifying the Purpose of the Physics Knowledge Assessment
Before diving into assessment creation, it’s crucial to determine the primary purpose of the assessment. Are you testing students’ basic understanding of physics concepts, evaluating their problem-solving skills, or assessing their ability to apply physics principles in real-world scenarios? Clarifying your assessment’s purpose will guide the entire design process.

B. Determining the Target Audience and Their Proficiency Level
Consider the audience that will take the assessment. Are you creating an assessment for high school students, undergraduate physics majors, or professionals seeking certification? The complexity and depth of the questions should align with the proficiency level of your audience.
C. Setting Clear and Measurable Objectives for the Assessment
Establish specific learning objectives that your assessment aims to address. These objectives should be aligned with your curriculum and clearly articulated. Having measurable goals will help you design assessment items that effectively measure students’ knowledge and skills.
Designing the Assessment
A. Choosing the Assessment Format
Physics assessments can take various formats, including multiple-choice questions, short-answer questions, problem-solving tasks, and even practical experiments. The format you choose should align with your assessment’s purpose and the type of knowledge and skills you want to evaluate.
B. Selecting Appropriate Assessment Tools
Depending on your assessment format, you may need specific tools or resources. Paper-based assessments are common, but online assessment platforms can streamline the process and provide instant feedback. For practical experiments, ensure you have the necessary lab equipment and materials.
C. Ensuring the Assessment Aligns with Learning Objectives and Curriculum
Every question or task in your assessment should directly relate to the learning objectives and content covered in your physics course or program. Ensure that the assessment content is a faithful reflection of what students were taught.
Crafting Effective Questions and Tasks
A. Writing Clear and Concise Questions
Clarity is paramount in physics assessments. Ensure that questions are free from ambiguity or convoluted language. Use straightforward and concise language to convey the intended concepts.
B. Avoiding Ambiguous or Misleading Language
Ambiguity can confuse students and lead to inaccurate assessments of their knowledge. Be cautious of vague terms or phrasing that could have multiple interpretations.
C. Balancing the Difficulty Level of Questions
Strive for a balanced mix of easy, moderate, and challenging questions. A well-rounded assessment should challenge students while also allowing them to demonstrate their grasp of foundational concepts.
D. Incorporating Real-World Scenarios and Applications
To make your assessment more engaging and practical, consider incorporating real-world scenarios or applications of physics principles. This not only tests knowledge but also evaluates students’ ability to apply physics to everyday situations.
Piloting and Testing the Assessment
A. Conducting a Trial Run with a Sample Group
Before administering the assessment to your target audience, conduct a trial run with a small sample group. This step allows you to identify any flaws, ambiguities, or unexpected challenges in the assessment.
B. Gathering Feedback from Students or Participants
Seek feedback from students or participants who took the trial assessment. Their insights can provide valuable perspectives on the assessment’s clarity, fairness, and difficulty level.
C. Adjusting the Assessment Based on the Trial Results
Based on the feedback and results from the trial run, make necessary adjustments to improve the assessment’s quality and effectiveness. This iterative process ensures that the final assessment is robust and reliable.
Administering and Scoring the Assessment
A. Setting Up a Controlled and Standardized Testing Environment
When administering the assessment, ensure that the testing environment is controlled and standardized. Minimize distractions, maintain test security, and provide clear instructions to all participants.
B. Ensuring Fairness and Impartiality in Assessment Administration
Administer the assessment impartially, treating all participants equally. Avoid favoritism or bias in the administration process.
C. Developing a Reliable Scoring Rubric or Guidelines
A well-defined scoring rubric or set of guidelines is essential for consistency in grading. It provides clear criteria for assessors and ensures that every participant’s work is evaluated fairly.
D. Training Assessors or Graders, If Necessary
If multiple assessors or graders are involved, ensure they are trained to apply the scoring rubric consistently. Calibration sessions can help align grading standards.
Analyzing and Using Assessment Results
A. Collating and Analyzing Assessment Data
After collecting assessment data, collate and analyze the results. Look for trends, patterns, and areas of strength and weakness in participants’ performance.
B. Identifying Areas of Improvement
Use the assessment data to identify areas where participants may need additional support or where the curriculum may need adjustments. This data-driven approach can lead to targeted improvements in physics education.
C. Using Assessment Results to Inform Teaching Strategies and Curriculum Improvements
Share assessment results with educators to inform their teaching strategies. Knowing where students excel or struggle can help tailor instruction for better learning outcomes.
D. Providing Feedback to Students for Their Learning Enhancement
Offer individualized feedback to students based on their performance in the assessment. This constructive feedback can guide them in their studies and help them understand where they need improvement.
Continuous Improvement
A. Revising and Refining the Assessment Based on Feedback and Results
Assessment should be an ongoing process. Continuously gather feedback from participants and assessors to make iterative improvements to the assessment over time.
B. Staying Current with Advancements in Physics Education and Assessment Techniques
Stay informed about developments in physics education and assessment methods. Incorporate new techniques and technologies that enhance the assessment process.
C. Encouraging a Culture of Lifelong Learning and Improvement in Physics Education
Promote a culture of lifelong learning and improvement within your educational institution. Encourage educators and students to embrace assessments as opportunities for growth and development.
OnlineExamMaker: Free Auto-Grading Physics Testing Platform for Teachers
OnlineExamMaker is a comprehensive and user-friendly software for creating interactive online Physics assessments. With its intuitive interface, customizable templates, and extensive range of features, the software empowers educators, and trainers to engage learners, measure knowledge retention, and assess performance effectively.
Key Features
Mathematical Equations: Allow maths, physics teachers to create professional questions with mathematical equations to assess students.
Webcam Monitoring: The webcam will take photos and record video to monitor the candidate during the exam. The exam organizers can view the photos and video in real-time. The photos and videos will also be hosted on the server, and they can be seen after the test is complete as well.
Automated Grading: OnlineExamMaker grades exams automatically & instantly, and allow exam administrators to access to detailed results reports and statistics.
Create Your Next Quiz/Exam with OnlineExamMaker
4 Steps Create A Physics Assessment with OnlineExamMaker
Step 1: Get started with OnlineExamMaker >
Step 2: Prepare Physics quiz questions
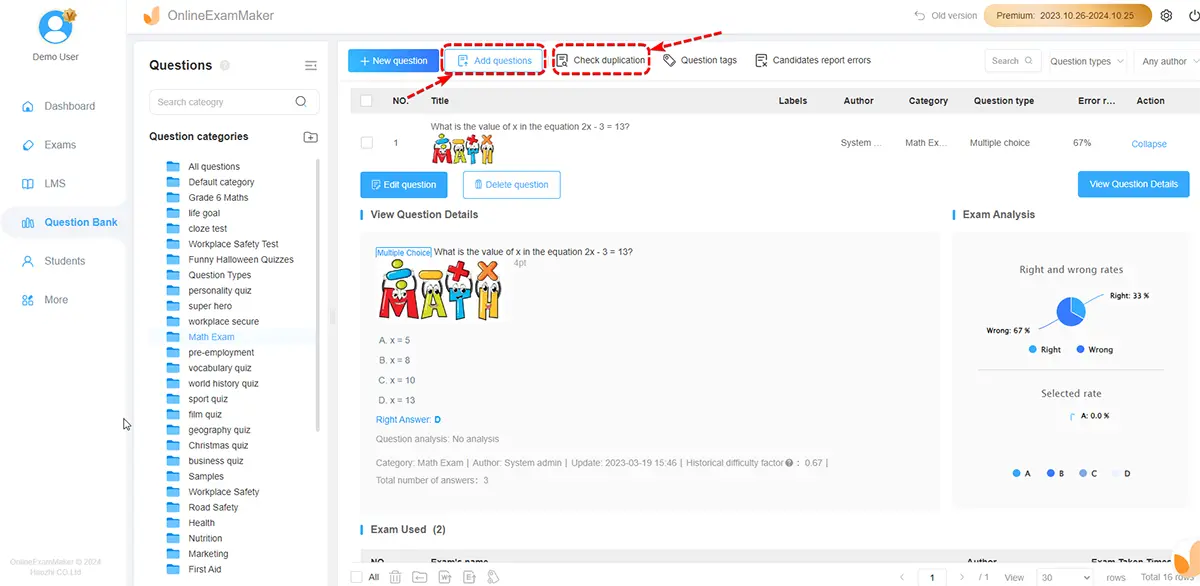
Step 3: Create a new assessment, add questions, and configure quiz settings.
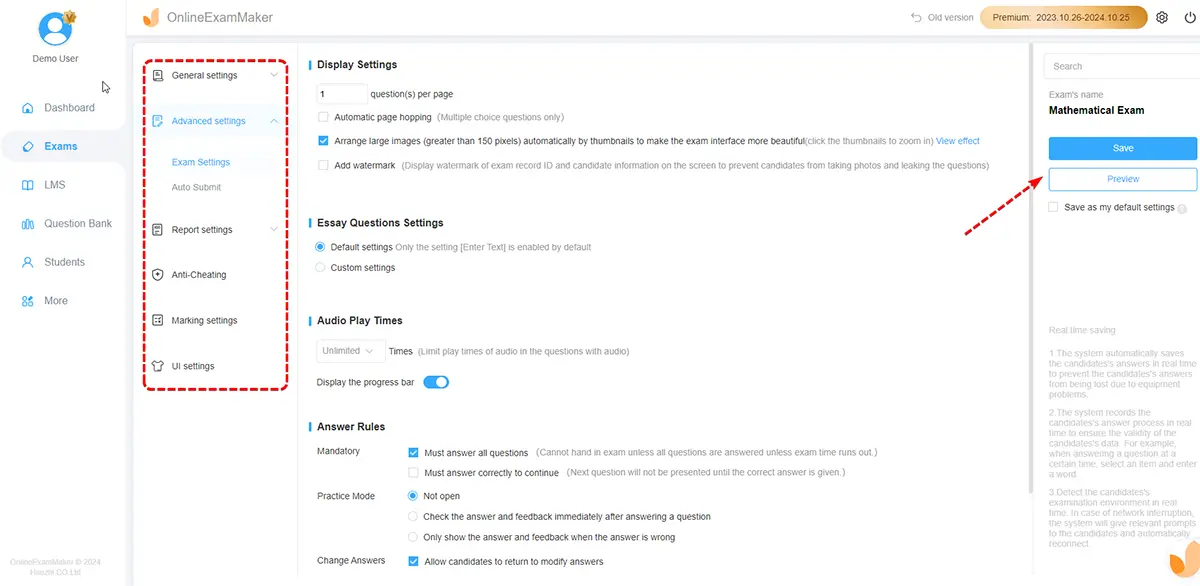
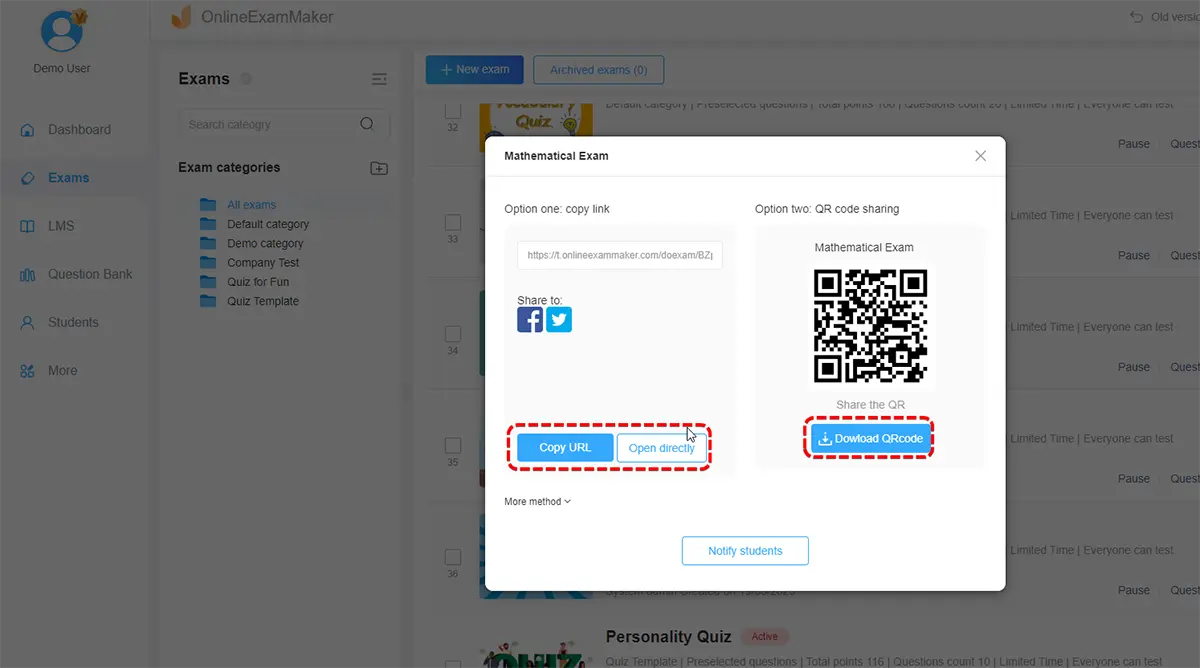
Step 4: Save settings, publish your quiz, and share it via email, direct link, or QR code.
Conclusion
Creating effective physics knowledge assessments is essential for evaluating students’ understanding and promoting learning. By following these five tips, educators and institutions can design assessments that align with their goals, provide valuable insights, and contribute to continuous improvement in physics education. Assessments should not be viewed as mere evaluations but as integral tools in fostering a deeper understanding of physics concepts and promoting excellence in the field.