Topology is a branch of mathematics that explores the properties of space and shapes that remain unchanged under continuous deformations, such as stretching or bending, without tearing or gluing. Unlike geometry, which focuses on precise measurements like distances and angles, topology emphasizes concepts like continuity, connectedness, and compactness.
At its core, a topological space is a set of points equipped with a topology—a collection of open sets that satisfy specific axioms, such as being closed under arbitrary unions and finite intersections. This framework allows mathematicians to study spaces in a more abstract way, revealing intrinsic qualities that persist even when the space is distorted.
For instance, a doughnut (torus) and a coffee mug are topologically equivalent because they both have one hole, meaning one can be deformed into the other without cutting or altering the fundamental structure. Key ideas in topology include:
Connectedness: Whether a space can be divided into separate pieces.
Compactness: A property where every open cover has a finite subcover, often implying “boundedness” in a generalized sense.
Homeomorphisms: Continuous functions with continuous inverses that map one space onto another, preserving topological features.
Topology has applications beyond pure math, influencing fields like physics, computer science, and data analysis, where understanding the “shape” of complex systems is crucial.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Create an amazing topology quiz using AI instantly in OnlineExamMaker
- Part 2: 20 topology quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Automatically generate quiz questions using AI Question Generator
Part 1: Create an amazing topology quiz using AI instantly in OnlineExamMaker
The quickest way to assess the topology knowledge of candidates is using an AI assessment platform like OnlineExamMaker. With OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, you are able to input content—like text, documents, or topics—and then automatically generate questions in various formats (multiple-choice, true/false, short answer). Its AI Exam Grader can automatically grade the exam and generate insightful reports after your candidate submit the assessment.
Overview of its key assessment-related features:
● Create up to 10 question types, including multiple-choice, true/false, fill-in-the-blank, matching, short answer, and essay questions.
● Automatically generates detailed reports—individual scores, question report, and group performance.
● Instantly scores objective questions and subjective answers use rubric-based scoring for consistency.
● API and SSO help trainers integrate OnlineExamMaker with Google Classroom, Microsoft Teams, CRM and more.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 topology quiz questions & answers
or
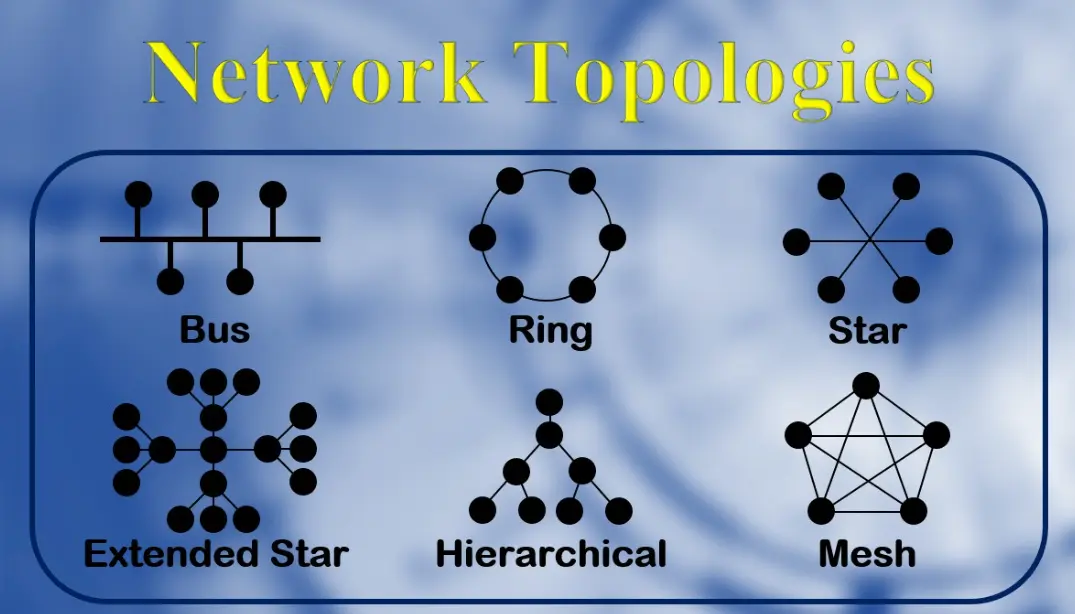
1. Question: What is a bus topology?
A. All devices connected to a central hub.
B. Devices connected in a circular manner.
C. All devices connected to a single central cable.
D. Devices connected in a hierarchical tree structure.
Answer: C
Explanation: In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single central cable, which acts as a shared communication medium, making it simple and cost-effective but prone to failures if the cable is damaged.
2. Question: Which topology is most commonly used in local area networks (LANs) due to its reliability and ease of fault detection?
A. Ring topology.
B. Star topology.
C. Mesh topology.
D. Bus topology.
Answer: B
Explanation: Star topology connects all devices to a central hub or switch, allowing easy identification and isolation of faults, which enhances reliability in LAN environments.
3. Question: In a ring topology, how does data travel between devices?
A. Through a central hub.
B. In a bidirectional manner around the ring.
C. Directly from one device to another without a path.
D. Via a backbone cable.
Answer: B
Explanation: Data in a ring topology travels in one direction (or both in dual-ring setups) around the circle, passing through each device until it reaches the destination, which can lead to issues if one device fails.
4. Question: What is a key advantage of a mesh topology?
A. Low cost of implementation.
B. High redundancy and fault tolerance.
C. Simple cable management.
D. Easy scalability.
Answer: B
Explanation: Mesh topology provides multiple paths between devices, ensuring that if one path fails, data can still be routed through another, making it highly reliable for critical networks.
5. Question: Which topology uses a hierarchical structure similar to an organizational chart?
A. Star topology.
B. Bus topology.
C. Tree topology.
D. Ring topology.
Answer: C
Explanation: Tree topology combines star and bus topologies, creating a hierarchical structure where multiple star networks are connected to a central bus, ideal for larger networks.
6. Question: In a star topology, what happens if the central hub fails?
A. The network operates normally.
B. Only the affected device is impacted.
C. The entire network goes down.
D. Data transmission speeds increase.
Answer: C
Explanation: All devices in a star topology depend on the central hub for communication, so a hub failure disconnects the entire network, highlighting a key disadvantage.
7. Question: What type of topology is used in wireless networks like Wi-Fi?
A. Bus topology.
B. Ring topology.
C. Star topology.
D. It varies and can be hybrid.
Answer: D
Explanation: Wireless networks often use a hybrid topology, combining elements like star (with a central access point) and mesh for better coverage and redundancy.
8. Question: Which topology is least scalable due to the difficulty in adding new devices?
A. Mesh topology.
B. Star topology.
C. Ring topology.
D. Bus topology.
Answer: C
Explanation: Adding devices in a ring topology requires breaking the ring and reconfiguring, which can disrupt the network, making it less scalable compared to others.
9. Question: What is a hybrid topology?
A. A combination of two or more different topologies.
B. A single type of topology used exclusively.
C. Only bus and star combined.
D. A topology used in small networks only.
Answer: A
Explanation: Hybrid topology integrates multiple topologies, such as star-bus or ring-mesh, to leverage the advantages of each, making it flexible for complex networks.
10. Question: In a full mesh topology, how many direct connections are there for n devices?
A. n connections.
B. n(n-1)/2 connections.
C. n^2 connections.
D. 2n connections.
Answer: B
Explanation: A full mesh requires every device to connect to every other, resulting in n(n-1)/2 connections, which provides maximum redundancy but is costly for large networks.
11. Question: Which topology is most vulnerable to a single point of failure in the backbone?
A. Star topology.
B. Mesh topology.
C. Bus topology.
D. Ring topology.
Answer: C
Explanation: In bus topology, the entire network can fail if the central cable (backbone) is damaged, as all devices rely on it for communication.
12. Question: What is the primary disadvantage of a ring topology?
A. High cost.
B. Network collapse if one device fails.
C. Difficult installation.
D. Limited speed.
Answer: B
Explanation: If any device in a ring topology fails, it can break the ring and halt data flow for the entire network until the issue is resolved.
13. Question: In which topology are devices connected point-to-point?
A. Bus topology.
B. Star topology.
C. Mesh topology.
D. Tree topology.
Answer: C
Explanation: Mesh topology features direct point-to-point links between devices, enabling multiple communication paths and enhancing reliability.
14. Question: Which topology is best for a small office with low budget constraints?
A. Full mesh topology.
B. Ring topology.
C. Bus topology.
D. Star topology.
Answer: C
Explanation: Bus topology uses minimal cabling and is inexpensive to set up, making it suitable for small networks despite its vulnerability to failures.
15. Question: How does a tree topology improve upon a simple bus topology?
A. By adding more central hubs.
B. By allowing for easier expansion and segmentation.
C. By reducing cable length.
D. By eliminating the need for a backbone.
Answer: B
Explanation: Tree topology extends bus topology by adding layers of star networks, enabling better scalability and management for larger networks.
16. Question: What is a common application of star topology?
A. Wide area networks (WANs).
B. Ethernet-based LANs.
C. Token ring networks.
D. Wireless ad-hoc networks.
Answer: B
Explanation: Star topology is widely used in Ethernet LANs because it supports easy maintenance and uses a central switch or hub for device connections.
17. Question: In a partial mesh topology, what is the key feature?
A. Every device connects to every other.
B. Only critical devices are fully connected.
C. It uses a single cable for all.
D. Data flows in a ring.
Answer: B
Explanation: Partial mesh connects only essential devices directly, reducing costs while maintaining some redundancy, unlike a full mesh.
18. Question: Which topology requires the most cabling?
A. Bus topology.
B. Star topology.
C. Mesh topology.
D. Ring topology.
Answer: C
Explanation: Mesh topology demands extensive cabling due to the multiple connections between devices, making it resource-intensive.
19. Question: What happens in a ring topology when a token is used?
A. It allows only one device to transmit at a time.
B. All devices transmit simultaneously.
C. Data is sent without any control mechanism.
D. The network switches to star mode.
Answer: A
Explanation: In token ring variations of ring topology, a token passes around the ring, giving exclusive transmission rights to the device holding it, preventing collisions.
20. Question: Which topology is ideal for networks requiring high security and direct communication?
A. Bus topology.
B. Star topology.
C. Mesh topology.
D. Hybrid topology.
Answer: C
Explanation: Mesh topology offers direct paths and multiple routes, enhancing security through redundancy and allowing encrypted point-to-point communications.
or
Part 3: Automatically generate quiz questions using OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator
Automatically generate questions using AI