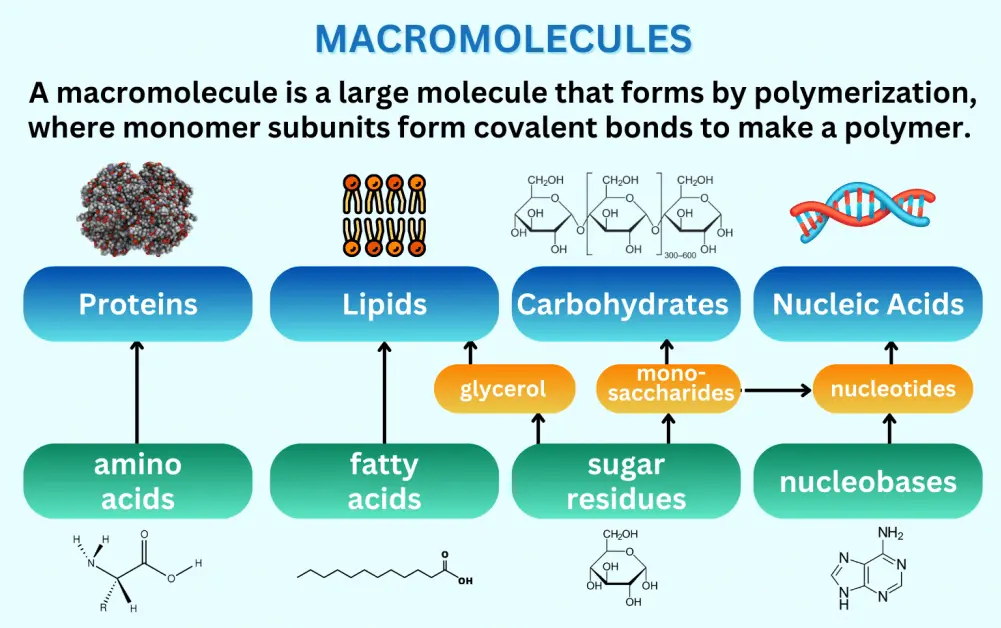
Macromolecules are large molecules essential to life, formed by the polymerization of smaller units called monomers. They are categorized into four main types:
1. Proteins: Composed of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds, proteins exhibit complex three-dimensional structures and perform diverse functions such as enzymatic catalysis, structural support, transport, and immune response.
2. Nucleic Acids: Made up of nucleotide monomers, these include DNA and RNA. DNA stores genetic information as a double helix, while RNA facilitates protein synthesis and gene regulation.
3. Carbohydrates: Polymers of simple sugars like glucose, carbohydrates serve as energy sources (e.g., starch, glycogen) and structural components (e.g., cellulose in plant cell walls).
4. Lipids: Not true polymers, lipids consist of fatty acids and other components, providing energy storage (e.g., fats, oils), cell membrane structure (e.g., phospholipids), and signaling functions (e.g., steroids).
Macromolecules are synthesized through dehydration reactions and broken down via hydrolysis, playing critical roles in cellular processes, metabolism, and organismal development.
Table of contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI quiz maker – Make a free quiz in minutes
- Part 2: 20 macromolecule quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate questions for any topic
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI quiz maker – Make a free quiz in minutes
Still spend a lot of time in editing questions for your next macromolecule assessment? OnlineExamMaker is an AI quiz maker that leverages artificial intelligence to help users create quizzes, tests, and assessments quickly and efficiently. You can start by inputting a topic or specific details into the OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, and the AI will generate a set of questions almost instantly. It also offers the option to include answer explanations, which can be short or detailed, helping learners understand their mistakes.
What you may like:
● Automatic grading and insightful reports. Real-time results and interactive feedback for quiz-takers.
● The exams are automatically graded with the results instantly, so that teachers can save time and effort in grading.
● LockDown Browser to restrict browser activity during quizzes to prevent students searching answers on search engines or other software.
● Create certificates with personalized company logo, certificate title, description, date, candidate’s name, marks and signature.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 macromolecule quiz questions & answers
or
1. Question: Which of the following is a monomer of proteins?
Options:
A. Glucose
B. Amino acid
C. Nucleotide
D. Fatty acid
Answer: B
Explanation: Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, linked together by peptide bonds to form polypeptide chains.
2. Question: What is the primary function of carbohydrates in living organisms?
Options:
A. Energy storage
B. Genetic information storage
C. Structural support
D. All of the above
Answer: D
Explanation: Carbohydrates provide energy storage (e.g., glycogen), structural support (e.g., cellulose), and other functions, making all options correct.
3. Question: Which macromolecule is composed of nucleotides?
Options:
A. Proteins
B. Lipids
C. Nucleic acids
D. Carbohydrates
Answer: C
Explanation: Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are polymers made up of nucleotide monomers, which include a sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base.
4. Question: What type of bond holds the two strands of DNA together?
Options:
A. Hydrogen bonds
B. Covalent bonds
C. Ionic bonds
D. Peptide bonds
Answer: A
Explanation: Hydrogen bonds form between complementary base pairs (e.g., A with T, C with G) in the double helix structure of DNA.
5. Question: Which of the following is an example of a lipid?
Options:
A. Starch
B. Cholesterol
C. Glycogen
D. Cellulose
Answer: B
Explanation: Cholesterol is a steroid lipid, while starch, glycogen, and cellulose are carbohydrates.
6. Question: What is the main storage form of carbohydrates in animals?
Options:
A. Cellulose
B. Glycogen
C. Starch
D. Chitin
Answer: B
Explanation: Glycogen is the polysaccharide stored in animal liver and muscle cells for quick energy release.
7. Question: Proteins are denatured by which of the following?
Options:
A. High temperature
B. pH changes
C. Both A and B
D. Neither A nor B
Answer: C
Explanation: High temperatures and pH changes can disrupt the hydrogen bonds and other interactions that maintain a protein’s three-dimensional structure.
8. Question: Which macromolecule is hydrophobic?
Options:
A. Proteins
B. Nucleic acids
C. Lipids
D. Carbohydrates
Answer: C
Explanation: Lipids are generally nonpolar and hydrophobic, meaning they do not dissolve in water, unlike the polar nature of proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates.
9. Question: What is the function of enzymes in biological systems?
Options:
A. Provide energy
B. Catalyze chemical reactions
C. Store genetic information
D. Form cell membranes
Answer: B
Explanation: Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions without being consumed.
10. Question: Which of the following is a disaccharide?
Options:
A. Glucose
B. Sucrose
C. Fructose
D. Ribose
Answer: B
Explanation: Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose monomers linked by a glycosidic bond.
11. Question: What element is found in proteins but not in carbohydrates?
Options:
A. Carbon
B. Nitrogen
C. Hydrogen
D. Oxygen
Answer: B
Explanation: Proteins contain nitrogen in their amino acid structure, while carbohydrates typically consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen only.
12. Question: Nucleic acids are involved in which process?
Options:
A. Protein synthesis
B. Lipid metabolism
C. Energy production
D. Carbohydrate breakdown
Answer: A
Explanation: Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA direct the synthesis of proteins through processes such as transcription and translation.
13. Question: Which macromolecule provides the most energy per gram?
Options:
A. Carbohydrates
B. Proteins
C. Lipids
D. Nucleic acids
Answer: C
Explanation: Lipids yield about 9 calories per gram, more than carbohydrates or proteins, which yield about 4 calories per gram.
14. Question: What is the basic structure of a nucleotide?
Options:
A. Sugar, phosphate, and base
B. Amino acid chain
C. Fatty acid tails
D. Monosaccharide units
Answer: A
Explanation: A nucleotide consists of a five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
15. Question: Which level of protein structure involves hydrogen bonding between the backbone?
Options:
A. Primary
B. Secondary
C. Tertiary
D. Quaternary
Answer: B
Explanation: Secondary structure, such as alpha helices and beta sheets, is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the polypeptide backbone.
16. Question: Lipids are not typically polymers because:
Options:
A. They are made of monomers
B. They do not form long chains
C. They are hydrophilic
D. They contain nitrogen
Answer: B
Explanation: Unlike proteins or carbohydrates, lipids do not form long, repeating polymer chains; they are usually smaller molecules or aggregates.
17. Question: What is the role of phospholipids in cells?
Options:
A. Energy storage
B. Forming cell membranes
C. Catalyzing reactions
D. Storing genetic code
Answer: B
Explanation: Phospholipids have hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails, allowing them to form the bilayer structure of cell membranes.
18. Question: Which macromolecule is responsible for the immune response?
Options:
A. Carbohydrates
B. Lipids
C. Proteins (e.g., antibodies)
D. Nucleic acids
Answer: C
Explanation: Proteins, such as antibodies and antigens, play a key role in the immune system by recognizing and neutralizing pathogens.
19. Question: What bond links fatty acids to glycerol in triglycerides?
Options:
A. Glycosidic bond
B. Peptide bond
C. Ester bond
D. Hydrogen bond
Answer: C
Explanation: Ester bonds form between the carboxyl group of fatty acids and the hydroxyl group of glycerol in triglycerides.
20. Question: RNA and DNA differ in that RNA has:
Options:
A. A double helix structure
B. Thymine as a base
C. Uracil instead of thymine
D. Deoxyribose sugar only
Answer: C
Explanation: RNA contains uracil as a nitrogenous base, while DNA contains thymine; RNA also has a ribose sugar, not deoxyribose.
or
Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate questions for any topic
Automatically generate questions using AI