Isotopes are variants of a chemical element that have the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei but differ in the number of neutrons. This results in atoms of the same element having different atomic masses. For example, carbon has three naturally occurring isotopes: carbon-12 (6 protons and 6 neutrons), carbon-13 (6 protons and 7 neutrons), and carbon-14 (6 protons and 8 neutrons).
Isotopes can be stable or radioactive. Stable isotopes do not undergo radioactive decay, while radioactive isotopes, such as uranium-235, decay over time, emitting radiation and transforming into other elements. This property makes isotopes valuable in various applications, including radiometric dating, medical imaging (e.g., technetium-99m in scans), and nuclear energy.
The concept of isotopes was first proposed by Frederick Soddy in 1913, building on discoveries from radioactive elements. In nature, isotopes occur in specific ratios, which can vary and provide insights into geological and environmental processes. For instance, oxygen isotopes in ice cores help reconstruct past climates.
Isotopes are identified by their mass number, which is the sum of protons and neutrons. They play a crucial role in fields like chemistry, physics, biology, and industry, enabling techniques such as mass spectrometry for precise measurements and isotopic labeling for tracking chemical reactions.
Table of contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI quiz generator – The easiest way to make quizzes online
- Part 2: 20 isotope quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Automatically generate quiz questions using AI Question Generator
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI quiz generator – The easiest way to make quizzes online
When it comes to ease of creating a isotope assessment, OnlineExamMaker is one of the best AI-powered quiz making software for your institutions or businesses. With its AI Question Generator, just upload a document or input keywords about your assessment topic, you can generate high-quality quiz questions on any topic, difficulty level, and format.
What you will like:
● AI Question Generator to help you save time in creating quiz questions automatically.
● Share your online exam with audiences on social platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Reddit and more.
● Display the feedback for correct or incorrect answers instantly after a question is answered.
● Create a lead generation form to collect an exam taker’s information, such as email, mobile phone, work title, company profile and so on.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 isotope quiz questions & answers
or
1. Question: What is an isotope?
Options:
A) Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
B) Atoms of different elements with the same atomic mass
C) Molecules with identical chemical formulas
D) Elements with the same electron configuration
Answer: A
Explanation: Isotopes are variants of the same element that have the same number of protons (atomic number) but differ in the number of neutrons, leading to different atomic masses.
2. Question: Which of the following pairs are isotopes?
Options:
A) Carbon-12 and Carbon-14
B) Hydrogen-1 and Helium-4
C) Oxygen-16 and Nitrogen-14
D) Sodium-23 and Chlorine-35
Answer: A
Explanation: Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are both forms of carbon, with the same number of protons (6) but different numbers of neutrons (6 and 8, respectively), making them isotopes.
3. Question: What does the atomic mass of an element represent in relation to isotopes?
Options:
A) The weighted average of the masses of its naturally occurring isotopes
B) The mass of the most abundant isotope only
C) The total number of protons and electrons
D) The mass of a single proton in the nucleus
Answer: A
Explanation: The atomic mass listed on the periodic table is a weighted average that accounts for the abundance of each isotope in nature.
4. Question: Which isotope is commonly used in carbon dating?
Options:
A) Carbon-14
B) Carbon-12
C) Carbon-13
D) Carbon-15
Answer: A
Explanation: Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope with a known half-life, allowing scientists to determine the age of organic materials by measuring its decay.
5. Question: How do isotopes of an element differ in terms of stability?
Options:
A) Some isotopes are stable, while others are radioactive and decay over time
B) All isotopes of an element are equally stable
C) Isotopes differ only in chemical stability, not nuclear stability
D) Stable isotopes have more protons than neutrons
Answer: A
Explanation: Isotopes can be stable (non-decaying) or unstable (radioactive), depending on the neutron-to-proton ratio in the nucleus.
6. Question: What is the mass number of an isotope?
Options:
A) The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
B) The number of electrons in the atom
C) The atomic number plus the number of electrons
D) The weight of the atom in grams
Answer: A
Explanation: The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons, which defines the specific isotope of an element.
7. Question: Which of the following is an example of a radioactive isotope?
Options:
A) Uranium-238
B) Oxygen-16
C) Hydrogen-1
D) Carbon-12
Answer: A
Explanation: Uranium-238 is unstable and undergoes radioactive decay, emitting radiation over time.
8. Question: In nuclear notation, what does the superscript represent for an isotope like \( ^{14}_6C \)?
Options:
A) The mass number (protons + neutrons)
B) The atomic number (number of protons)
C) The number of electrons
D) The charge of the ion
Answer: A
Explanation: In \( ^{14}_6C \), the superscript 14 is the mass number, indicating the total of protons and neutrons.
9. Question: Why do isotopes of an element have nearly identical chemical properties?
Options:
A) They have the same number of protons, which determines chemical behavior
B) They have the same number of electrons
C) Chemical properties depend only on atomic mass
D) Isotopes do not affect chemical reactions
Answer: A
Explanation: Chemical properties are primarily determined by the number of protons (atomic number), which is the same for all isotopes of an element.
10. Question: What is isotopic abundance?
Options:
A) The percentage of each isotope in a naturally occurring sample of an element
B) The total mass of all isotopes combined
C) The rate at which isotopes decay
D) The difference in neutron counts between isotopes
Answer: A
Explanation: Isotopic abundance refers to the relative proportions of different isotopes in a natural sample, which affects the element’s average atomic mass.
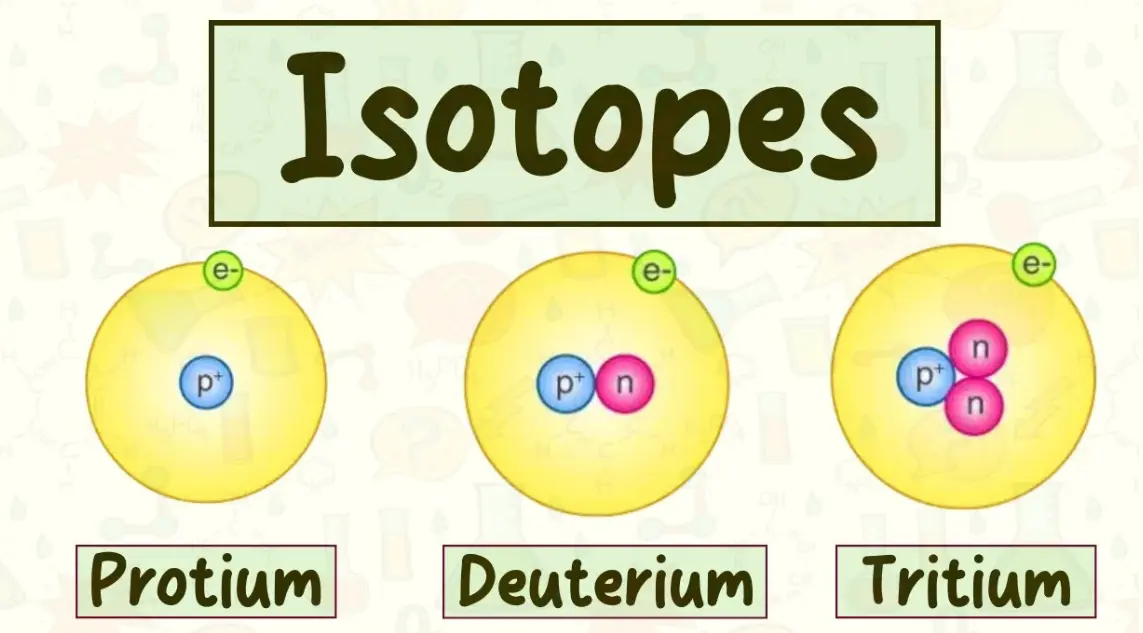
11. Question: Which hydrogen isotope has two neutrons?
Options:
A) Tritium (Hydrogen-3)
B) Deuterium (Hydrogen-2)
C) Protium (Hydrogen-1)
D) None of the above
Answer: A
Explanation: Tritium has 1 proton and 2 neutrons, making its mass number 3, whereas Deuterium has 1 neutron.
12. Question: How are isotopes used in medical imaging?
Options:
A) Radioactive isotopes like Technetium-99m emit radiation that can be detected to create images
B) Stable isotopes block X-rays for clearer pictures
C) Isotopes change the color of tissues for visibility
D) All isotopes are used equally in medicine
Answer: A
Explanation: Radioactive isotopes are used because their emitted radiation can be traced to visualize internal body structures.
13. Question: What happens to an unstable isotope over time?
Options:
A) It undergoes radioactive decay to become more stable
B) It remains unchanged indefinitely
C) It gains protons to stabilize
D) It loses electrons
Answer: A
Explanation: Unstable isotopes decay by emitting particles or radiation until they reach a stable form.
14. Question: Which element has isotopes that are used in nuclear reactors?
Options:
A) Uranium
B) Gold
C) Helium
D) Neon
Answer: A
Explanation: Uranium isotopes, such as Uranium-235, are fissionable and used as fuel in nuclear reactors.
15. Question: How does the number of neutrons affect an isotope’s mass?
Options:
A) More neutrons increase the mass number
B) Neutrons have no effect on mass
C) More neutrons decrease the atomic mass
D) Neutrons only affect stability, not mass
Answer: A
Explanation: Neutrons contribute to the atomic mass, so isotopes with more neutrons have a higher mass number.
16. Question: What is the half-life of an isotope?
Options:
A) The time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay
B) The total lifespan of the isotope
C) The time for all atoms to decay
D) The period between neutron emissions
Answer: A
Explanation: Half-life is a measure of radioactive decay rate, indicating when half of the sample has transformed.
17. Question: Which isotope is most abundant in nature for chlorine?
Options:
A) Chlorine-35
B) Chlorine-37
C) Chlorine-36
D) Chlorine-38
Answer: A
Explanation: Chlorine-35 makes up about 75% of natural chlorine, while Chlorine-37 is about 25%.
18. Question: In mass spectrometry, how are isotopes distinguished?
Options:
A) By their mass-to-charge ratio
B) By their color under light
C) By their reactivity with chemicals
D) By their electron count
Answer: A
Explanation: Mass spectrometry separates ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio, allowing detection of different isotopes.
19. Question: What is an application of stable isotopes in environmental science?
Options:
A) Tracing water cycles using isotopes like Oxygen-18
B) Generating energy from decay
C) Creating new elements
D) Measuring temperature changes directly
Answer: A
Explanation: Stable isotopes like Oxygen-18 are used to track the movement of water in ecosystems and climate studies.
20. Question: Why are some isotopes useful as tracers in biological research?
Options:
A) They can be detected without altering the biological process
B) They change the speed of reactions
C) They are always radioactive and easy to see
D) They increase the size of molecules
Answer: A
Explanation: Isotopes like Carbon-13 or Deuterium can be incorporated into biological molecules and tracked without significantly affecting the system’s behavior.
or
Part 3: Automatically generate quiz questions using OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator
Automatically generate questions using AI