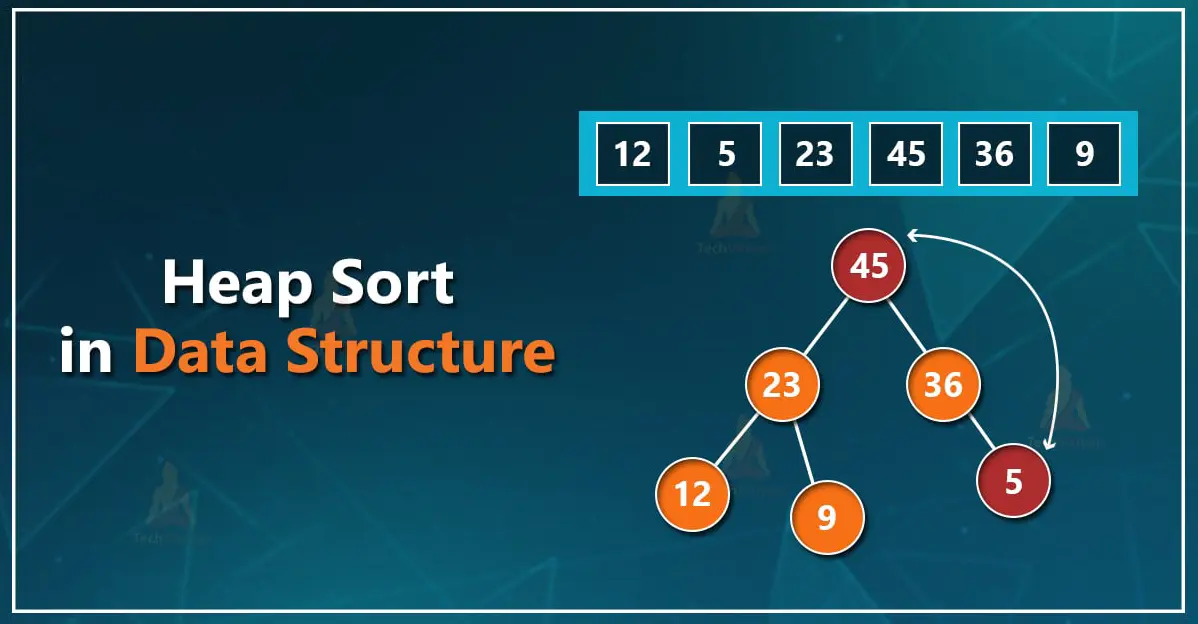
Heap Sort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm that utilizes a binary heap data structure to sort elements efficiently. It begins by rearranging the array into a max heap, where the parent node is always greater than or equal to its children. Once the heap is built, the largest element (at the root) is swapped with the last element in the heap. The heap is then reduced in size and restructured (heapified) to maintain the heap property. This process repeats until the entire array is sorted in ascending order.
Heap Sort operates in two main phases: building the initial heap, which takes O(n) time, and then performing n extractions, each taking O(log n) time, resulting in an overall time complexity of O(n log n). It is an in-place algorithm, meaning it requires no additional memory space beyond the input array, making it suitable for large datasets. However, it is not stable, as the relative order of equal elements may change during the sorting process. Overall, Heap Sort is valued for its consistent performance and efficiency in worst-case scenarios.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Generator – The Easiest Way to Make Quizzes Online
- Part 2: 20 Heap Sort Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Generator – The Easiest Way to Make Quizzes Online
When it comes to ease of creating a Heap Sort skills assessment, OnlineExamMaker is one of the best AI-powered quiz making software for your institutions or businesses. With its AI Question Generator, just upload a document or input keywords about your assessment topic, you can generate high-quality quiz questions on any topic, difficulty level, and format.
What you will like:
● AI Question Generator to help you save time in creating quiz questions automatically.
● Share your online exam with audiences on social platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Reddit and more.
● Display the feedback for correct or incorrect answers instantly after a question is answered.
● Create a lead generation form to collect an exam taker’s information, such as email, mobile phone, work title, company profile and so on.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Heap Sort Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is Heap Sort?
Options:
A. A comparison-based sorting algorithm that uses a binary heap data structure.
B. A sorting algorithm that uses recursion and divides the array into halves.
C. A sorting algorithm that relies on swapping adjacent elements.
D. A non-comparison-based sorting algorithm like Counting Sort.
Answer: A
Explanation: Heap Sort is a comparison-based sorting technique that builds a binary heap from the input array and repeatedly extracts the maximum element to sort the array.
2. Question: In a max heap, where is the largest element located?
Options:
A. At the root node.
B. At the last leaf node.
C. At a random position.
D. At the middle of the heap.
Answer: A
Explanation: In a max heap, the largest element is always at the root (index 0) to satisfy the heap property where each parent node is greater than or equal to its children.
3. Question: What is the time complexity of the Heap Sort algorithm?
Options:
A. O(n log n)
B. O(n^2)
C. O(n)
D. O(log n)
Answer: A
Explanation: Heap Sort has a time complexity of O(n log n) for both best and worst cases, due to the heap building phase (O(n)) and the extraction phase (O(n log n)).
4. Question: How does Heap Sort achieve in-place sorting?
Options:
A. By building the heap in the same array and swapping elements within it.
B. By creating a separate array for the sorted output.
C. By using external memory for temporary storage.
D. By recursively sorting subarrays.
Answer: A
Explanation: Heap Sort is in-place because it modifies the original array by building the heap and performing swaps directly within the array, without requiring additional space proportional to the input size.
5. Question: What is the first step in the Heap Sort algorithm?
Options:
A. Build a max heap from the input array.
B. Extract the maximum element and place it at the end.
C. Swap the root with the last element.
D. Perform heapify on the entire array.
Answer: A
Explanation: The first step is to build a max heap from the unsorted array, which rearranges the elements to satisfy the heap property.
6. Question: Is Heap Sort a stable sorting algorithm?
Options:
A. No
B. Yes
C. It depends on the implementation
D. Only for even-sized arrays
Answer: A
Explanation: Heap Sort is not stable because it may change the relative order of equal elements during the swapping process in the heap.
7. Question: What is the space complexity of Heap Sort?
Options:
A. O(1) auxiliary space
B. O(n)
C. O(log n)
D. O(n log n)
Answer: A
Explanation: Heap Sort uses O(1) auxiliary space since it performs operations directly on the input array without needing extra space for another array.
8. Question: In Heap Sort, after building the max heap, what happens next?
Options:
A. Swap the root with the last element and heapify the reduced heap.
B. Sort the array using insertion sort.
C. Double the array size.
D. Rebuild the heap from scratch.
Answer: A
Explanation: After building the max heap, the algorithm swaps the root (largest element) with the last element, then heapifies the reduced heap to maintain the heap property.
9. Question: For an array of n elements, what is the time complexity to build a heap?
Options:
A. O(n)
B. O(n log n)
C. O(n^2)
D. O(1)
Answer: A
Explanation: Building a heap can be done in O(n) time using the bottom-up approach, which processes non-leaf nodes and heapifies them.
10. Question: Which of the following is a key operation in Heap Sort?
Options:
A. Heapify
B. Merge
C. Partition
D. Binary search
Answer: A
Explanation: Heapify is the key operation that ensures the heap property is maintained by sifting down elements in the subtree.
11. Question: How many swaps are performed in the worst case for Heap Sort on an array of n elements?
Options:
A. O(n log n)
B. O(n)
C. O(1)
D. O(n^2)
Answer: A
Explanation: In the worst case, Heap Sort performs O(n log n) swaps due to the n extractions from the heap, each taking O(log n) time.
12. Question: What type of heap is typically used in Heap Sort for ascending order sorting?
Options:
A. Max heap
B. Min heap
C. Binary search heap
D. Balanced heap
Answer: A
Explanation: A max heap is used in Heap Sort for ascending order because it allows extracting the largest element repeatedly to build the sorted array.
13. Question: In a binary heap, how is the parent index related to a child index i?
Options:
A. Floor of (i/2)
B. i * 2
C. i * 2 + 1
D. i + 1
Answer: A
Explanation: For a child at index i, the parent is at index floor(i/2), which is used to navigate and maintain the heap structure.
14. Question: Can Heap Sort be used on arrays with duplicate elements?
Options:
A. Yes
B. No
C. Only if duplicates are at the end
D. Only for unique elements
Answer: A
Explanation: Heap Sort can handle arrays with duplicate elements, as it maintains the heap property regardless of duplicates, though it is not stable.
15. Question: What is the worst-case performance of Heap Sort compared to Quick Sort?
Options:
A. Heap Sort is O(n log n), while Quick Sort can be O(n^2)
B. Both are O(n^2)
C. Heap Sort is O(n), while Quick Sort is O(n log n)
D. Both are O(1)
Answer: A
Explanation: Heap Sort guarantees O(n log n) in the worst case, whereas Quick Sort can degrade to O(n^2) with poor pivot choices.
16. Question: After the first pass of Heap Sort on an array, where is the largest element?
Options:
A. At the end of the array
B. At the beginning
C. In the middle
D. Randomly placed
Answer: A
Explanation: After the first extraction, the largest element is swapped to the end of the array, and the heap is reduced by one element.
17. Question: Which data structure is Heap Sort based on?
Options:
A. Binary heap
B. Linked list
C. Hash table
D. Queue
Answer: A
Explanation: Heap Sort is based on the binary heap, a complete binary tree that satisfies the heap property.
18. Question: How does Heap Sort handle negative numbers in an array?
Options:
A. It sorts them correctly as per their values
B. It cannot handle negative numbers
C. It treats them as positive
D. It requires conversion to positive
Answer: A
Explanation: Heap Sort compares elements based on their values, so it can sort arrays with negative numbers without any special handling.
19. Question: What is the height of a heap with n elements?
Options:
A. Floor of log n (base 2)
B. n
C. n/2
D. 1
Answer: A
Explanation: The height of a heap is floor(log n base 2), as it is a complete binary tree, and operations like heapify take O(log n) time.
20. Question: In what scenarios is Heap Sort preferred over other sorting algorithms?
Options:
A. When guaranteed worst-case performance is needed
B. For nearly sorted arrays
C. When stability is required
D. For very small arrays
Answer: A
Explanation: Heap Sort is preferred when a consistent O(n log n) performance is required, making it suitable for large datasets where worst-case efficiency matters.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI