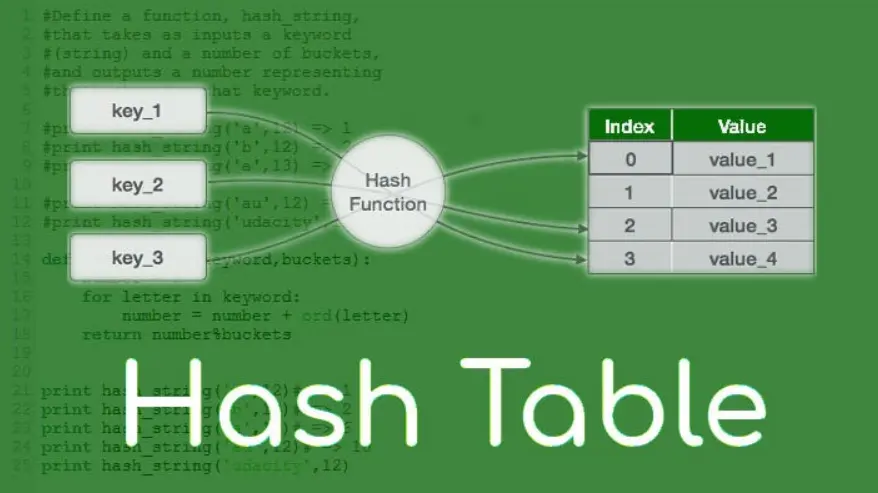
A hash table is a fundamental data structure in computer science that stores key-value pairs for efficient data retrieval. It operates by using a hash function to compute an index into an array of buckets, allowing for quick insertion, deletion, and search operations.
The hash function takes a key as input and produces a fixed-size string of characters, or a hash value, which determines the bucket where the corresponding value is stored. This enables average-case constant time complexity (O(1)) for basic operations, making hash tables ideal for applications like dictionaries, caches, and databases.
However, hash tables can encounter collisions, where two different keys produce the same hash value. Common collision resolution techniques include chaining, which links multiple elements in the same bucket, or open addressing, which probes for the next available slot.
Due to their speed and efficiency, hash tables are widely used in programming languages (e.g., Python’s dictionaries, Java’s HashMap) for tasks involving fast lookups, such as symbol tables in compilers, caching mechanisms in web browsers, and associative arrays in data processing.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Generator – Save Time and Efforts
- Part 2: 20 Hash Table Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Generator – Save Time and Efforts
Still spend a lot of time in editing questions for your next Hash Table assessment? OnlineExamMaker is an AI quiz maker that leverages artificial intelligence to help users create quizzes, tests, and assessments quickly and efficiently. You can start by inputting a topic or specific details into the OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, and the AI will generate a set of questions almost instantly. It also offers the option to include answer explanations, which can be short or detailed, helping learners understand their mistakes.
What you may like:
● Automatic grading and insightful reports. Real-time results and interactive feedback for quiz-takers.
● The exams are automatically graded with the results instantly, so that teachers can save time and effort in grading.
● LockDown Browser to restrict browser activity during quizzes to prevent students searching answers on search engines or other software.
● OnlineExamMaker API offers private access for developers to extract your exam data back into your system automatically.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Hash Table Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is a hash table?
Options:
A) A data structure for storing key-value pairs using a hash function.
B) A type of linked list.
C) A sorting algorithm.
D) A database management system.
Answer: A
Explanation: A hash table is designed to implement an associative array, allowing for efficient insertion, deletion, and lookup of key-value pairs by using a hash function to map keys to array indices.
2. Question: Which of the following is a common hash function?
Options:
A) Division method.
B) Bubble sort.
C) Binary search.
D) Quick sort.
Answer: A
Explanation: The division method is a hash function that computes the hash value by taking the key modulo the size of the hash table, helping to distribute keys evenly.
3. Question: What happens when two keys hash to the same index in a hash table?
Options:
A) Collision.
B) Overflow.
C) Segmentation fault.
D) Key duplication.
Answer: A
Explanation: A collision occurs when two different keys produce the same hash value, requiring resolution techniques like chaining or open addressing.
4. Question: Which collision resolution technique uses linked lists at each slot?
Options:
A) Chaining.
B) Linear probing.
C) Quadratic probing.
D) Double hashing.
Answer: A
Explanation: Chaining resolves collisions by maintaining a linked list of elements at each hash table index, allowing multiple keys to be stored at the same slot.
5. Question: What is the average time complexity for a successful search in a hash table?
Options:
A) O(1).
B) O(n).
C) O(log n).
D) O(n log n).
Answer: A
Explanation: Under ideal conditions with a good hash function and low load factor, the average time complexity for search operations in a hash table is constant time, O(1).
6. Question: In open addressing, how is a collision handled?
Options:
A) By probing other slots in the table.
B) By increasing the table size.
C) By deleting the entry.
D) By ignoring the new key.
Answer: A
Explanation: Open addressing resolves collisions by searching for the next available slot using methods like linear probing, ensuring all elements are stored within the table array.
7. Question: What is the load factor of a hash table?
Options:
A) The ratio of the number of elements to the size of the table.
B) The total number of elements.
C) The size of the hash function.
D) The number of collisions.
Answer: A
Explanation: The load factor is calculated as (number of elements) / (size of the hash table), and it influences the likelihood of collisions and performance.
8. Question: Which of the following is an advantage of hash tables?
Options:
A) Fast access times for average cases.
B) Guaranteed sorted order.
C) Efficient for sequential access.
D) Low memory usage regardless of size.
Answer: A
Explanation: Hash tables provide average-case constant time complexity for insertions, deletions, and lookups, making them ideal for applications requiring quick data retrieval.
9. Question: What is double hashing in collision resolution?
Options:
A) Using a second hash function to determine the next slot.
B) Hashing the key twice with the same function.
C) Combining two keys into one hash.
D) Doubling the table size.
Answer: A
Explanation: Double hashing uses a secondary hash function to compute the increment for probing, reducing clustering and improving distribution in open addressing.
10. Question: When should you rehash a hash table?
Options:
A) When the load factor exceeds a certain threshold.
B) After every insertion.
C) Only during deletion.
D) When the table is empty.
Answer: A
Explanation: Rehashing, or resizing the table, is typically done when the load factor becomes too high to maintain efficiency and reduce collisions.
11. Question: Which data structure is commonly used in chaining for hash tables?
Options:
A) Linked lists.
B) Stacks.
C) Queues.
D) Binary trees.
Answer: A
Explanation: Linked lists are used in chaining to store multiple elements at the same hash index, allowing for easy insertion and deletion without shifting elements.
12. Question: What is the worst-case time complexity of a hash table operation?
Options:
A) O(n).
B) O(1).
C) O(log n).
D) O(n^2).
Answer: A
Explanation: In the worst case, such as when all keys hash to the same index, operations like search can degenerate to linear time, O(n), requiring examination of all elements.
13. Question: How does a good hash function behave?
Options:
A) It minimizes collisions by distributing keys uniformly.
B) It always produces the same output for any input.
C) It sorts the keys before hashing.
D) It only works with numeric keys.
Answer: A
Explanation: A good hash function aims for uniform distribution of keys across the table to minimize collisions and optimize performance.
14. Question: What is linear probing?
Options:
A) Checking sequential slots until an empty one is found.
B) Using a linked list for each slot.
C) Hashing the key multiple times.
D) Removing elements on collision.
Answer: A
Explanation: Linear probing is a collision resolution technique in open addressing where the algorithm searches linearly through the table for the next available slot.
15. Question: In which scenario are hash tables less efficient?
Options:
A) When frequent deletions occur and the table is nearly full.
B) For small datasets.
C) When keys are already sorted.
D) For sequential data access.
Answer: A
Explanation: Hash tables can become inefficient with a high load factor due to increased collisions and longer probe sequences, especially during deletions.
16. Question: What is the purpose of a hash table in databases?
Options:
A) To provide fast retrieval of records using keys.
B) To store data in sorted order.
C) To handle transactions only.
D) To encrypt data.
Answer: A
Explanation: Hash tables are used in databases for indexing, enabling quick lookups and insertions based on primary keys or unique identifiers.
17. Question: Which probing technique can lead to primary clustering?
Options:
A) Linear probing.
B) Quadratic probing.
C) Double hashing.
D) Chaining.
Answer: A
Explanation: Linear probing can cause primary clustering, where collided elements form clusters, increasing the time for subsequent insertions and searches.
18. Question: How is the hash value typically used?
Options:
A) As an index into the array.
B) To sort the array.
C) To count elements.
D) To merge arrays.
Answer: A
Explanation: The hash value is computed from the key and used as an index to directly access the corresponding slot in the hash table array.
19. Question: What is the difference between closed hashing and open hashing?
Options:
A) Closed hashing stores all elements in the table array, while open hashing uses external structures like linked lists.
B) They are the same thing.
C) Closed hashing uses sorting, open hashing does not.
D) Open hashing is faster.
Answer: A
Explanation: Closed hashing (open addressing) resolves collisions by staying within the table, whereas open hashing (chaining) uses additional data structures outside the table.
20. Question: Why might you choose a hash table over a binary search tree?
Options:
A) For average-case faster operations without the need for balanced trees.
B) Because binary search trees require sorting.
C) Hash tables use less memory.
D) Binary search trees are not dynamic.
Answer: A
Explanation: Hash tables offer average O(1) time complexity for operations, making them preferable for unsorted data and frequent access, compared to the O(log n) of balanced binary search trees.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI