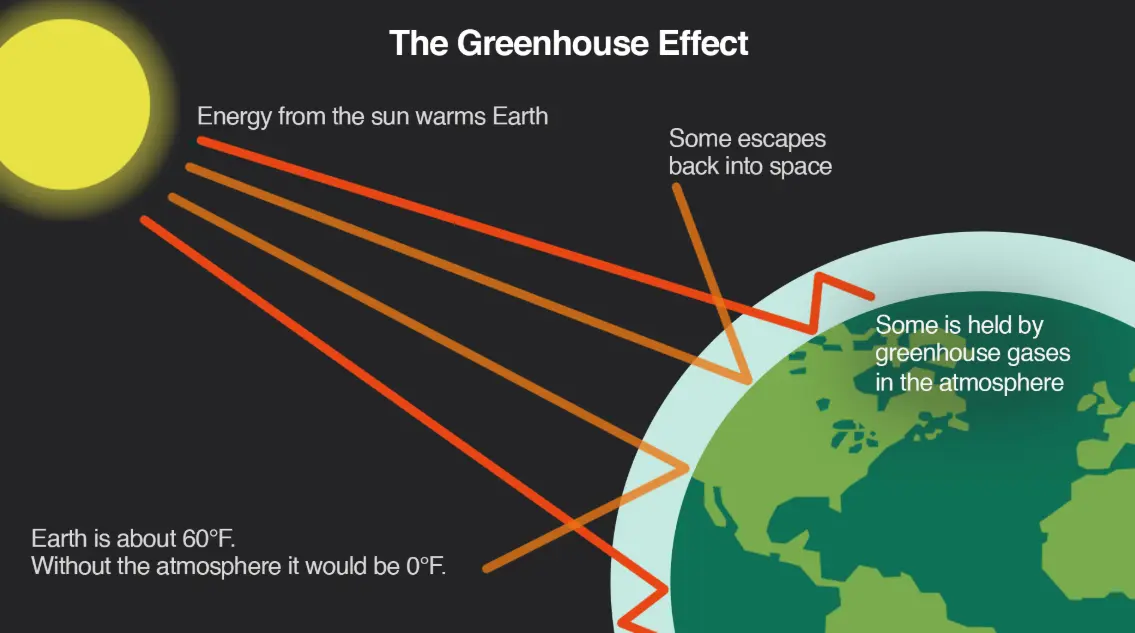
The greenhouse effect is a natural process where certain gases in Earth’s atmosphere, known as greenhouse gases (such as carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor), trap heat from the sun. This occurs when sunlight penetrates the atmosphere, warms the planet’s surface, and some of that heat is radiated back toward space. The gases act like a blanket, absorbing and re-emitting this heat, which helps maintain a stable temperature on Earth, making it habitable for life.
However, human activities, including burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, have increased the levels of these gases. This intensifies the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming, rising sea levels, and more frequent extreme weather events. While essential for life, an unchecked greenhouse effect poses significant risks to the planet’s climate balance.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Create a greenhouse effect quiz in minutes using AI with OnlineExamMaker
- Part 2: 20 greenhouse effect quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Try OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to create quiz questions
Part 1: Create a greenhouse effect quiz in minutes using AI with OnlineExamMaker
When it comes to ease of creating a greenhouse effect assessment, OnlineExamMaker is one of the best AI-powered quiz making software for your institutions or businesses. With its AI Question Generator, just upload a document or input keywords about your assessment topic, you can generate high-quality quiz questions on any topic, difficulty level, and format.
Overview of its key assessment-related features:
● AI Question Generator to help you save time in creating quiz questions automatically.
● Share your online exam with audiences on social platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Reddit and more.
● Instantly scores objective questions and subjective answers use rubric-based scoring for consistency.
● Simply copy and insert a few lines of embed codes to display your online exams on your website or WordPress blog.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 greenhouse effect quiz questions & answers
or
1. Question: What is the greenhouse effect?
Options:
A) A process where the Earth cools down rapidly
B) The trapping of heat in the Earth’s atmosphere by gases
C) The release of gases from volcanoes
D) The reflection of sunlight back into space
Answer: B
Explanation: The greenhouse effect occurs when gases like carbon dioxide absorb and re-emit infrared radiation, warming the planet and maintaining habitable temperatures.
2. Question: Which gas is the most significant contributor to the enhanced greenhouse effect?
Options:
A) Oxygen
B) Carbon dioxide
C) Nitrogen
D) Argon
Answer: B
Explanation: Carbon dioxide is the primary greenhouse gas from human activities like burning fossil fuels, leading to increased atmospheric concentrations and global warming.
3. Question: How do greenhouse gases affect Earth’s temperature?
Options:
A) They reflect sunlight away from Earth
B) They allow more heat to escape into space
C) They trap heat in the atmosphere
D) They cool the oceans
Answer: C
Explanation: Greenhouse gases form a layer that absorbs and re-radiates heat, preventing it from escaping, which raises the Earth’s surface temperature.
4. Question: What role does methane play in the greenhouse effect?
Options:
A) It has no effect on global temperatures
B) It is a potent greenhouse gas from sources like livestock and landfills
C) It helps reduce other greenhouse gases
D) It only affects the ozone layer
Answer: B
Explanation: Methane is about 25 times more effective at trapping heat than carbon dioxide over a 100-year period, contributing significantly to global warming.
5. Question: Which human activity is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions?
Options:
A) Planting trees
B) Burning fossil fuels
C) Recycling materials
D) Using solar energy
Answer: B
Explanation: Burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas releases carbon dioxide, a key greenhouse gas, exacerbating the greenhouse effect.
6. Question: What is the difference between the natural and enhanced greenhouse effect?
Options:
A) The natural one is caused by humans
B) The enhanced one is due to human activities increasing gas levels
C) There is no difference
D) The natural one only occurs at night
Answer: B
Explanation: The natural greenhouse effect keeps Earth warm enough for life, while the enhanced version results from human-induced increases in greenhouse gases, leading to rapid climate change.
7. Question: How does deforestation contribute to the greenhouse effect?
Options:
A) By increasing oxygen levels
B) By releasing stored carbon dioxide from trees
C) By cooling the atmosphere
D) By blocking sunlight
Answer: B
Explanation: Trees absorb carbon dioxide; cutting them down releases this gas and reduces the planet’s capacity to sequester carbon, intensifying the greenhouse effect.
8. Question: What is the main impact of the greenhouse effect on oceans?
Options:
A) Freezing of polar ice caps
B) Acidification and rising sea levels
C) Decreased evaporation
D) Increased marine biodiversity
Answer: B
Explanation: Excess greenhouse gases lead to ocean warming and absorption of CO2, causing acidification and thermal expansion, which raises sea levels.
9. Question: Which factor does not contribute to the greenhouse effect?
Options:
A) Water vapor
B) Chlorofluorocarbons
C) Ozone depletion
D) Stratospheric ozone
Answer: D
Explanation: Stratospheric ozone protects from UV rays but is not a primary greenhouse gas; other options like water vapor and CFCs directly trap heat.
10. Question: How does the greenhouse effect relate to global warming?
Options:
A) They are unrelated processes
B) Global warming is the result of the enhanced greenhouse effect
C) The greenhouse effect cools the planet
D) Global warming only affects land areas
Answer: B
Explanation: The enhanced greenhouse effect traps more heat, causing the average global temperature to rise, which is defined as global warming.
11. Question: What is a positive feedback loop in the context of the greenhouse effect?
Options:
A) A process that reduces greenhouse gases
B) Melting permafrost releasing more methane, amplifying warming
C) Planting more trees to absorb CO2
D) Reducing industrial emissions
Answer: B
Explanation: As temperatures rise, permafrost thaws and releases methane, a greenhouse gas, which further increases warming in a self-reinforcing cycle.
12. Question: Which international agreement aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions?
Options:
A) The Kyoto Protocol
B) The Geneva Convention
C) The Paris Agreement
D) Both A and C
Answer: D
Explanation: The Kyoto Protocol and Paris Agreement are key treaties designed to limit greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the greenhouse effect.
13. Question: How do clouds influence the greenhouse effect?
Options:
A) They have no influence
B) They can both trap heat and reflect sunlight, depending on conditions
C) They only cool the Earth
D) They increase greenhouse gas levels
Answer: B
Explanation: Clouds act as a double-edged sword, trapping outgoing heat like greenhouse gases while also reflecting incoming solar radiation, affecting overall warming.
14. Question: What is the approximate percentage of the greenhouse effect attributed to water vapor?
Options:
A) 10%
B) 50%
C) 95%
D) 0%
Answer: B
Explanation: Water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas, contributing about 50% to the natural greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation.
15. Question: How does urbanization exacerbate the greenhouse effect?
Options:
A) By increasing green spaces
B) Through higher energy consumption and heat absorption by buildings
C) By reducing vehicle use
D) By promoting natural habitats
Answer: B
Explanation: Urban areas with concrete and buildings absorb and retain heat, while increased energy use for heating and cooling releases more greenhouse gases.
16. Question: What is albedo in relation to the greenhouse effect?
Options:
A) The ability of surfaces to absorb heat
B) The reflection of solar radiation by surfaces
C) A type of greenhouse gas
D) The process of gas emission
Answer: B
Explanation: Albedo measures how much sunlight is reflected; lower albedo (e.g., from ice melt) means more absorption, enhancing the greenhouse effect.
17. Question: Which sector is the largest emitter of greenhouse gases globally?
Options:
A) Agriculture
B) Energy production
C) Transportation
D) Manufacturing
Answer: B
Explanation: Energy production, primarily from fossil fuels, accounts for the majority of global greenhouse gas emissions, driving the enhanced greenhouse effect.
18. Question: How can individuals help mitigate the greenhouse effect?
Options:
A) By increasing car usage
B) Through energy conservation and using renewable sources
C) By wasting resources
D) By avoiding public transport
Answer: B
Explanation: Personal actions like reducing energy use and adopting renewables lower greenhouse gas emissions, helping to counteract the greenhouse effect.
19. Question: What is the projected consequence of unchecked greenhouse effect?
Options:
A) Global cooling
B) Extreme weather events and biodiversity loss
C) Decreased sea levels
D) Improved crop yields everywhere
Answer: B
Explanation: Continued greenhouse gas emissions could lead to more frequent storms, droughts, and habitat destruction due to rising temperatures.
20. Question: How does the greenhouse effect vary by latitude?
Options:
A) It is stronger at the equator due to more sunlight
B) It is the same everywhere
C) It only occurs in polar regions
D) It is weaker near the equator
Answer: A
Explanation: The greenhouse effect is more pronounced in tropical regions where there is more incoming solar radiation, leading to greater heat trapping.
or
Part 3: Try OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to create quiz questions
Automatically generate questions using AI