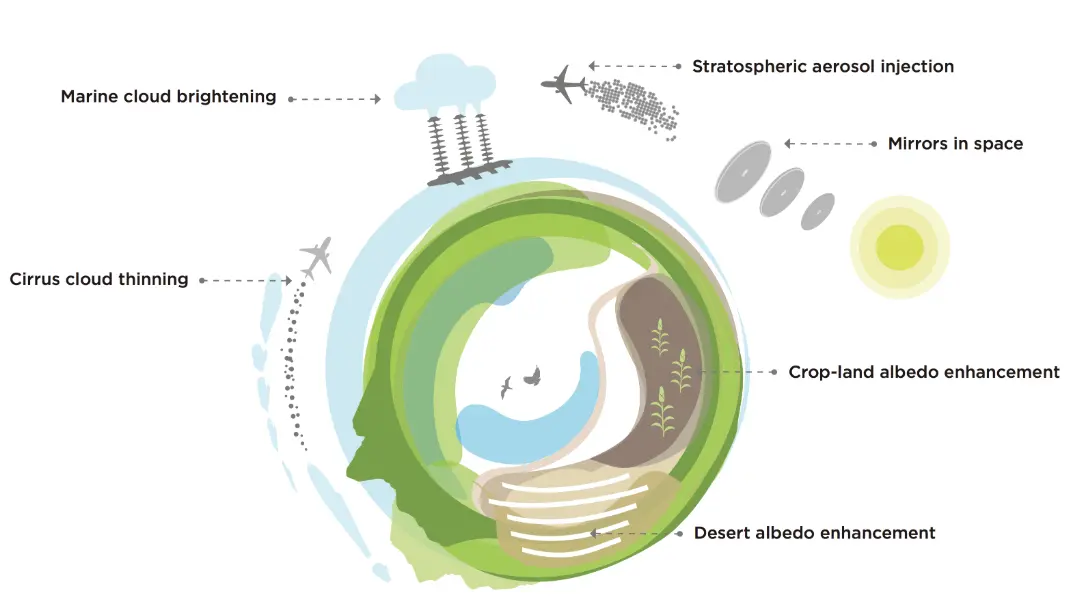
Climate Engineering, also known as geoengineering, involves deliberate, large-scale interventions in the Earth’s climate system to mitigate or reverse the effects of global warming. It encompasses two main categories: Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR), which focuses on extracting greenhouse gases from the atmosphere through methods like direct air capture, afforestation, and ocean fertilization; and Solar Radiation Management (SRM), which aims to reduce incoming solar energy by techniques such as stratospheric aerosol injection or marine cloud brightening. These approaches seek to address climate change challenges but require careful evaluation of potential environmental, social, and ethical implications.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Generator – The Easiest Way to Make Quizzes Online
- Part 2: 20 Climate Engineering Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: Automatically Generate Quiz Questions Using AI Question Generator
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Generator – The Easiest Way to Make Quizzes Online
Are you looking for an online assessment to test the Climate Engineering skills of your learners? OnlineExamMaker uses artificial intelligence to help quiz organizers to create, manage, and analyze exams or tests automatically. Apart from AI features, OnlineExamMaker advanced security features such as full-screen lockdown browser, online webcam proctoring, and face ID recognition.
Take a product tour of OnlineExamMaker:
● Includes a safe exam browser (lockdown mode), webcam and screen recording, live monitoring, and chat oversight to prevent cheating.
● AI Exam Grader for efficiently grading quizzes and assignments, offering inline comments, automatic scoring, and “fudge points” for manual adjustments.
● Embed quizzes on websites, blogs, or share via email, social media (Facebook, Twitter), or direct links.
● Handles large-scale testing (thousands of exams/semester) without internet dependency, backed by cloud infrastructure.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Climate Engineering Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is the primary goal of climate engineering?
Options:
A. To reduce greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels
B. To deliberately manipulate the Earth’s climate system to counteract global warming
C. To adapt human societies to the effects of climate change
D. To promote renewable energy sources worldwide
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Climate engineering, or geoengineering, involves intentional interventions to alter the climate, such as removing CO2 or reflecting sunlight, specifically to mitigate the effects of global warming.
2. Question: Which of the following is an example of carbon dioxide removal (CDR) techniques?
Options:
A. Stratospheric aerosol injection
B. Direct air capture and storage
C. Marine cloud brightening
D. Space-based sun shields
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Direct air capture involves removing CO2 directly from the atmosphere and storing it, which is a key CDR method aimed at reducing atmospheric greenhouse gases.
3. Question: What is solar radiation management (SRM)?
Options:
A. A process to enhance plant growth to absorb more CO2
B. Techniques to reflect a portion of the sun’s radiation back into space
C. Methods for capturing methane from industrial sources
D. Strategies for increasing ocean absorption of CO2
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: SRM focuses on reducing incoming solar energy to cool the planet, such as through aerosols or mirrors, rather than addressing greenhouse gas concentrations directly.
4. Question: Which gas is most commonly targeted in climate engineering for removal?
Options:
A. Methane
B. Carbon dioxide
C. Nitrous oxide
D. Water vapor
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Carbon dioxide is the primary greenhouse gas responsible for global warming, making it the main focus of many climate engineering efforts like CDR.
5. Question: What are the potential risks associated with stratospheric aerosol injection?
Options:
A. Ocean acidification
B. Disruption of regional weather patterns and ozone depletion
C. Increased biodiversity in forests
D. Enhanced agricultural yields
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Injecting aerosols into the stratosphere could alter precipitation, cause acid rain, and damage the ozone layer, leading to unintended global weather changes.
6. Question: How does bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) work?
Options:
A. By planting trees to naturally sequester carbon
B. By burning biomass for energy and capturing the emitted CO2 for storage
C. By reflecting sunlight with artificial clouds
D. By cooling the oceans to absorb more CO2
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: BECCS combines bioenergy production with CO2 capture technology to remove carbon from the atmosphere while generating energy, making it a hybrid CDR approach.
7. Question: What is a major ethical concern with climate engineering?
Options:
A. It could lead to over-reliance on technology instead of emission reductions
B. It promotes more fossil fuel use
C. It has no impact on biodiversity
D. It only affects developed countries
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Ethical issues include the risk of moral hazard, where climate engineering might delay necessary emission cuts by providing a perceived quick fix to warming.
8. Question: Which international agreement discusses the potential regulation of geoengineering?
Options:
A. The Kyoto Protocol
B. The Paris Agreement
C. The Convention on Biological Diversity
D. All of the above
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: While the Paris Agreement addresses climate change broadly, the Convention on Biological Diversity specifically calls for a moratorium on geoengineering, and the Kyoto Protocol touches on related emissions.
9. Question: What is the difference between mitigation and climate engineering?
Options:
A. Mitigation focuses on preventing emissions, while climate engineering intervenes after emissions occur
B. They are the same thing
C. Mitigation involves solar radiation techniques
D. Climate engineering is always cheaper
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Mitigation aims to reduce or prevent greenhouse gas emissions at the source, whereas climate engineering seeks to alter the climate directly to counteract existing warming.
10. Question: Which technique involves enhancing the reflectivity of clouds?
Options:
A. Iron fertilization of oceans
B. Marine cloud brightening
C. Afforestation
D. Direct air capture
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Marine cloud brightening uses sea salt aerosols to make clouds more reflective, thereby reducing the amount of solar radiation absorbed by the Earth.
11. Question: What could be a side effect of large-scale ocean iron fertilization?
Options:
A. Increased oxygen levels in the atmosphere
B. Algal blooms that deplete oxygen and create dead zones
C. Global cooling without any risks
D. Enhanced coral reef growth
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Fertilizing oceans with iron to promote algae growth could lead to harmful algal blooms, which consume oxygen and harm marine life, disrupting ecosystems.
12. Question: Why is climate engineering considered a controversial solution?
Options:
A. It is inexpensive and risk-free
B. It may have unforeseen global impacts and unequal effects on regions
C. It has been proven effective in all trials
D. It requires no international cooperation
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: The potential for irreversible environmental damage, geopolitical conflicts, and unequal benefits or harms makes climate engineering highly debated.
13. Question: What role do satellites play in climate engineering?
Options:
A. They monitor the effects of geoengineering techniques
B. They generate energy for CDR processes
C. They directly inject aerosols into the atmosphere
D. They have no role
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Satellites provide data on climate parameters, helping to assess the impacts and effectiveness of engineering interventions like SRM.
14. Question: Which method aims to mimic the cooling effects of volcanic eruptions?
Options:
A. Reforestation
B. Stratospheric aerosol injection
C. Carbon taxation
D. Wind energy development
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: By releasing aerosols into the stratosphere, this method replicates the global cooling observed after large volcanic eruptions, such as Mount Pinatubo.
15. Question: How does enhanced weathering work in climate engineering?
Options:
A. By spreading rocks that react with CO2 to form stable minerals
B. By increasing solar reflection with mirrors
C. By capturing CO2 in urban areas
D. By planting genetically modified crops
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Enhanced weathering accelerates the natural process where minerals like olivine react with CO2, turning it into stable compounds and removing it from the atmosphere.
16. Question: What is a key challenge in implementing direct air capture?
Options:
A. It is too effective and inexpensive
B. High energy requirements and costs make it impractical at scale
C. It has no environmental footprint
D. It only works in cold climates
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: The process demands significant energy to operate the fans and chemicals needed for capture, making it costly and energy-intensive for widespread use.
17. Question: Which organization is actively researching climate engineering?
Options:
A. The World Health Organization
B. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
C. The International Monetary Fund
D. The World Trade Organization
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: The IPCC assesses scientific literature on climate engineering as part of its reports, evaluating its potential risks and benefits alongside other climate strategies.
18. Question: What is the termination effect in solar radiation management?
Options:
A. A sudden warming if the technique is stopped
B. Permanent cooling of the planet
C. Increased CO2 levels without side effects
D. Enhanced biodiversity
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: If SRM is halted, the blocked solar radiation would no longer be reflected, potentially causing rapid warming as the full effects of greenhouse gases resume.
19. Question: How might climate engineering affect biodiversity?
Options:
A. It always increases species diversity
B. It could disrupt ecosystems through altered temperatures and precipitation
C. It has no impact on natural habitats
D. It only benefits marine life
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Interventions like SRM might change weather patterns, leading to habitat loss or shifts that negatively affect biodiversity in unpredictable ways.
20. Question: What is the main advantage of climate engineering over traditional mitigation?
Options:
A. It addresses existing warming more quickly
B. It is easier to implement without global cooperation
C. It eliminates the need for renewable energy
D. It has fewer side effects
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Climate engineering can potentially provide rapid cooling effects, offering a faster response to current climate impacts compared to long-term emission reductions.
or
Part 3: Automatically generate quiz questions using OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator
Automatically generate questions using AI