Clauses
A clause is a group of words containing a subject and a predicate (verb). Clauses form the building blocks of sentences and can be independent or dependent.
– Independent Clauses (Main Clauses): These express a complete thought and can stand alone as a sentence.
Example: “She runs every morning.”
– Dependent Clauses (Subordinate Clauses): These cannot stand alone and rely on an independent clause to form a complete sentence. They function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs.
Subtypes include:
– Noun Clauses: Act as nouns and often begin with words like “that,” “what,” or “who.”
Example: “I know what you mean.”
– Adjective Clauses: Modify nouns and usually start with relative pronouns like “which,” “that,” or “who.”
Example: “The book that I read was fascinating.”
– Adverb Clauses: Modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs and begin with subordinating conjunctions like “because,” “although,” or “when.”
Example: “She left because it was late.”
Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses, improving sentence flow and structure.
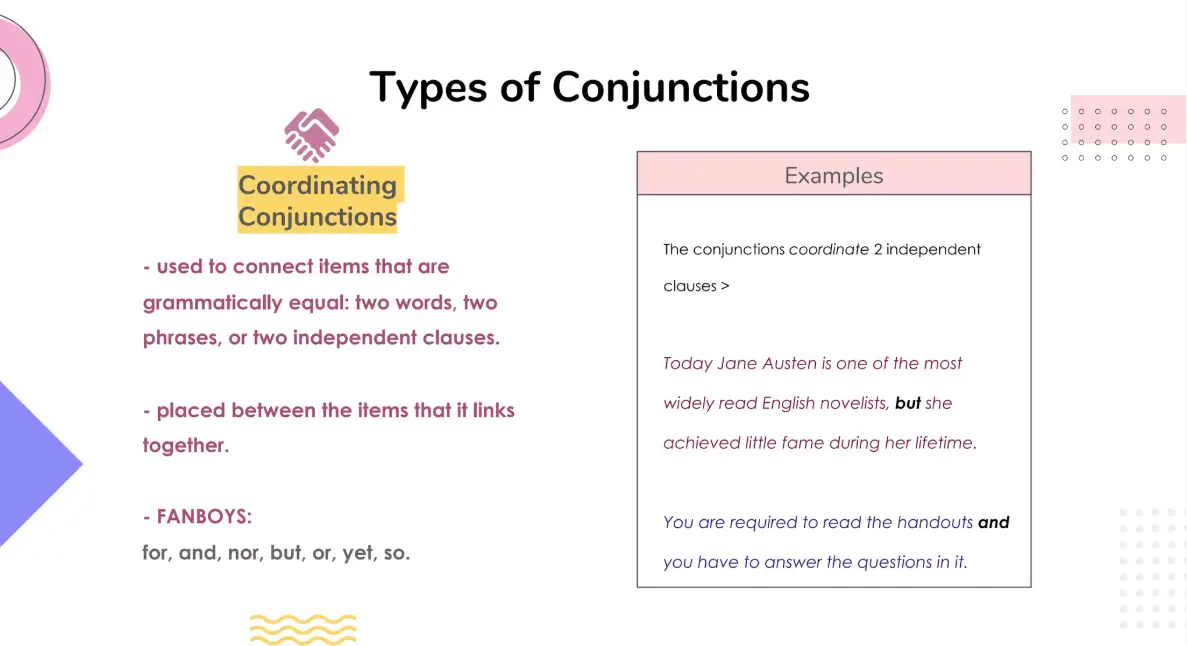
– Coordinating Conjunctions: Join elements of equal importance (words, phrases, or independent clauses). Common ones: and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet.
Example: “I wanted tea, but she preferred coffee.”
– Subordinating Conjunctions: Connect a dependent clause to an independent clause, showing relationships like time, cause, or condition. Examples: because, although, if, when, while.
Example: “Although it was raining, we went for a walk.”
– Correlative Conjunctions: Used in pairs to join balanced elements. Common pairs: either…or, neither…nor, both…and, not only…but also.
Example: “Not only did he finish the project, but he also exceeded expectations.”
How Clauses and Conjunctions Interact
Conjunctions link clauses to create complex sentences. For instance, coordinating conjunctions combine independent clauses, while subordinating conjunctions attach dependent clauses. This allows for varied sentence structures, such as:
– Simple: One independent clause.
– Compound: Two or more independent clauses joined by coordinating conjunctions.
Example: “I studied hard, and I passed the exam.”
– Complex: An independent clause and one or more dependent clauses joined by subordinating conjunctions.
Example: “Because I studied hard, I passed the exam.”
– Compound-Complex: Multiple independent clauses and at least one dependent clause.
Example: “I studied hard, and because I was prepared, I passed the exam.”
Effective use of clauses and conjunctions enhances clarity, rhythm, and coherence in writing.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Best AI quiz making software for creating a clauses and conjunctions quiz
- Part 2: 20 clauses and conjunctions quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate questions for any topic
Part 1: Best AI quiz making software for creating a clauses and conjunctions quiz
Nowadays more and more people create clauses and conjunctions quizzes using AI technologies, OnlineExamMaker a powerful AI-based quiz making tool that can save you time and efforts. The software makes it simple to design and launch interactive quizzes, assessments, and surveys. With the Question Editor, you can create multiple-choice, open-ended, matching, sequencing and many other types of questions for your tests, exams and inventories. You are allowed to enhance quizzes with multimedia elements like images, audio, and video to make them more interactive and visually appealing.
Take a product tour of OnlineExamMaker:
● Create a question pool through the question bank and specify how many questions you want to be randomly selected among these questions.
● Build and store questions in a centralized portal, tagged by categories and keywords for easy reuse and organization.
● Simply copy a few lines of codes, and add them to a web page, you can present your online quiz in your website, blog, or landing page.
● Randomize questions or change the order of questions to ensure exam takers don’t get the same set of questions each time.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 clauses and conjunctions quiz questions & answers
or
Question 1:
Which of the following is an example of an independent clause?
A) Because it was raining
B) Although she studied hard
C) The dog barked loudly
D) Whenever I go to the park
Answer: C
Explanation: An independent clause can stand alone as a complete sentence, and “The dog barked loudly” expresses a complete thought.
Question 2:
What type of conjunction is used in the sentence: “I wanted to go, but it was too late”?
A) Subordinating conjunction
B) Correlative conjunction
C) Coordinating conjunction
D) Prepositional conjunction
Answer: C
Explanation: “But” is a coordinating conjunction that joins two independent clauses of equal importance.
Question 3:
In the sentence: “After the meeting ended, we went for lunch,” what is “After the meeting ended” classified as?
A) Independent clause
B) Noun clause
C) Adjective clause
D) Dependent clause
Answer: D
Explanation: “After the meeting ended” is a dependent clause because it cannot stand alone and begins with a subordinating conjunction.
Question 4:
Which conjunction would best join these two sentences: “She likes tea. He prefers coffee”?
A) Although
B) Or
C) Because
D) While
Answer: B
Explanation: “Or” is a coordinating conjunction that shows a choice between two independent clauses.
Question 5:
Identify the subordinating conjunction in: “We stayed inside since it was storming outside.”
A) We
B) Stayed
C) Inside
D) Since
Answer: D
Explanation: “Since” is a subordinating conjunction that introduces a dependent clause explaining the reason.
Question 6:
What type of clause is “that he won the game” in the sentence: “I am happy that he won the game”?
A) Independent clause
B) Adverb clause
C) Noun clause
D) Adjective clause
Answer: C
Explanation: “That he won the game” functions as a noun clause acting as the object of the verb “am happy.”
Question 7:
In the sentence: “Either you clean your room or I will,” what type of conjunction is “Either…or”?
A) Coordinating conjunction
B) Subordinating conjunction
C) Correlative conjunction
D) Interjection
Answer: C
Explanation: “Either…or” is a pair of correlative conjunctions that connect two equal elements in a sentence.
Question 8:
Which of the following sentences correctly uses a conjunction to combine clauses?
A) The book is interesting although I haven’t finished it.
B) The book is interesting and I haven’t finished it.
C) The book is interesting because I haven’t finished it.
D) The book is interesting or I haven’t finished it.
Answer: A
Explanation: “Although” is a subordinating conjunction that properly links the dependent clause to the independent clause, showing contrast.
Question 9:
What is the function of the clause “who lives next door” in: “The girl who lives next door is my friend”?
A) It acts as an adverb clause.
B) It acts as a noun clause.
C) It acts as an adjective clause.
D) It acts as an independent clause.
Answer: C
Explanation: “Who lives next door” is an adjective clause that modifies the noun “girl.”
Question 10:
Choose the correct conjunction to complete: “I will go to the store _____ I finish my work.”
A) And
B) After
C) But
D) Or
Answer: B
Explanation: “After” is a subordinating conjunction that indicates time, linking the dependent clause to the independent one.
Question 11:
In the sentence: “Neither the teacher nor the students knew the answer,” what type of conjunction is used?
A) Coordinating conjunction
B) Subordinating conjunction
C) Correlative conjunction
D) Adverbial conjunction
Answer: C
Explanation: “Neither…nor” is a correlative conjunction that connects two subjects.
Question 12:
Which sentence contains a dependent clause?
A) Birds fly south in winter.
B) She runs every morning.
C) Because the sun set early.
D) The cat slept peacefully.
Answer: C
Explanation: “Because the sun set early” is a dependent clause as it starts with a subordinating conjunction and cannot stand alone.
Question 13:
What conjunction is missing in: “He studied hard _____ he passed the exam.”
A) So
B) Although
C) While
D) Before
Answer: A
Explanation: “So” is a coordinating conjunction that shows result, connecting the two independent clauses.
Question 14:
In “The reason I left early was that I felt ill,” what type of clause is “that I felt ill”?
A) Independent clause
B) Adjective clause
C) Noun clause
D) Adverb clause
Answer: C
Explanation: “That I felt ill” functions as a noun clause, serving as the subject complement.
Question 15:
Which is an example of an adverb clause?
A) The book that I read
B) Whoever arrives first
C) Because she was tired
D) The tall building
Answer: C
Explanation: “Because she was tired” is an adverb clause as it modifies the verb in the main clause by showing reason.
Question 16:
Correct the conjunction in: “I like apples and I don’t like oranges.” (If it’s already correct, select that option.)
A) But
B) And (correct as is)
C) Or
D) Although
Answer: B
Explanation: “And” is the appropriate coordinating conjunction here, as it joins two independent clauses without contradiction.
Question 17:
What role does “yet” play in: “He tried hard, yet he failed”?
A) It introduces a dependent clause.
B) It is a coordinating conjunction joining clauses.
C) It acts as a preposition.
D) It is a correlative conjunction.
Answer: B
Explanation: “Yet” is a coordinating conjunction that connects two independent clauses, indicating contrast.
Question 18:
In the sentence: “While we waited, the bus arrived,” what is “While we waited”?
A) An independent clause
B) A noun clause
C) An adjective clause
D) A dependent clause
Answer: D
Explanation: “While we waited” is a dependent clause introduced by a subordinating conjunction, showing time.
Question 19:
Choose the sentence with proper use of correlative conjunctions:
A) Both I like tea and coffee.
B) Either I like tea or coffee.
C) Neither I like tea nor coffee.
D) Not only I like tea but also coffee.
Answer: D
Explanation: “Not only…but also” is correctly used as correlative conjunctions to connect parallel elements.
Question 20:
What type of clause modifies a noun in: “The car that is red is mine”?
A) Noun clause
B) Adverb clause
C) Adjective clause
D) Independent clause
Answer: C
Explanation: “That is red” is an adjective clause that describes the noun “car.”
or
Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate questions for any topic
Automatically generate questions using AI