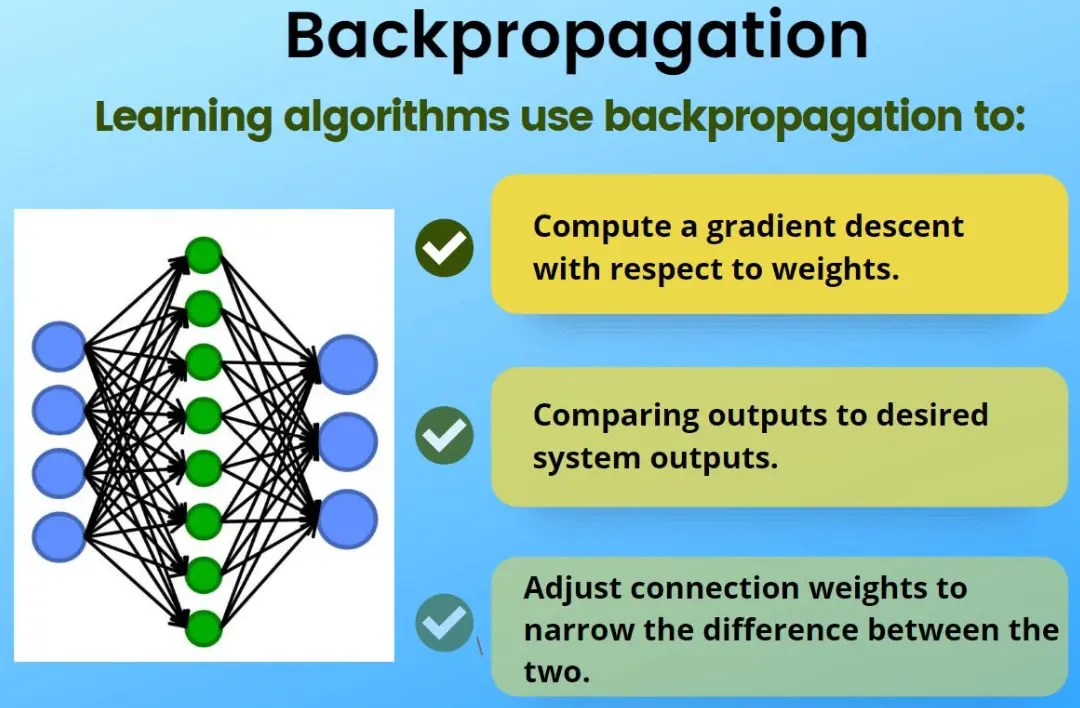
Backpropagation is a fundamental algorithm in training artificial neural networks, particularly in supervised learning. It calculates the gradient of the loss function with respect to the network’s weights by propagating the error backward from the output layer to the input layer. This process begins with a forward pass, where input data flows through the network to produce an output. The output is then compared to the actual target, generating an error value. This error is used to compute gradients for each weight through the chain rule of calculus, allowing adjustments to minimize the loss in the next iteration. By iteratively updating weights via gradient descent or its variants, backpropagation enables the network to learn complex patterns and improve performance over time. It is essential for deep learning models, forming the backbone of modern applications like image recognition and natural language processing.
Table of contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and share backpropagation quiz with AI automatically
- Part 2: 20 backpropagation quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and share backpropagation quiz with AI automatically
The quickest way to assess the backpropagation knowledge of candidates is using an AI assessment platform like OnlineExamMaker. With OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, you are able to input content—like text, documents, or topics—and then automatically generate questions in various formats (multiple-choice, true/false, short answer). Its AI Exam Grader can automatically grade the exam and generate insightful reports after your candidate submit the assessment.
What you will like:
● Create a question pool through the question bank and specify how many questions you want to be randomly selected among these questions.
● Allow the quiz taker to answer by uploading video or a Word document, adding an image, and recording an audio file.
● Display the feedback for correct or incorrect answers instantly after a question is answered.
● Create a lead generation form to collect an exam taker’s information, such as email, mobile phone, work title, company profile and so on.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 backpropagation quiz questions & answers
or
1. Question: What is the primary purpose of backpropagation in neural networks?
A. To perform forward propagation
B. To compute the gradients of the loss function with respect to the weights
C. To initialize the weights randomly
D. To select the activation function
Answer: B
Explanation: Backpropagation is used to calculate the gradients of the loss function relative to each weight by propagating the error from the output layer back to the input layer, enabling weight updates via gradient descent.
2. Question: In backpropagation, which mathematical concept is essential for computing gradients in a multi-layer network?
A. Matrix multiplication
B. The chain rule
C. Linear algebra determinants
D. Fourier transforms
Answer: B
Explanation: The chain rule allows the computation of gradients for each layer by multiplying the gradients from the subsequent layer with the local gradients of the current layer.
3. Question: During the backpropagation process, what happens in the backward pass?
A. The network processes input data
B. Gradients are calculated and propagated from the output to the input
C. Weights are randomly adjusted
D. The loss is minimized directly
Answer: B
Explanation: The backward pass computes the derivatives of the loss with respect to each parameter, starting from the output layer and moving backwards, to update the weights.
4. Question: What does the learning rate control in backpropagation?
A. The size of the weight updates
B. The number of hidden layers
C. The type of activation function
D. The input data scaling
Answer: A
Explanation: The learning rate determines how much the weights are adjusted based on the gradient; a smaller rate leads to smaller updates, preventing overshooting.
5. Question: In a neural network, how are weights updated after backpropagation?
A. By adding the gradient to the weight
B. By subtracting the learning rate times the gradient from the weight
C. By multiplying the weight by the gradient
D. By setting the weight to zero
Answer: B
Explanation: Weights are updated using the formula: new weight = old weight – (learning rate × gradient), which moves the weights in the direction that reduces the loss.
6. Question: What is a vanishing gradient problem in backpropagation?
A. Gradients become too large
B. Gradients become too small, hindering weight updates
C. Gradients are always zero
D. Gradients are computed incorrectly
Answer: B
Explanation: In deep networks, gradients can diminish exponentially through layers, especially with activation functions like sigmoid, making it hard to train early layers effectively.
7. Question: Which activation function is commonly used to mitigate the vanishing gradient problem?
A. Sigmoid
B. Tanh
C. ReLU
D. Linear
Answer: C
Explanation: ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) helps avoid vanishing gradients by outputting the input directly if positive, allowing gradients to flow more effectively.
8. Question: In backpropagation, the loss function is typically computed during which phase?
A. Forward pass
B. Backward pass
C. Weight initialization
D. Data preprocessing
Answer: A
Explanation: The loss is calculated in the forward pass after propagating the input through the network, and then used in the backward pass to compute gradients.
9. Question: What role does the bias term play in backpropagation?
A. It is not used in gradients
B. It is updated similarly to weights to shift the activation function
C. It determines the learning rate
D. It only affects the output layer
Answer: B
Explanation: Biases are treated like weights in backpropagation; their gradients are computed and used to update them, allowing the model to fit the data better by shifting the decision boundary.
10. Question: If the output of a neuron is y = σ(z), where z is the weighted sum, what is the derivative used in backpropagation for this neuron?
A. σ(z) * (1 – σ(z))
B. z
C. 1 / z
D. σ(z)
Answer: A
Explanation: For the sigmoid activation function, the derivative is σ(z) * (1 – σ(z)), which is multiplied by the incoming gradient during backpropagation.
11. Question: How does backpropagation handle multiple output neurons in a network?
A. It computes gradients only for the first output
B. It computes gradients for each output separately and sums them
C. It ignores outputs
D. It only works for single-output networks
Answer: B
Explanation: For multi-output networks, backpropagation calculates gradients for each output relative to the loss and propagates them back, often summing contributions if the loss is aggregated.
12. Question: What is the effect of a high learning rate in backpropagation?
A. Slower convergence
B. Overshooting the minimum, leading to instability
C. No effect on training
D. Reduced gradient computation
Answer: B
Explanation: A high learning rate can cause the weights to update too aggressively, potentially causing the loss to increase or oscillate instead of converging.
13. Question: In backpropagation, which layer’s gradients are computed first?
A. Input layer
B. Hidden layer
C. Output layer
D. All layers simultaneously
Answer: C
Explanation: Gradients start from the output layer, where the loss is directly computed, and then propagate backwards to the hidden and input layers.
14. Question: What happens if the gradient is zero during backpropagation?
A. Weights are updated normally
B. No update occurs for those weights
C. The network stops training
D. The learning rate increases
Answer: B
Explanation: A zero gradient means there is no change in the loss with respect to that weight, so the weight remains unchanged in that iteration.
15. Question: Which optimization algorithm is often used with backpropagation to update weights?
A. Gradient descent
B. Binary search
C. K-means clustering
D. Principal component analysis
Answer: A
Explanation: Backpropagation computes the gradients, which are then used by gradient descent or its variants to iteratively update the weights and minimize the loss.
16. Question: In a network with two hidden layers, how are gradients propagated?
A. From the first hidden layer to the output
B. From the output layer back to the first hidden layer
C. Only through the second hidden layer
D. Forward from input to output
Answer: B
Explanation: Gradients are propagated from the output layer back through the second hidden layer, then to the first hidden layer, applying the chain rule at each step.
17. Question: What is the chain rule’s role in computing the gradient for a hidden layer?
A. It multiplies the gradient from the next layer by the local derivative
B. It adds gradients directly
C. It divides gradients
D. It ignores hidden layers
Answer: A
Explanation: For a hidden layer, the gradient is the product of the gradient from the subsequent layer and the derivative of the activation function for that layer.
18. Question: How does backpropagation deal with mini-batch training?
A. It processes one sample at a time
B. It averages gradients over a batch before updating weights
C. It skips batches
D. It only uses full batches
Answer: B
Explanation: In mini-batch backpropagation, gradients are computed for a subset of data and averaged, then used to update weights, improving efficiency and generalization.
19. Question: What type of error is minimized using backpropagation?
A. Syntax error
B. Loss function error
C. Hardware error
D. Input error
Answer: B
Explanation: Backpropagation aims to minimize the loss function, such as mean squared error or cross-entropy, by adjusting weights based on gradients.
20. Question: In backpropagation, why is the activation function’s derivative needed?
A. To compute the forward pass
B. To calculate the gradient for the weights connected to that neuron
C. To select the input data
D. To initialize biases
Answer: B
Explanation: The derivative of the activation function is used in the chain rule to determine how changes in the weights affect the output, thus computing the necessary gradients for updates.
or
Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Automatically generate questions using AI