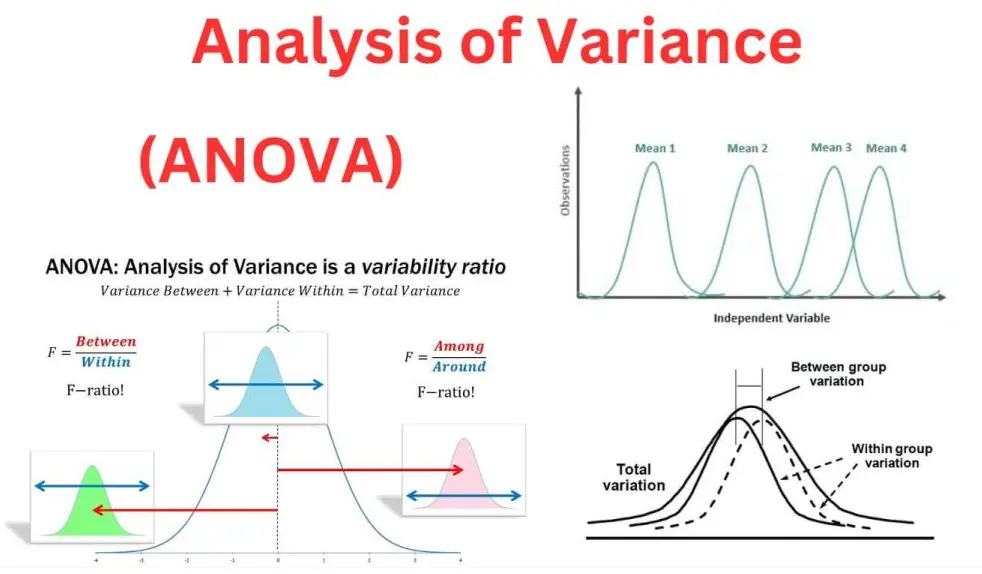
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) is a statistical method used to compare the means of three or more groups to determine if there are significant differences among them. It works by partitioning the total variability in a dataset into components: the variance between groups (which reflects differences due to the treatments or factors) and the variance within groups (which accounts for random variation). If the between-group variance is substantially larger than the within-group variance, it suggests that the group means are not equal. ANOVA is particularly useful in experimental designs, such as in agriculture, medicine, and social sciences, where researchers test hypotheses about multiple conditions. There are various types, including one-way ANOVA for a single factor and two-way ANOVA for two factors, each helping to identify interactions and main effects while controlling for error.
Table of contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and share analysis of variance quiz with AI automatically
- Part 2: 20 analysis of variance quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Automatically generate quiz questions using AI Question Generator
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and share analysis of variance quiz with AI automatically
OnlineExamMaker is a powerful AI-powered assessment platform to create auto-grading analysis of variance assessments. It’s designed for educators, trainers, businesses, and anyone looking to generate engaging quizzes without spending hours crafting questions manually. The AI Question Generator feature allows you to input a topic or specific details, and it generates a variety of question types automatically.
Top features for assessment organizers:
● Prevent cheating by randomizing questions or changing the order of questions, so learners don’t get the same set of questions each time.
● AI Exam Grader for efficiently grading quizzes and assignments, offering inline comments, automatic scoring, and “fudge points” for manual adjustments.
● Embed quizzes on websites, blogs, or share via email, social media (Facebook, Twitter), or direct links.
● Handles large-scale testing (thousands of exams/semester) without internet dependency, backed by cloud infrastructure.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 analysis of variance quiz questions & answers
or
1. Question: What is the primary purpose of Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)?
A. To compare the means of two groups
B. To compare the means of three or more groups
C. To measure the variability within a single group
D. To calculate the correlation between variables
Answer: B
Explanation: ANOVA is used to determine if there are any statistically significant differences between the means of three or more independent groups.
2. Question: In a one-way ANOVA, what does the F-statistic represent?
A. The ratio of between-group variability to within-group variability
B. The difference between group means
C. The total variability in the data
D. The standard deviation of the samples
Answer: A
Explanation: The F-statistic in one-way ANOVA is the ratio of the mean square between groups to the mean square within groups, testing if the group means are significantly different.
3. Question: Which assumption is NOT required for ANOVA?
A. Independence of observations
B. Homogeneity of variance
C. Normality of the dependent variable
D. Paired samples
Answer: D
Explanation: ANOVA requires independence, homogeneity of variance, and normality, but not paired samples, which are more relevant to t-tests.
4. Question: If the p-value in an ANOVA test is less than 0.05, what can be concluded?
A. There is no significant difference between groups
B. There is a significant difference between at least two groups
C. All groups have equal means
D. The variances are unequal
Answer: B
Explanation: A p-value below 0.05 indicates that the null hypothesis (no difference between group means) can be rejected, suggesting at least one group mean differs.
5. Question: What is the null hypothesis in a one-way ANOVA?
A. All group means are equal
B. At least one group mean is different
C. The variances are equal
D. The samples are not independent
Answer: A
Explanation: The null hypothesis in ANOVA states that there are no differences among the group means.
6. Question: In two-way ANOVA, how many independent variables are typically analyzed?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. None
Answer: B
Explanation: Two-way ANOVA examines the effects of two independent variables and their interaction on the dependent variable.
7. Question: What does a significant interaction effect in two-way ANOVA indicate?
A. One independent variable affects the dependent variable
B. The effect of one independent variable depends on the level of the other
C. Both independent variables have no effect
D. The dependent variable is normally distributed
Answer: B
Explanation: A significant interaction means the impact of one factor on the dependent variable varies depending on the level of the second factor.
8. Question: Which post-hoc test is commonly used after ANOVA to identify which groups differ?
A. Chi-square test
B. Tukey’s HSD test
C. T-test
D. Pearson correlation
Answer: B
Explanation: Tukey’s HSD (Honestly Significant Difference) test is used post-ANOVA to determine which specific groups have statistically significant differences.
9. Question: What is the formula for the degrees of freedom for the numerator in one-way ANOVA?
A. Number of groups minus 1
B. Total number of observations minus number of groups
C. Total number of observations
D. Number of groups
Answer: A
Explanation: The degrees of freedom for the between-groups sum of squares is the number of groups minus 1.
10. Question: When is a repeated measures ANOVA appropriate?
A. When groups are independent
B. When the same subjects are measured multiple times
C. When there are only two groups
D. When variances are unequal
Answer: B
Explanation: Repeated measures ANOVA is used when the same participants are tested under different conditions, accounting for within-subject variability.
11. Question: What does the term “factor” refer to in ANOVA?
A. The dependent variable
B. The independent variable
C. The error term
D. The p-value
Answer: B
Explanation: In ANOVA, a factor is an independent variable that is manipulated to observe its effect on the dependent variable.
12. Question: If ANOVA assumptions are violated, what alternative test might be used?
A. Kruskal-Wallis test
B. Pearson’s r
C. Linear regression
D. Z-test
Answer: A
Explanation: The Kruskal-Wallis test is a non-parametric alternative to one-way ANOVA when data do not meet assumptions like normality.
13. Question: In ANOVA, what is the mean square error (MSE)?
A. The average of the squared differences between group means
B. An estimate of the population variance based on within-group variability
C. The total sum of squares divided by degrees of freedom
D. The F-statistic value
Answer: B
Explanation: MSE is calculated from the within-group variability and serves as an unbiased estimator of the population variance.
14. Question: What is the critical value in ANOVA used for?
A. To determine the p-value
B. To compare against the calculated F-statistic
C. To calculate the degrees of freedom
D. To compute the sum of squares
Answer: B
Explanation: The critical value from the F-distribution is compared to the calculated F-statistic to decide whether to reject the null hypothesis.
15. Question: Which type of ANOVA is used for experiments with a blocking variable?
A. One-way ANOVA
B. Two-way ANOVA
C. Repeated measures ANOVA
D. Randomized block ANOVA
Answer: D
Explanation: Randomized block ANOVA accounts for a blocking variable to reduce variability and improve the accuracy of the test.
16. Question: If the F-statistic is greater than 1, what does this suggest?
A. Between-group variability is greater than within-group variability
B. All groups have equal means
C. The test is invalid
D. Within-group variability is greater than between-group variability
Answer: A
Explanation: An F-statistic greater than 1 indicates that the variability between groups is larger relative to within groups, suggesting potential differences.
17. Question: What is the effect size measure commonly used in ANOVA?
A. Cohen’s d
B. Eta-squared (η²)
C. Pearson’s r
D. Standard error
Answer: B
Explanation: Eta-squared measures the proportion of variance in the dependent variable that is explained by the independent variable(s) in ANOVA.
18. Question: In a factorial ANOVA, what is an interaction plot used for?
A. To visualize main effects only
B. To show how the effect of one factor changes across levels of another
C. To calculate the F-statistic
D. To test for normality
Answer: B
Explanation: An interaction plot graphically represents the interaction between factors, helping to interpret how one factor’s effect depends on another.
19. Question: What happens if you perform ANOVA on data with unequal sample sizes?
A. It is not possible
B. The results are invalid
C. ANOVA can still be performed if other assumptions are met
D. Only t-tests can be used
Answer: C
Explanation: ANOVA can handle unequal sample sizes as long as assumptions like homogeneity of variance are satisfied.
20. Question: Why is it important to check for outliers before conducting ANOVA?
A. Outliers can violate the normality assumption
B. Outliers do not affect ANOVA results
C. Outliers increase the degrees of freedom
D. Outliers are required for ANOVA
Answer: A
Explanation: Outliers can distort the data distribution, potentially violating the normality assumption and leading to inaccurate ANOVA results.
or
Part 3: Automatically generate quiz questions using OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator
Automatically generate questions using AI