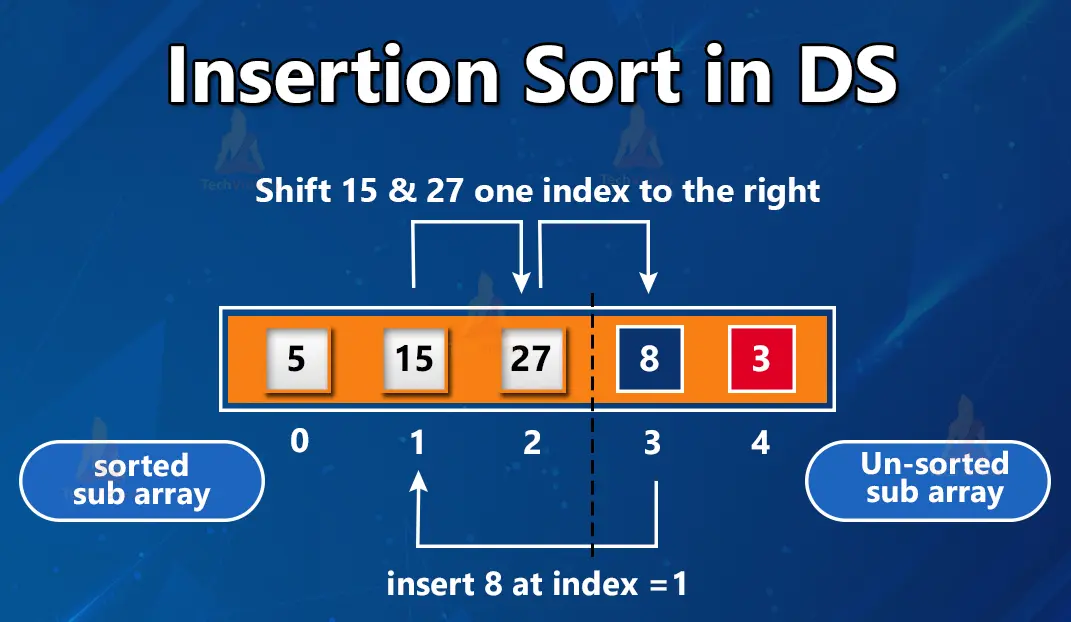
Insertion Sort is a simple sorting algorithm that builds a final sorted array one element at a time. It works by iterating through an array, starting from the second element, and for each element, it compares it with the elements before it and inserts it into its correct position in the already sorted portion of the array.
For example, consider an unsorted array: [5, 2, 4, 6, 1].
– Start with the first element, which is already sorted: [5].
– Take the second element (2) and insert it into the sorted portion: [2, 5].
– Take the third element (4) and insert it: [2, 4, 5].
– Take the fourth element (6) and insert it: [2, 4, 5, 6].
– Take the fifth element (1) and insert it: [1, 2, 4, 5, 6].
The array is now fully sorted. This algorithm is efficient for small datasets or nearly sorted arrays, with a time complexity of O(n) in the best case and O(n²) in the worst case. It operates in-place, meaning it uses only a constant amount of extra space, and it is stable, preserving the order of equal elements.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Maker – Make A Free Quiz in Minutes
- Part 2: 20 Insertion Sort Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Maker – Make A Free Quiz in Minutes
What’s the best way to create a Insertion Sort quiz online? OnlineExamMaker is the best AI quiz making software for you. No coding, and no design skills required. If you don’t have the time to create your online quiz from scratch, you are able to use OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to create question automatically, then add them into your online assessment. What is more, the platform leverages AI proctoring and AI grading features to streamline the process while ensuring exam integrity.
Key features of OnlineExamMaker:
● Create up to 10 question types, including multiple-choice, true/false, fill-in-the-blank, matching, short answer, and essay questions.
● Build and store questions in a centralized portal, tagged by categories and keywords for easy reuse and organization.
● Automatically scores multiple-choice, true/false, and even open-ended/audio responses using AI, reducing manual work.
● Create certificates with personalized company logo, certificate title, description, date, candidate’s name, marks and signature.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Insertion Sort Quiz Questions & Answers
or
Question 1:
What is the primary operation in Insertion Sort?
A) Swapping elements
B) Dividing the array into halves
C) Shifting elements to make space
D) Merging sorted subarrays
Answer: C
Explanation: Insertion Sort builds the sorted array one item at a time by shifting elements in the sorted portion to insert the new element.
Question 2:
In Insertion Sort, how is the array initially treated?
A) As two halves
B) As a single element considered sorted
C) As fully sorted
D) As reversed
Answer: B
Explanation: Insertion Sort starts with the second element, assuming the first element is already sorted, and inserts subsequent elements into the sorted subarray.
Question 3:
What is the worst-case time complexity of Insertion Sort?
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(n log n)
D) O(n^2)
Answer: D
Explanation: The worst case occurs when the array is sorted in reverse order, requiring comparisons and shifts for nearly every element, leading to quadratic time complexity.
Question 4:
Which of the following best describes Insertion Sort?
A) A divide-and-conquer algorithm
B) An in-place sorting algorithm
C) A recursive algorithm
D) A stable external sort
Answer: B
Explanation: Insertion Sort is an in-place algorithm that sorts the array by swapping or shifting elements within the same array space.
Question 5:
In Insertion Sort, what happens when an element is smaller than the previous one?
A) It is swapped immediately
B) It is moved to the end
C) It is shifted right until the correct position is found
D) The array is reversed
Answer: C
Explanation: The element is compared with the previous elements and shifted right in the sorted subarray until it reaches its correct position.
Question 6:
What is the space complexity of Insertion Sort?
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(n log n)
D) O(n^2)
Answer: A
Explanation: Insertion Sort uses a constant amount of extra space, as it only requires a few variables for swapping or shifting, making it an in-place sort.
Question 7:
For an already sorted array, what is the number of comparisons in Insertion Sort?
A) 0
B) n-1
C) n
D) n^2
Answer: B
Explanation: In the best case, for an array of n elements, Insertion Sort makes n-1 comparisons, as each element is already in its correct position relative to the previous ones.
Question 8:
Which sorting algorithm is similar to how people sort playing cards in their hands?
A) Quick Sort
B) Merge Sort
C) Insertion Sort
D) Heap Sort
Answer: C
Explanation: Insertion Sort mimics the way a person inserts a card into the correct position in a sorted hand, one card at a time.
Question 9:
Is Insertion Sort stable?
A) Yes
B) No
Answer: A
Explanation: Insertion Sort maintains the relative order of equal elements because it only shifts elements when necessary and inserts the new element in the correct position without swapping equal ones.
Question 10:
What is the best-case time complexity of Insertion Sort?
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(n log n)
D) O(n^2)
Answer: B
Explanation: When the array is already sorted, Insertion Sort runs in linear time, performing only one pass through the array.
Question 11:
In Insertion Sort, how many passes are made through the array?
A) 1
B) n-1
C) n
D) Depends on the array size
Answer: C
Explanation: Insertion Sort processes each element from the second to the last, making a total of n-1 insertions, but it effectively passes through the array once for each element after the first.
Question 12:
Which of the following arrays will take the most time for Insertion Sort?
A) Already sorted array
B) Random array
C) Reverse sorted array
D) Array with duplicates
Answer: C
Explanation: A reverse sorted array requires the maximum number of shifts and comparisons, leading to the worst-case time complexity.
Question 13:
Can Insertion Sort be used for linked lists efficiently?
A) Yes
B) No
Answer: A
Explanation: Insertion Sort can be efficient for linked lists because inserting an element into a sorted sublist only requires pointer manipulation, without shifting elements.
Question 14:
What does Insertion Sort do in the first iteration?
A) Sorts the entire array
B) Compares the first two elements
C) Swaps the last two elements
D) Does nothing
Answer: B
Explanation: In the first iteration, it compares the second element with the first and inserts it into the correct position if needed.
Question 15:
How does Insertion Sort handle duplicates?
A) It removes them
B) It swaps them randomly
C) It maintains their order
D) It places them at the end
Answer: C
Explanation: As a stable sort, Insertion Sort keeps the original order of duplicate elements when they are equal.
Question 16:
What is a key advantage of Insertion Sort over Bubble Sort?
A) Faster in best case
B) Uses less space
C) Always stable
D) Requires less code
Answer: A
Explanation: Insertion Sort performs better in the best case (already sorted array) with O(n) time, while Bubble Sort is always O(n^2).
Question 17:
In an array of 5 elements, how many elements are in the initial sorted subarray?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 5
D) 4
Answer: B
Explanation: Insertion Sort begins with the first element as the initial sorted subarray.
Question 18:
Why is Insertion Sort adaptive?
A) It works on any data type
B) It performs better on nearly sorted arrays
C) It adapts to the machine’s speed
D) It changes its algorithm dynamically
Answer: B
Explanation: Insertion Sort is adaptive because its performance improves on partially sorted arrays, reducing the number of operations needed.
Question 19:
What is the average time complexity of Insertion Sort?
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(n log n)
D) O(n^2)
Answer: D
Explanation: On average, for a random array, Insertion Sort has a quadratic time complexity due to the nested loop structure.
Question 20:
Insertion Sort is most efficient for:
A) Large datasets
B) Small or nearly sorted arrays
C) Reverse sorted arrays
D) Arrays with negative numbers
Answer: B
Explanation: Insertion Sort is efficient for small arrays or arrays that are already nearly sorted, as it requires fewer operations in such cases.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI