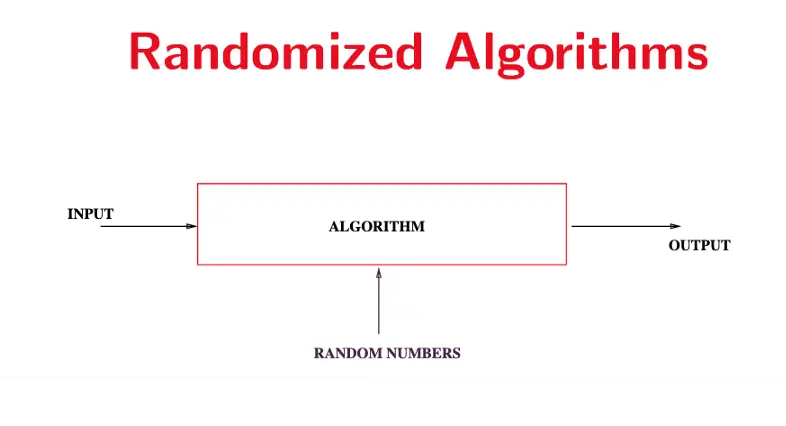
Randomized algorithms are a class of computational procedures that incorporate randomness in their decision-making process to solve problems more efficiently or effectively. Unlike deterministic algorithms, which follow a fixed path for any given input, randomized algorithms make random choices during execution, leading to varying outcomes for the same input.
These algorithms are particularly valuable for tackling complex problems where deterministic approaches might be computationally expensive or impractical. For example, in quicksort, selecting a random pivot element helps achieve an expected time complexity of O(n log n), reducing the risk of worst-case performance. Another application is the Monte Carlo method, used in simulations to approximate solutions to mathematical problems by generating random samples.
Key advantages include simplicity in design, faster average-case performance, and the ability to handle uncertainty. However, they may produce incorrect results with a small probability, necessitating techniques like repeated trials for greater accuracy. Randomized algorithms are widely used in areas such as cryptography, network optimization, and machine learning, making them a powerful tool in modern computer science.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and Share Randomized Algorithms Quiz with AI Automatically
- Part 2: 20 Randomized Algorithms Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and Share Randomized Algorithms Quiz with AI Automatically
OnlineExamMaker is a powerful AI-powered assessment platform to create auto-grading Randomized Algorithms skills assessments. It’s designed for educators, trainers, businesses, and anyone looking to generate engaging quizzes without spending hours crafting questions manually. The AI Question Generator feature allows you to input a topic or specific details, and it generates a variety of question types automatically.
Top features for assessment organizers:
● Prevent cheating by randomizing questions or changing the order of questions, so learners don’t get the same set of questions each time.
● AI Exam Grader for efficiently grading quizzes and assignments, offering inline comments, automatic scoring, and “fudge points” for manual adjustments.
● Embed quizzes on websites, blogs, or share via email, social media (Facebook, Twitter), or direct links.
● Handles large-scale testing (thousands of exams/semester) without internet dependency, backed by cloud infrastructure.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Randomized Algorithms Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is a randomized algorithm?
Options:
A) An algorithm that always produces deterministic outputs.
B) An algorithm that uses randomness to make decisions.
C) An algorithm that runs in random order of operations.
D) An algorithm that only works with random data inputs.
Answer: B
Explanation: A randomized algorithm incorporates randomness in its steps, which can lead to different outputs for the same input, providing benefits like efficiency or simplicity in analysis.
2. Question: Which of the following best describes a Las Vegas randomized algorithm?
Options:
A) It always produces the correct output but the running time varies.
B) It may produce incorrect output but always runs in expected time.
C) It produces output with a certain probability and fixed time.
D) It never uses randomness.
Answer: A
Explanation: Las Vegas algorithms guarantee the correct output while their running time is randomized, making them useful for scenarios where accuracy is paramount.
3. Question: In a Monte Carlo randomized algorithm, what is typically randomized?
Options:
A) The input data.
B) The output verification process.
C) The computation steps to estimate a result.
D) The algorithm’s termination condition.
Answer: C
Explanation: Monte Carlo algorithms use randomness in their computations to approximate solutions, accepting a probability of error for faster execution.
4. Question: What is the primary advantage of using randomized quicksort over deterministic quicksort?
Options:
A) It always sorts in O(n) time.
B) It reduces the worst-case time complexity in practice.
C) It eliminates the need for pivot selection.
D) It works only on sorted arrays.
Answer: B
Explanation: Randomized quicksort selects a random pivot, which minimizes the probability of worst-case performance, making the expected time complexity O(n log n).
5. Question: In randomized algorithms, what does “expected time complexity” refer to?
Options:
A) The average time over all possible inputs.
B) The time taken in the best case.
C) The time weighted by the probability of random choices.
D) The worst-case time for any input.
Answer: C
Explanation: Expected time complexity accounts for the probabilistic nature of random decisions, providing an average performance metric based on randomness.
6. Question: Which randomized algorithm is commonly used for primality testing?
Options:
A) Bubble sort.
B) Miller-Rabin test.
C) Binary search.
D) Depth-first search.
Answer: B
Explanation: The Miller-Rabin test uses randomness to determine if a number is prime with high probability, making it efficient for large numbers.
7. Question: In a skip list data structure, what role does randomness play?
Options:
A) It determines the height of nodes.
B) It sorts the elements automatically.
C) It decides the search path only.
D) It is not used at all.
Answer: A
Explanation: Randomness in skip lists determines the level of each node, which helps in achieving an expected O(log n) search time similar to balanced trees.
8. Question: Why might a randomized algorithm have a lower probability of adversarial inputs?
Options:
A) It avoids inputs entirely.
B) Randomness makes worst-case inputs less likely.
C) It only processes random data.
D) Adversarial inputs are impossible.
Answer: B
Explanation: By incorporating randomness, the algorithm reduces the chance that an attacker can craft inputs that exploit worst-case scenarios, enhancing robustness.
9. Question: What is universal hashing in randomized algorithms?
Options:
A) A hashing method that works for all data types.
B) A family of hash functions where any two keys collide with low probability.
C) A deterministic hashing technique.
D) A method that randomizes output only.
Answer: B
Explanation: Universal hashing uses a randomly chosen hash function from a universal family, ensuring that collisions between keys are minimized on average.
10. Question: In randomized binary search, how is randomness typically introduced?
Options:
A) By shuffling the array first.
B) By randomly selecting the pivot element.
C) By randomizing the comparison operator.
D) It is not randomized.
Answer: B
Explanation: Randomizing the pivot in binary search helps avoid worst-case scenarios in unbalanced trees or arrays, improving average performance.
11. Question: Which of the following is an example of a Monte Carlo algorithm for integration?
Options:
A) Simpson’s rule.
B) Monte Carlo integration method.
C) Gaussian elimination.
D) Quick sort.
Answer: B
Explanation: Monte Carlo integration uses random sampling to estimate integrals, providing an approximation with a controllable error probability.
12. Question: What is the expected time complexity of a successful randomized quickselect?
Options:
A) O(1).
B) O(n).
C) O(n log n).
D) O(n^2).
Answer: C
Explanation: Randomized quickselect has an expected time complexity of O(n log n) due to the random pivot selection, which balances the partitioning.
13. Question: In graph algorithms, what does a randomized minimum spanning tree algorithm use randomness for?
Options:
A) To select edges randomly.
B) To verify the tree structure.
C) To approximate the MST with high probability.
D) To sort the edges.
Answer: C
Explanation: Algorithms like Karger’s for MST use randomness to find an approximate solution efficiently, reducing computation time.
14. Question: How does randomness help in analyzing algorithms with adversarial inputs?
Options:
A) It eliminates adversarial inputs.
B) It makes the analysis probabilistic and harder for adversaries to exploit.
C) It speeds up the algorithm always.
D) It is irrelevant to analysis.
Answer: B
Explanation: Randomness introduces uncertainty, making it difficult for adversaries to predict and exploit specific inputs, thus improving overall reliability.
15. Question: What is a key limitation of Monte Carlo algorithms?
Options:
A) They are always accurate.
B) They may produce incorrect results with some probability.
C) They run in constant time.
D) They do not use randomness.
Answer: B
Explanation: Monte Carlo algorithms trade off accuracy for speed, potentially outputting incorrect results, which requires multiple runs for verification.
16. Question: In randomized incremental algorithms, what is typically randomized?
Options:
A) The order of processing elements.
B) The output format.
C) The input size.
D) The algorithm’s loops.
Answer: A
Explanation: Randomizing the order of elements helps achieve expected linear time complexity in algorithms like building convex hulls.
17. Question: Which property ensures that a randomized algorithm is unbiased?
Options:
A) It always outputs the correct answer.
B) The probability distribution is symmetric.
C) It runs in expected polynomial time.
D) Randomness is evenly distributed.
Answer: B
Explanation: An unbiased randomized algorithm has a symmetric probability distribution, ensuring fair treatment of all possible outcomes.
18. Question: What is the role of randomness in the probabilistic quicksort analysis?
Options:
A) To guarantee O(n) time.
B) To analyze the average-case performance.
C) To make the algorithm fail-safe.
D) To handle only random inputs.
Answer: B
Explanation: Randomness allows for average-case analysis, showing that quicksort performs well in O(n log n) time with high probability.
19. Question: In a randomized algorithm for load balancing, what does randomness achieve?
Options:
A) Equal distribution always.
B) Probabilistic even distribution of tasks.
C) Faster computation without balancing.
D) No distribution at all.
Answer: B
Explanation: Randomness in load balancing ensures that tasks are distributed evenly on average, reducing the chance of overload on any single processor.
20. Question: Why are randomized algorithms useful in cryptography?
Options:
A) They encrypt data deterministically.
B) They introduce unpredictability for security.
C) They speed up decryption only.
D) They avoid keys entirely.
Answer: B
Explanation: Randomized algorithms in cryptography, like randomized encryption, add unpredictability, making it harder for attackers to predict or reverse engineer processes.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI