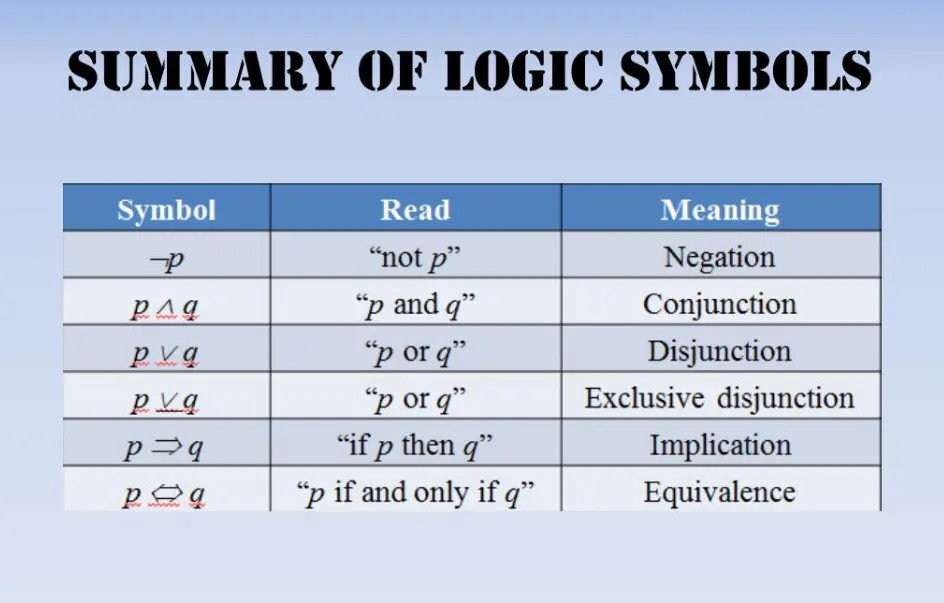
Logical symbols are essential tools in formal logic, mathematics, and computer science, used to represent relationships, operations, and quantifiers. Below is a structured overview categorized by common types:
#Propositional Logic Symbols
– Conjunction (AND): ∧
Represents the logical AND operation, true only if both operands are true (e.g., P ∧ Q).
– Disjunction (OR): ∨
Represents the logical OR operation, true if at least one operand is true (e.g., P ∨ Q).
– Negation (NOT): ¬
Inverts the truth value of a proposition (e.g., ¬P).
– Implication (IF-THEN): ⇒
Indicates that if the antecedent is true, the consequent must be true (e.g., P ⇒ Q).
– Biconditional (IF AND ONLY IF): ⇔
True when both sides have the same truth value (e.g., P ⇔ Q).
#Predicate Logic Symbols
– Universal Quantifier (FOR ALL): ∀
Asserts that a statement holds for every element in a domain (e.g., ∀x P(x)).
– Existential Quantifier (THERE EXISTS): ∃
Asserts that a statement holds for at least one element in a domain (e.g., ∃x P(x)).
#Set Theory and Equality Symbols
– Equality: =
Denotes that two expressions are equal (e.g., x = y).
– Subset: ⊆
Indicates that one set is a subset of another (e.g., A ⊆ B).
– Element Of: ∈
Shows that an element belongs to a set (e.g., x ∈ S).
#Other Common Symbols
– Tautology (TRUE): ⊤
Represents a statement that is always true.
– Contradiction (FALSE): ⊥
Represents a statement that is always false.
– Exclusive OR (XOR): ⊕
True if exactly one operand is true.
These symbols facilitate precise communication in logical reasoning, proofs, and algorithms. They are foundational in fields like philosophy, AI, and programming, enabling the formalization of arguments and computations.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and Share Logical Symbols Quiz with AI Automatically
- Part 2: 20 Logical Symbols Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate Questions for Any Topic
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and Share Logical Symbols Quiz with AI Automatically
The quickest way to assess the Logical Symbols knowledge of candidates is using an AI assessment platform like OnlineExamMaker. With OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, you are able to input content—like text, documents, or topics—and then automatically generate questions in various formats (multiple-choice, true/false, short answer). Its AI Exam Grader can automatically grade the exam and generate insightful reports after your candidate submit the assessment.
What you will like:
● Create a question pool through the question bank and specify how many questions you want to be randomly selected among these questions.
● Allow the quiz taker to answer by uploading video or a Word document, adding an image, and recording an audio file.
● Display the feedback for correct or incorrect answers instantly after a question is answered.
● Create a lead generation form to collect an exam taker’s information, such as email, mobile phone, work title, company profile and so on.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Logical Symbols Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What does the symbol ∧ represent in logic?
Options:
A) Or
B) And
C) Not
D) Implies
Answer: B) And
Explanation: The ∧ symbol denotes logical conjunction, which is true only if both operands are true.
2. Question: What does the symbol ∨ represent in logic?
Options:
A) And
B) Or
C) Not
D) If-then
Answer: B) Or
Explanation: The ∨ symbol denotes logical disjunction, which is true if at least one operand is true.
3. Question: What does the symbol ¬ represent in logic?
Options:
A) And
B) Or
C) Not
D) Equivalent
Answer: C) Not
Explanation: The ¬ symbol denotes negation, which reverses the truth value of the operand.
4. Question: What does the symbol → represent in logic?
Options:
A) And
B) Or
C) Not
D) Implies
Answer: D) Implies
Explanation: The → symbol denotes material implication, which is false only when the antecedent is true and the consequent is false.
5. Question: What does the symbol ↔ represent in logic?
Options:
A) Implies
B) Equivalent
C) Or
D) And
Answer: B) Equivalent
Explanation: The ↔ symbol denotes logical equivalence, which is true when both operands have the same truth value.
6. Question: In a truth table for P ∧ Q, what is the output when P is true and Q is false?
Options:
A) True
B) False
C) Sometimes true
D) Undefined
Answer: B) False
Explanation: For conjunction (∧), the result is true only if both P and Q are true; otherwise, it is false.
7. Question: In a truth table for P ∨ Q, what is the output when both P and Q are false?
Options:
A) True
B) False
C) True if P is true
D) Undefined
Answer: B) False
Explanation: For disjunction (∨), the result is false only if both P and Q are false.
8. Question: What is the result of ¬(P ∧ Q) according to De Morgan’s laws?
Options:
A) ¬P ∧ ¬Q
B) ¬P ∨ ¬Q
C) P ∨ Q
D) P ∧ Q
Answer: B) ¬P ∨ ¬Q
Explanation: De Morgan’s law states that the negation of a conjunction is equivalent to the disjunction of the negations.
9. Question: What is the result of ¬(P ∨ Q) according to De Morgan’s laws?
Options:
A) ¬P ∨ ¬Q
B) ¬P ∧ ¬Q
C) P ∧ Q
D) P ∨ Q
Answer: B) ¬P ∧ ¬Q
Explanation: De Morgan’s law states that the negation of a disjunction is equivalent to the conjunction of the negations.
10. Question: Which logical expression is a tautology?
Options:
A) P ∧ ¬P
B) P ∨ ¬P
C) P → ¬P
D) ¬P ∧ P
Answer: B) P ∨ ¬P
Explanation: The law of excluded middle states that P or not P is always true.
11. Question: Which logical expression is a contradiction?
Options:
A) P ∨ ¬P
B) P ∧ ¬P
C) P → P
D) ¬P ∨ P
Answer: B) P ∧ ¬P
Explanation: A conjunction of a statement and its negation is always false.
12. Question: What is the logical equivalence of P → Q?
Options:
A) ¬P ∨ Q
B) P ∧ Q
C) ¬P ∧ Q
D) P ∨ Q
Answer: A) ¬P ∨ Q
Explanation: Implication (P → Q) is equivalent to the disjunction of the negation of P and Q.
13. Question: If P is true and Q is true, what is the value of P ↔ Q?
Options:
A) True
B) False
C) Depends on P
D) Undefined
Answer: A) True
Explanation: Biconditional (↔) is true when both operands have the same truth value.
14. Question: What does the symbol ∀ represent?
Options:
A) There exists
B) For all
C) Not
D) And
Answer: B) For all
Explanation: The ∀ symbol is used in predicate logic to denote universal quantification.
15. Question: What does the symbol ∃ represent?
Options:
A) For all
B) There exists
C) Implies
D) Or
Answer: B) There exists
Explanation: The ∃ symbol is used in predicate logic to denote existential quantification.
16. Question: In set theory, what does the symbol ∈ mean?
Options:
A) Subset
B) Element of
C) Union
D) Intersection
Answer: B) Element of
Explanation: The ∈ symbol indicates that an element is a member of a set.
17. Question: What is the logical expression for “if P then Q, and Q then P”?
Options:
A) P → Q
B) P ↔ Q
C) P ∧ Q
D) P ∨ Q
Answer: B) P ↔ Q
Explanation: Biconditional (↔) represents mutual implication.
18. Question: Which of the following is equivalent to ¬(P → Q)?
Options:
A) P ∧ ¬Q
B) ¬P ∨ Q
C) P ∨ Q
D) ¬P ∧ Q
Answer: A) P ∧ ¬Q
Explanation: The negation of implication (P → Q) is equivalent to P being true and Q being false.
19. Question: For the expression (P ∨ Q) ∧ ¬P, what is the simplified form?
Options:
A) Q
B) P
C) False
D) True
Answer: A) Q
Explanation: The expression simplifies to Q because if P is false, then Q must be true for the whole to be true.
20. Question: What is the truth value of (P ∧ Q) → (P ∨ Q)?
Options:
A) Always true
B) Always false
C) True only if P is true
D) True only if Q is true
Answer: A) Always true
Explanation: This is a tautology because if P and Q are both true, the consequent is true; otherwise, the antecedent is false, making the implication true.
or
Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate Questions for Any Topic
Automatically generate questions using AI