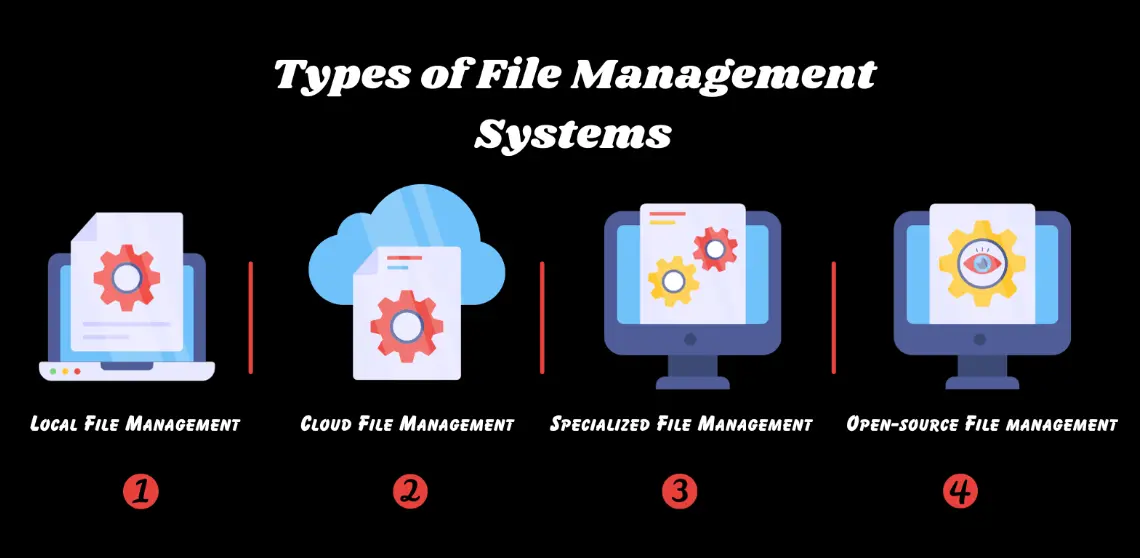
File management is the process of organizing, storing, and handling digital files on a computer or storage system. It ensures data accessibility, security, and efficiency.
Key Concepts
Files: Basic units of storage, containing data such as documents, images, or programs. Files have attributes like name, size, type, and permissions.
Directories/Folders: Containers that hold files and other directories, forming a hierarchical structure (e.g., tree structure) for organization.
File Systems: Methods or structures (e.g., NTFS, FAT32, ext4) that manage how files are stored and retrieved on storage devices.
Paths: Addresses that specify the location of a file or directory, such as absolute paths (e.g., C:\Users\Documents) or relative paths.
Common Operations
Create: Generating new files or directories using commands or applications (e.g., touch in Linux, New Folder in Windows).
Read: Accessing and viewing file contents without altering them.
Update: Modifying file data, such as editing text or updating metadata.
Delete: Removing files or directories to free up space, often with options for permanent deletion or recycling.
Copy/Move: Duplicating or relocating files between directories or devices.
Best Practices
Organize Hierarchically: Use folders to categorize files by project, date, or type to reduce clutter.
Name Files Consistently: Adopt naming conventions (e.g., YYYY-MM-DD_filename.ext) for easy searching.
Backup Regularly: Use tools like cloud storage (e.g., Google Drive) or external drives to prevent data loss.
Manage Permissions: Set access controls to protect sensitive files from unauthorized users.
Monitor Storage: Regularly check disk space and delete unnecessary files to maintain performance.
Tools and Software
Operating System Features: Built-in tools like File Explorer (Windows), Finder (macOS), or Nautilus (Linux).
Third-Party Applications: Programs such as Total Commander, FileZilla (for transfers), or cloud services like Dropbox for remote management.
Effective file management enhances productivity, data security, and system performance.
Table of contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and share file management quiz with AI automatically
- Part 2: 20 file management quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and share file management quiz with AI automatically
The quickest way to assess the file management knowledge of candidates is using an AI assessment platform like OnlineExamMaker. With OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, you are able to input content—like text, documents, or topics—and then automatically generate questions in various formats (multiple-choice, true/false, short answer). Its AI Exam Grader can automatically grade the exam and generate insightful reports after your candidate submit the assessment.
What you will like:
● Create a question pool through the question bank and specify how many questions you want to be randomly selected among these questions.
● Allow the quiz taker to answer by uploading video or a Word document, adding an image, and recording an audio file.
● Display the feedback for correct or incorrect answers instantly after a question is answered.
● Create a lead generation form to collect an exam taker’s information, such as email, mobile phone, work title, company profile and so on.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 file management quiz questions & answers
or
1. Question: What is a file directory?
A. A type of data storage device
B. A hierarchical structure to organize files and subdirectories
C. A software program for editing files
D. A network connection for file sharing
Answer: B
Explanation: A directory, often called a folder, is a hierarchical structure that helps in organizing files and other directories, making it easier to manage and locate data on a storage system.
2. Question: Which command is used to list files and directories in a Unix-based system?
A. dir
B. ls
C. copy
D. cd
Answer: B
Explanation: The ‘ls’ command in Unix-based systems displays the contents of a directory, including files and subdirectories, allowing users to view the file structure.
3. Question: What does the ‘mv’ command do in a Linux environment?
A. Create a new file
B. Move or rename a file or directory
C. Delete a file permanently
D. Copy a file to another location
Answer: B
Explanation: The ‘mv’ command is used to move files or directories from one location to another or to rename them, effectively changing their path or name.
4. Question: In Windows, what extension is commonly associated with executable files?
A. .txt
B. .exe
C. .doc
D. .jpg
Answer: B
Explanation: The .exe extension indicates an executable file in Windows, which can be run as a program, as opposed to other file types used for documents or images.
5. Question: What is the purpose of a file path?
A. To encrypt file data
B. To specify the exact location of a file in a directory structure
C. To compress files for storage
D. To share files over the internet
Answer: B
Explanation: A file path provides the complete address of a file, including directories and subdirectories, enabling the operating system to locate and access it accurately.
6. Question: Which file system is commonly used in modern Windows operating systems?
A. FAT32
B. NTFS
C. HFS+
D. ext4
Answer: B
Explanation: NTFS (New Technology File System) is the default file system for modern Windows, offering features like file permissions, encryption, and better performance compared to older systems like FAT32.
7. Question: How can you delete a file permanently in Windows without using the Recycle Bin?
A. Use the ‘del’ command with the /P option
B. Use Shift + Delete
C. Drag the file to the Trash folder
D. Rename the file
Answer: B
Explanation: Pressing Shift + Delete bypasses the Recycle Bin and permanently deletes the file, which is useful for immediate removal without recovery options.
8. Question: What does the ‘chmod’ command do in Linux?
A. Change the file’s owner
B. Modify the file’s permissions
C. Copy the file to another directory
D. Display file contents
Answer: B
Explanation: The ‘chmod’ command changes the read, write, and execute permissions of a file or directory, controlling who can access or modify it.
9. Question: In file management, what is a root directory?
A. The main folder where all files are stored
B. The top-level directory in a file system hierarchy
C. A subdirectory for temporary files
D. A hidden folder for system files
Answer: B
Explanation: The root directory is the highest level in a file system, from which all other directories and files branch out, serving as the starting point of the hierarchy.
10. Question: Which option is true about file extensions?
A. They are optional and can be hidden
B. They define the file type and how it is handled by software
C. They must be at least 10 characters long
D. They are used only for images
Answer: B
Explanation: File extensions indicate the format of the file, helping the operating system and applications determine how to open or process it correctly.
11. Question: What is the function of the ‘cp’ command in Linux?
A. Compare two files
B. Copy files or directories
C. Create a new directory
D. Change file permissions
Answer: B
Explanation: The ‘cp’ command is used to copy files and directories from one location to another, preserving the original while creating a duplicate.
12. Question: In macOS, what is the default file system?
A. NTFS
B. APFS
C. FAT32
D. ext4
Answer: B
Explanation: APFS (Apple File System) is the default for macOS, providing optimized performance, security features, and support for modern storage devices.
13. Question: How do you create a new directory in Windows Command Prompt?
A. Use the ‘mkdir’ command
B. Use the ‘newdir’ command
C. Use the ‘create folder’ command
D. Use the ‘dir’ command
Answer: A
Explanation: The ‘mkdir’ command in Windows Command Prompt creates a new directory, allowing users to organize files into folders.
14. Question: What is file fragmentation?
A. Breaking a file into smaller pieces for sharing
B. Scattering a file’s data across the disk, potentially slowing access
C. Compressing a file to save space
D. Encrypting a file for security
Answer: B
Explanation: File fragmentation occurs when a file’s data is stored in non-contiguous blocks on the disk, which can lead to slower read/write speeds and is managed by defragmentation tools.
15. Question: Which permission allows a user to view the contents of a file?
A. Write
B. Execute
C. Read
D. Delete
Answer: C
Explanation: The read permission enables a user to view or open a file’s contents without making changes, which is essential for accessing information.
16. Question: What does the ‘rm’ command do in Linux?
A. Rename a file
B. Remove a file or directory
C. Run a file as a program
D. Restore a deleted file
Answer: B
Explanation: The ‘rm’ command deletes files or directories permanently, requiring caution as it does not move items to a trash bin by default.
17. Question: In file management, what is a symbolic link?
A. A direct copy of a file
B. A file that points to another file or directory
C. A locked file that cannot be edited
D. A compressed version of a file
Answer: B
Explanation: A symbolic link acts as a shortcut that references another file or directory, allowing quick access without duplicating the original data.
18. Question: How can you search for a file in Windows?
A. Use the ‘find’ command in Command Prompt
B. Use the Search bar in File Explorer
C. Use the ‘locate’ command
D. All of the above
Answer: D
Explanation: Windows offers multiple ways to search for files, including the Search bar in File Explorer and commands like ‘find’, providing flexibility in file management.
19. Question: What is the benefit of using subdirectories?
A. They increase file size
B. They help organize files into logical categories
C. They slow down file access
D. They require more storage space
Answer: B
Explanation: Subdirectories allow for better organization by grouping related files, making it easier to navigate and manage large volumes of data.
20. Question: Which file attribute makes a file hidden in Windows?
A. The .hidden extension
B. The hidden attribute set in file properties
C. Renaming the file with an underscore
D. Placing it in a system folder
Answer: B
Explanation: Setting the hidden attribute in Windows file properties makes the file invisible in normal views, protecting it from accidental access or deletion.
or
Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Automatically generate questions using AI