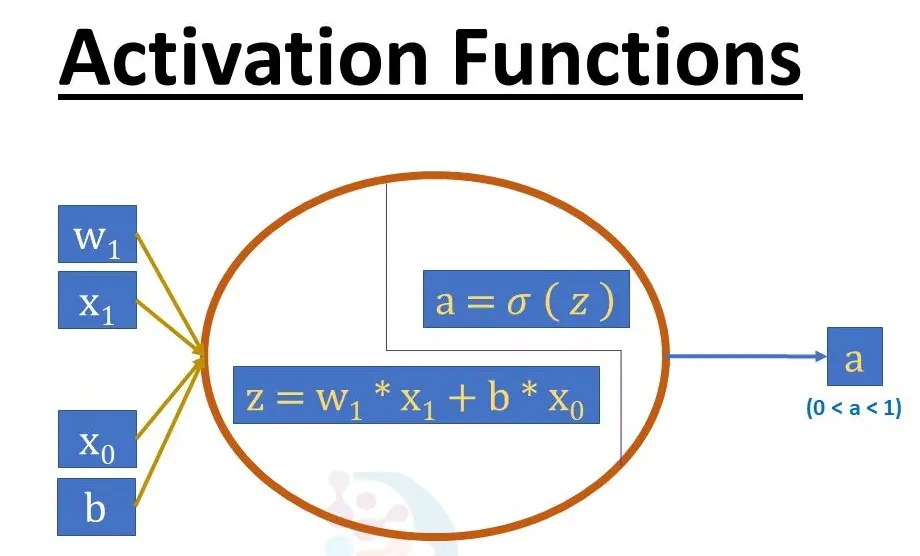
Activation functions are crucial elements in neural networks, serving as the decision-making mechanisms that introduce non-linearity into the model. By transforming the input from a neuron, they determine the output based on specific mathematical operations, enabling the network to learn complex patterns and perform tasks beyond simple linear transformations.
Common types of activation functions include:
Sigmoid: Maps any input to a value between 0 and 1, making it useful for binary classification tasks where outputs represent probabilities.
ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit): Outputs the input value if it is positive; otherwise, it outputs zero. This function helps mitigate the vanishing gradient problem and is computationally efficient.
Tanh (Hyperbolic Tangent): Similar to sigmoid but scales outputs to a range between -1 and 1, which can aid in centering data and improving gradient flow.
Softmax: Applied in the output layer for multi-class classification, converting a vector of values into a probability distribution where the sum of outputs equals 1.
The choice of activation function significantly impacts a neural network’s training speed, convergence, and overall performance, as it influences how gradients are propagated during backpropagation.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Create a activation functions quiz in minutes using AI with OnlineExamMaker
- Part 2: 20 activation functions quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Part 1: Create a activation functions quiz in minutes using AI with OnlineExamMaker
When it comes to ease of creating a activation functions assessment, OnlineExamMaker is one of the best AI-powered quiz making software for your institutions or businesses. With its AI Question Generator, just upload a document or input keywords about your assessment topic, you can generate high-quality quiz questions on any topic, difficulty level, and format.
Overview of its key assessment-related features:
● AI Question Generator to help you save time in creating quiz questions automatically.
● Share your online exam with audiences on social platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Reddit and more.
● Instantly scores objective questions and subjective answers use rubric-based scoring for consistency.
● Simply copy and insert a few lines of embed codes to display your online exams on your website or WordPress blog.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 activation functions quiz questions & answers
or
Question 1:
What is the primary output range of the Sigmoid activation function?
A. [0, 1]
B. [-1, 1]
C. [0, ∞]
D. [-∞, ∞]
Answer: A
Explanation: The Sigmoid function outputs values between 0 and 1, making it useful for binary classification tasks as it squashes input to a probability-like range.
Question 2:
Which activation function is defined as f(x) = max(0, x)?
A. Tanh
B. ReLU
C. Sigmoid
D. Softmax
Answer: B
Explanation: ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) applies the function f(x) = max(0, x), which helps mitigate the vanishing gradient problem and speeds up training in neural networks.
Question 3:
What is a key advantage of the ReLU activation function over Sigmoid?
A. It has a wider output range
B. It avoids the vanishing gradient problem for positive values
C. It is differentiable everywhere
D. It is used only for binary outputs
Answer: B
Explanation: ReLU does not saturate for positive inputs, reducing the risk of vanishing gradients, unlike Sigmoid which can saturate and slow down learning.
Question 4:
Which activation function outputs values in the range [-1, 1]?
A. ReLU
B. Sigmoid
C. Tanh
D. Leaky ReLU
Answer: C
Explanation: The Tanh (Hyperbolic Tangent) function maps inputs to the range [-1, 1], centering the output around zero, which can help in training deeper networks.
Question 5:
What does the acronym “ReLU” stand for?
A. Rectified Linear Unit
B. Reduced Linear Utility
C. Recurrent Linear Update
D. Regularized Linear Unit
Answer: A
Explanation: ReLU stands for Rectified Linear Unit, a simple and effective activation function that introduces non-linearity by outputting the input if positive, otherwise zero.
Question 6:
In which scenario is the Softmax activation function commonly used?
A. Regression tasks
B. Multi-class classification
C. Binary classification
D. Autoencoders
Answer: B
Explanation: Softmax converts logits into probabilities that sum to 1, making it ideal for multi-class classification by outputting a probability distribution over classes.
Question 7:
What is a potential drawback of the Sigmoid activation function?
A. It can cause exploding gradients
B. It suffers from vanishing gradients for extreme inputs
C. It is computationally expensive
D. It outputs negative values
Answer: B
Explanation: Sigmoid’s gradient becomes very small for large positive or negative inputs, leading to vanishing gradients and slower learning in deep networks.
Question 8:
Which activation function is a variation of ReLU that allows a small, non-zero gradient for negative inputs?
A. Tanh
B. Leaky ReLU
C. Sigmoid
D. ELU
Answer: B
Explanation: Leaky ReLU modifies ReLU by allowing a small linear component for negative inputs (e.g., f(x) = 0.01x if x < 0), helping to avoid dead neurons.
Question 9:
What is the output of the ReLU function for x = -2?
A. -2
B. 0
C. 1
D. 2
Answer: B
Explanation: ReLU outputs 0 for any negative input, so for x = -2, the function returns 0, promoting sparsity in neural networks.
Question 10:
Which activation function is often used in the output layer for binary classification problems?
A. ReLU
B. Softmax
C. Sigmoid
D. Tanh
Answer: C
Explanation: Sigmoid is suitable for binary classification as it outputs a value between 0 and 1, interpretable as a probability.
Question 11:
What is the purpose of activation functions in neural networks?
A. To reduce the number of layers
B. To introduce non-linearity and enable learning complex patterns
C. To normalize input data
D. To increase computational speed
Answer: B
Explanation: Activation functions add non-linearity to the model, allowing neural networks to learn and approximate complex functions beyond linear transformations.
Question 12:
Which activation function is defined as f(x) = x * tanh(√(1 + x^2))?
A. Sigmoid
B. Swish
C. ReLU
D. ELU
Answer: B
Explanation: Swish is defined as f(x) = x * sigmoid(x), but a similar smooth variant exists; it provides better performance than ReLU in some cases by allowing negative values with a curve.
Question 13:
How does the ELU (Exponential Linear Unit) activation function differ from ReLU?
A. ELU outputs negative values for negative inputs
B. ELU is always positive
C. ELU is linear for positive inputs only
D. ELU is used for regression
Answer: A
Explanation: ELU allows negative outputs for negative inputs, which can speed up learning and reduce the bias shift effect compared to ReLU’s zero output.
Question 14:
In the Tanh activation function, what happens to the output as x approaches infinity?
A. Approaches 0
B. Approaches 1
C. Approaches -1
D. Approaches infinity
Answer: B
Explanation: Tanh asymptotically approaches 1 as x goes to positive infinity, providing a bounded output that helps in gradient flow.
Question 15:
Which activation function is prone to the “dying ReLU” problem?
A. Sigmoid
B. ReLU
C. Tanh
D. Softmax
Answer: B
Explanation: ReLU can cause neurons to “die” if they always output zero due to negative inputs and zero gradients, leading to inactive nodes in the network.
Question 16:
What is the derivative of the Sigmoid function at x = 0?
A. 0
B. 0.25
C. 0.5
D. 1
Answer: B
Explanation: The derivative of Sigmoid is σ(x) * (1 – σ(x)), and at x = 0, σ(0) = 0.5, so the derivative is 0.5 * 0.5 = 0.25.
Question 17:
Which activation function is typically not used in hidden layers due to its output summing to 1?
A. ReLU
B. Softmax
C. Tanh
D. Leaky ReLU
Answer: B
Explanation: Softmax is generally used in the output layer for multi-class problems, as it normalizes outputs to a probability distribution, unlike hidden layers which need more flexibility.
Question 18:
What is a benefit of using the Scaled Exponential Linear Unit (SELU)?
A. It prevents overfitting
B. It self-normalizes the network
C. It outputs only positive values
D. It is faster than ReLU
Answer: B
Explanation: SELU is designed to maintain a mean of 0 and variance of 1 across layers, enabling self-normalization and stable deep network training.
Question 19:
For the function f(x) = e^x / (e^x + 1), what activation function is this?
A. Tanh
B. Sigmoid
C. ReLU
D. Softmax
Answer: B
Explanation: This is the formula for the Sigmoid function, which maps any real number to (0, 1) and is commonly used for probabilistic outputs.
Question 20:
Which activation function helps in dealing with the vanishing gradient problem in recurrent neural networks?
A. Sigmoid
B. ReLU
C. GRU (with activation)
D. Variants like ReLU or Leaky ReLU in combination
Answer: D
Explanation: While not a single function, using ReLU or its variants in RNNs can help mitigate vanishing gradients, as they provide stronger gradients for positive inputs compared to Sigmoid or Tanh alone.
or
Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Automatically generate questions using AI