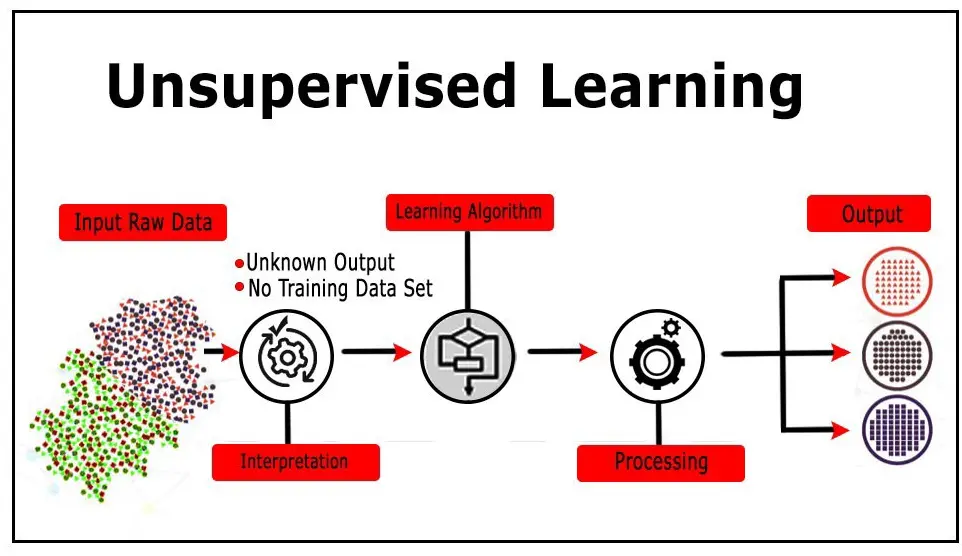
Unsupervised learning is a branch of machine learning where algorithms analyze unlabeled data to discover hidden patterns, structures, or relationships without explicit guidance on the desired output. Unlike supervised learning, it relies solely on input data to identify inherent groupings, similarities, or anomalies.
Key concepts include:
Clustering: Techniques like K-means or hierarchical clustering group similar data points into clusters, such as segmenting customers based on purchasing behavior.
Dimensionality Reduction: Methods such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA) or t-SNE reduce the number of features while preserving essential information, helping to visualize high-dimensional data or improve computational efficiency.
Association Rule Learning: Algorithms like Apriori uncover relationships between variables, for example, in market basket analysis to find items frequently bought together.
This approach is particularly useful for exploratory data analysis, as it enables insights from vast, unstructured datasets in fields like image recognition, anomaly detection, and recommendation systems. Its main challenge lies in evaluating results, as there are no predefined labels to measure accuracy against.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Best AI quiz making software for creating a unsupervised learning quiz
- Part 2: 20 unsupervised learning quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically create questions for your next assessment
Part 1: Best AI quiz making software for creating a unsupervised learning quiz
Nowadays more and more people create unsupervised learning quizzes using AI technologies, OnlineExamMaker a powerful AI-based quiz making tool that can save you time and efforts. The software makes it simple to design and launch interactive quizzes, assessments, and surveys. With the Question Editor, you can create multiple-choice, open-ended, matching, sequencing and many other types of questions for your tests, exams and inventories. You are allowed to enhance quizzes with multimedia elements like images, audio, and video to make them more interactive and visually appealing.
Take a product tour of OnlineExamMaker:
● Create a question pool through the question bank and specify how many questions you want to be randomly selected among these questions.
● Build and store questions in a centralized portal, tagged by categories and keywords for easy reuse and organization.
● Simply copy a few lines of codes, and add them to a web page, you can present your online quiz in your website, blog, or landing page.
● Randomize questions or change the order of questions to ensure exam takers don’t get the same set of questions each time.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 unsupervised learning quiz questions & answers
or
1. Question: What is the primary goal of unsupervised learning?
A. To predict outcomes based on input data
B. To find hidden patterns or structures in unlabeled data
C. To classify data into predefined categories
D. To minimize error in labeled datasets
Answer: B
Explanation: Unsupervised learning focuses on discovering inherent structures in data without any predefined labels, such as grouping similar data points.
2. Question: Which of the following is an example of an unsupervised learning algorithm?
A. Linear Regression
B. K-Means Clustering
C. Decision Trees
D. Support Vector Machines
Answer: B
Explanation: K-Means Clustering is an unsupervised algorithm that partitions data into clusters based on similarity, without requiring labeled outcomes.
3. Question: In unsupervised learning, what does dimensionality reduction aim to achieve?
A. Increase the number of features for better accuracy
B. Reduce the complexity of data while preserving key information
C. Add noise to the dataset for robustness
D. Convert categorical data to numerical data
Answer: B
Explanation: Dimensionality reduction techniques like PCA simplify datasets by reducing the number of features, making analysis more efficient without significant loss of information.
4. Question: What is clustering in unsupervised learning?
A. Assigning labels to data points based on rules
B. Grouping data points that are similar to each other
C. Predicting future trends from historical data
D. Optimizing model parameters through iteration
Answer: B
Explanation: Clustering involves organizing data into groups or clusters where points within a cluster are more similar to each other than to those in other clusters.
5. Question: Which technique is commonly used for anomaly detection in unsupervised learning?
A. Random Forest
B. Isolation Forest
C. Logistic Regression
D. Neural Networks
Answer: B
Explanation: Isolation Forest is an unsupervised method that identifies outliers by isolating anomalies from the rest of the data points.
6. Question: How does unsupervised learning differ from supervised learning?
A. Supervised learning uses labeled data, while unsupervised does not
B. Unsupervised learning always requires more data
C. Supervised learning focuses on clustering
D. Both use the same algorithms
Answer: A
Explanation: Unsupervised learning works with unlabeled data to find patterns, whereas supervised learning relies on labeled data to train models for prediction or classification.
7. Question: What is the role of the elbow method in unsupervised learning?
A. To determine the optimal number of clusters in K-Means
B. To evaluate the accuracy of predictions
C. To reduce dimensions in PCA
D. To handle missing data
Answer: A
Explanation: The elbow method helps identify the ideal number of clusters by plotting the explained variation as a function of the number of clusters, looking for the “elbow” point.
8. Question: In Principal Component Analysis (PCA), what do principal components represent?
A. The original features of the dataset
B. Directions of maximum variance in the data
C. Random projections of data points
D. Labels for classification
Answer: B
Explanation: PCA transforms data into a new coordinate system where the principal components capture the directions of greatest variance, aiding in dimensionality reduction.
9. Question: Which unsupervised learning method is used for finding associations between variables?
A. Linear Discriminant Analysis
B. Apriori Algorithm
C. K-Nearest Neighbors
D. Gradient Descent
Answer: B
Explanation: The Apriori Algorithm discovers frequent itemsets and association rules in large datasets, commonly used in market basket analysis.
10. Question: What challenge is often associated with unsupervised learning?
A. Overfitting due to labeled data
B. Difficulty in evaluating model performance without ground truth
C. High computational speed
D. Excessive data labeling requirements
Answer: B
Explanation: Without labeled data, it’s hard to measure the accuracy of unsupervised models, as evaluation relies on metrics like silhouette score rather than direct error comparison.
11. Question: In hierarchical clustering, what does a dendrogram represent?
A. A scatter plot of data points
B. A tree-like diagram showing cluster mergers
C. A line graph of algorithm iterations
D. A matrix of distances
Answer: B
Explanation: A dendrogram visually represents the arrangement of clusters in hierarchical clustering, illustrating how data points are merged at different levels.
12. Question: What is t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) primarily used for?
A. Classification tasks
B. Visualizing high-dimensional data in lower dimensions
C. Regression analysis
D. Feature selection
Answer: B
Explanation: t-SNE is an unsupervised technique that reduces dimensions while preserving the local structure of the data, making it ideal for visualization.
13. Question: Which metric is used to measure the quality of clusters in unsupervised learning?
A. Accuracy
B. Silhouette Score
C. Precision
D. F1-Score
Answer: B
Explanation: The Silhouette Score evaluates how similar an object is to its own cluster compared to other clusters, helping assess the effectiveness of clustering.
14. Question: In unsupervised learning, what is the purpose of autoencoders?
A. To generate new data labels
B. To compress and reconstruct data
C. To perform supervised classification
D. To optimize supervised models
Answer: B
Explanation: Autoencoders are neural networks that learn efficient data representations by encoding input into a lower-dimensional form and then decoding it back.
15. Question: What type of data is best suited for unsupervised learning?
A. Data with clear categories and labels
B. Unlabeled data with potential hidden patterns
C. Time-series data with predictions
D. Balanced datasets only
Answer: B
Explanation: Unsupervised learning excels with unlabeled data, as it identifies structures and relationships without prior knowledge of outcomes.
16. Question: How does the K-Means algorithm initialize clusters?
A. By randomly assigning labels
B. By selecting K random points as initial centroids
C. By using supervised labels
D. By minimizing global variance from the start
Answer: B
Explanation: K-Means starts by randomly selecting K data points as initial centroids, then iteratively assigns points and updates centroids based on distances.
17. Question: What is the main advantage of using unsupervised learning in real-world applications?
A. It requires less computational power
B. It can discover unknown patterns in data
C. It guarantees high accuracy
D. It eliminates the need for data preprocessing
Answer: B
Explanation: Unsupervised learning is valuable for exploratory analysis, as it uncovers hidden insights and patterns that may not be apparent through supervised methods.
18. Question: In association rule learning, what does support measure?
A. The probability of an item occurring
B. The frequency of a itemset in the dataset
C. The strength of association between items
D. The confidence level of predictions
Answer: B
Explanation: Support measures how frequently an itemset appears in the dataset, which is a key metric in algorithms like Apriori for rule generation.
19. Question: What is a common application of unsupervised learning in image processing?
A. Object detection with bounding boxes
B. Image segmentation through clustering
C. Facial recognition with labels
D. Video frame prediction
Answer: B
Explanation: Unsupervised learning, such as K-Means, is used for image segmentation to group similar pixels without prior labeling.
20. Question: Why might unsupervised learning be preferred over supervised learning for initial data exploration?
A. It provides immediate predictions
B. It doesn’t require labeled data, allowing for faster insights
C. It always yields better results
D. It integrates easily with databases
Answer: B
Explanation: Unsupervised learning enables the analysis of raw, unlabeled data to reveal patterns and structures, which is useful before investing in labeling for supervised tasks.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically create questions for your next assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI