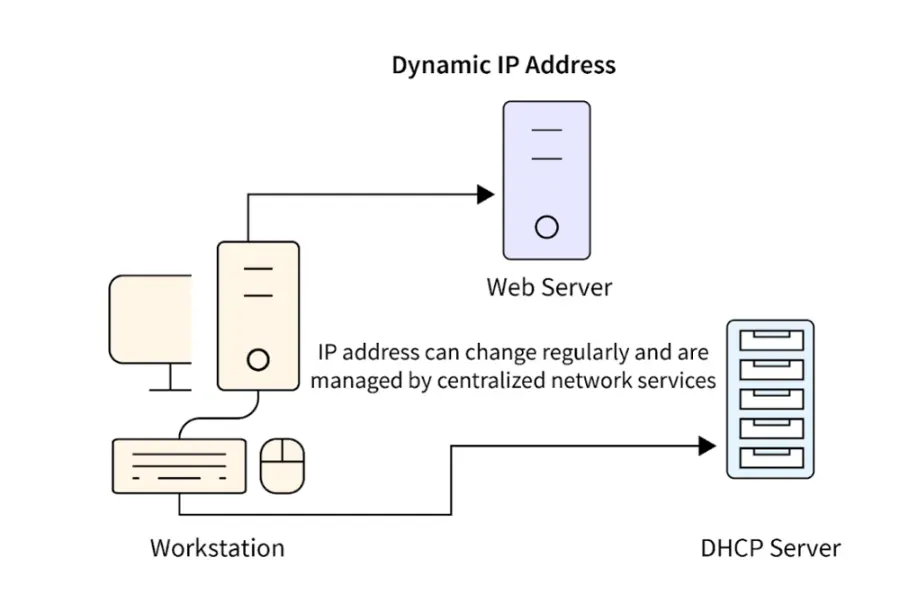
A dynamic IP address is a temporary numerical label assigned to a device on a network, typically by a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server. Unlike a static IP, which remains constant, a dynamic IP can change over time—often upon device restart or at set intervals—to optimize address allocation, enhance security by making devices harder to track, and accommodate the fluctuating demands of modern networks. This flexibility is commonly used in home internet connections, wireless networks, and large-scale environments where resources are shared efficiently.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Create a dynamic IP quiz in minutes using AI with OnlineExamMaker
- Part 2: 20 dynamic IP quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Part 1: Create a dynamic IP quiz in minutes using AI with OnlineExamMaker
Are you looking for an online assessment to test the dynamic IP knowledge of your learners? OnlineExamMaker uses artificial intelligence to help quiz organizers to create, manage, and analyze exams or tests automatically. Apart from AI features, OnlineExamMaker advanced security features such as full-screen lockdown browser, online webcam proctoring, and face ID recognition.
Recommended features for you:
● Includes a safe exam browser (lockdown mode), webcam and screen recording, live monitoring, and chat oversight to prevent cheating.
● Enhances assessments with interactive experience by embedding video, audio, image into quizzes and multimedia feedback.
● Once the exam ends, the exam scores, question reports, ranking and other analytics data can be exported to your device in Excel file format.
● Offers question analysis to evaluate question performance and reliability, helping instructors optimize their training plan.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 dynamic IP quiz questions & answers
or
Question 1: What is a dynamic IP address?
A. An IP address that never changes and is manually assigned.
B. An IP address that is automatically assigned and can change over time.
C. A permanent IP address used only in static networks.
D. An IP address that is shared among multiple devices simultaneously.
Answer: B
Explanation: A dynamic IP address is assigned by a DHCP server and can change periodically, allowing for efficient management of IP addresses in networks.
Question 2: Which protocol is primarily used to assign dynamic IP addresses?
A. FTP
B. HTTP
C. DHCP
D. TCP
Answer: C
Explanation: DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) automatically assigns IP addresses, subnet masks, and other network settings to devices, making IP management dynamic.
Question 3: What happens when a device’s DHCP lease expires?
A. The device loses its IP address permanently.
B. The device must request a new IP address from the DHCP server.
C. The IP address is converted to a static address.
D. The device keeps the same IP address indefinitely.
Answer: B
Explanation: When a DHCP lease expires, the device must renew or request a new IP address to continue network connectivity, ensuring efficient reuse of addresses.
Question 4: What is a key advantage of using dynamic IP addresses over static ones?
A. They provide better security through fixed assignments.
B. They allow for easier scalability in large networks.
C. They eliminate the need for a DHCP server.
D. They are always faster for data transmission.
Answer: B
Explanation: Dynamic IPs enable automatic assignment, making it easier to scale networks without manual configuration, which is ideal for environments with many devices.
Question 5: In a home network, how is a dynamic IP typically assigned to a device?
A. Through manual entry in the device’s settings.
B. Via a router acting as a DHCP server.
C. By connecting directly to the internet service provider.
D. Through a static IP reservation.
Answer: B
Explanation: Most home routers include a built-in DHCP server that assigns dynamic IPs to connected devices, simplifying network setup.
Question 6: What could cause an IP conflict in a network using dynamic IPs?
A. Two devices receiving the same IP from the DHCP server.
B. Using only static IPs on the network.
C. Devices with different subnet masks.
D. High-speed internet connections.
Answer: A
Explanation: An IP conflict occurs when the DHCP server assigns the same IP to multiple devices, leading to network errors until resolved.
Question 7: How does a device obtain a dynamic IP address initially?
A. By broadcasting a DHCP discovery message.
B. By sending a direct request to the router.
C. Through a pre-configured static assignment.
D. By manually renewing the lease.
Answer: A
Explanation: A device broadcasts a DHCP discovery message to locate available DHCP servers, which then offer an IP address for assignment.
Question 8: What is the typical lease time for a dynamic IP address in a corporate network?
A. Permanent until manually changed.
B. A few hours to a few days, depending on configuration.
C. Exactly 24 hours for all devices.
D. Only a few minutes for security reasons.
Answer: B
Explanation: Lease times for dynamic IPs are configurable and often set to hours or days to balance between address reuse and device stability.
Question 9: Why might an ISP use dynamic IPs for residential customers?
A. To ensure each customer has a unique static address.
B. To conserve the limited pool of available IP addresses.
C. To provide faster internet speeds.
D. To avoid using DHCP servers.
Answer: B
Explanation: ISPs use dynamic IPs to efficiently manage and reuse a finite number of IPv4 addresses among many users, reducing waste.
Question 10: What is Dynamic DNS (DDNS) used for in relation to dynamic IPs?
A. To assign static IPs dynamically.
B. To map a dynamic IP to a fixed domain name.
C. To prevent IP conflicts on networks.
D. To extend the DHCP lease time.
Answer: B
Explanation: DDNS allows a dynamic IP to be associated with a constant domain name, which updates automatically when the IP changes, useful for remote access.
Question 11: In IPv6, how are dynamic IP addresses typically assigned?
A. Only through manual configuration.
B. Using SLAAC or DHCPv6.
C. Via static routing tables.
D. Through NAT exclusively.
Answer: B
Explanation: IPv6 uses SLAAC (Stateless Address Autoconfiguration) or DHCPv6 to assign dynamic addresses, enabling automatic configuration in modern networks.
Question 12: What is a potential disadvantage of dynamic IPs?
A. They are more secure than static IPs.
B. They can change unexpectedly, disrupting services.
C. They require less network administration.
D. They always provide faster connectivity.
Answer: B
Explanation: Dynamic IPs may change without warning, which can interrupt services like servers or VPNs that rely on a consistent address.
Question 13: How does subnetting relate to dynamic IP assignment?
A. It has no relation to dynamic IPs.
B. DHCP servers can assign IPs within specific subnets.
C. Subnetting only works with static IPs.
D. It increases the lease time for dynamic IPs.
Answer: B
Explanation: DHCP servers assign dynamic IPs within defined subnets, helping organize and segment network traffic efficiently.
Question 14: What role does a DHCP relay agent play in dynamic IP assignment?
A. It assigns IPs directly to devices.
B. It forwards DHCP requests from clients to a remote DHCP server.
C. It renews leases automatically.
D. It prevents IP conflicts.
Answer: B
Explanation: In larger networks, a DHCP relay agent forwards broadcast DHCP requests to a DHCP server in a different subnet, enabling dynamic IP assignment across segments.
Question 15: Can dynamic IPs be used in a server environment?
A. No, servers must always use static IPs.
B. Yes, but with configurations like DDNS for stability.
C. Only in small home networks.
D. Yes, but they slow down server performance.
Answer: B
Explanation: Dynamic IPs can be used for servers, but tools like DDNS are needed to handle address changes and maintain reliable access.
Question 16: What is the process called when a device renews its DHCP lease?
A. IP regeneration
B. Lease extension
C. DHCP renewal
D. Static conversion
Answer: C
Explanation: DHCP renewal is the process where a device requests to extend or obtain a new IP lease before the current one expires, ensuring continuous connectivity.
Question 17: In a network with both dynamic and static IPs, how are they distinguished?
A. Dynamic IPs are always even numbers.
B. Static IPs are manually configured, while dynamic ones are assigned by DHCP.
C. Dynamic IPs have longer lease times.
D. They are not distinguishable.
Answer: B
Explanation: Static IPs are set manually by the administrator, whereas dynamic IPs are automatically assigned and managed by the DHCP server.
Question 18: Why are dynamic IPs more common in wireless networks?
A. They provide better signal strength.
B. Devices frequently connect and disconnect, requiring flexible addressing.
C. They reduce the need for encryption.
D. Wireless networks only support dynamic IPs.
Answer: B
Explanation: In wireless networks, devices often join and leave, so dynamic IPs allow for automatic assignment and efficient address management.
Question 19: What security risk is associated with dynamic IPs?
A. They are immune to hacking.
B. Attackers can exploit frequent IP changes to evade detection.
C. They require no firewalls.
D. They always block unauthorized access.
Answer: B
Explanation: Dynamic IPs can be used by malicious actors to change addresses frequently, making it harder to track and block threats.
Question 20: How can a user check if their device has a dynamic IP?
A. By pinging the router.
B. Using commands like ipconfig /release and ipconfig /renew on Windows.
C. By manually assigning a static IP.
D. By restarting the device repeatedly.
Answer: B
Explanation: Commands like ipconfig /release and ipconfig /renew show and manage dynamic IP assignments, confirming if the IP is dynamically allocated by DHCP.
or
Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Automatically generate questions using AI