Atomic structure refers to the organization and composition of an atom, which is the basic unit of matter. Atoms are made up of smaller subatomic particles, including protons, neutrons, and electrons. Understanding the atomic structure is crucial in various scientific fields, including chemistry and physics. Here’s an overview of the main components of atomic structure:
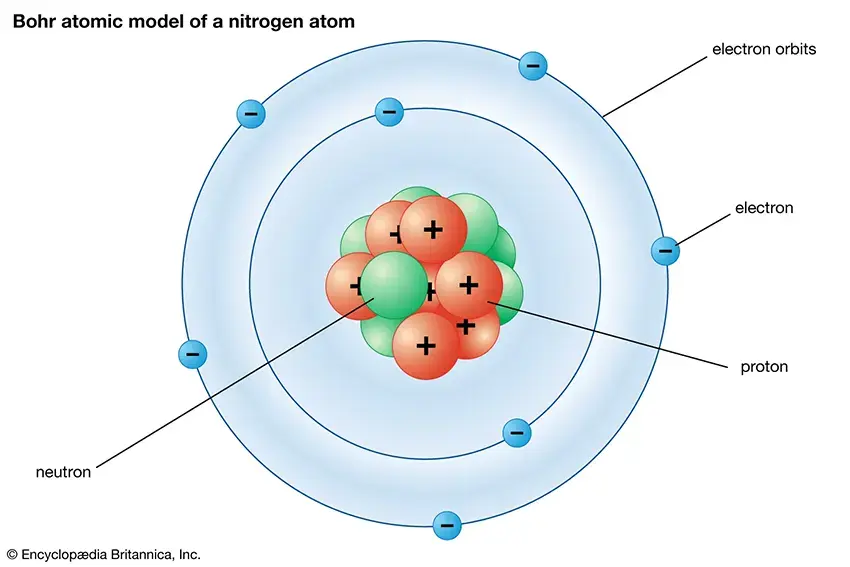
Protons: Protons are positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom. Each proton carries a charge of +1 and contributes to the atomic mass of the atom. The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus determines its atomic number, which defines the element’s identity. For example, all hydrogen atoms have one proton, and all carbon atoms have six protons.
Neutrons: Neutrons are neutral particles found alongside protons in the nucleus of an atom. They have no charge (electrically neutral) and contribute to the atomic mass of the atom without significantly affecting its chemical properties. The number of neutrons in an atom can vary, resulting in isotopes of the same element (atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons).
You might like to know
Create an auto-grading quiz/assessment without any coding – try OnlineExamMaker today!
Electrons: Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels or electron shells. They play a crucial role in chemical reactions and bonding between atoms. The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons in a neutral atom. Electrons are organized into different shells, with each shell holding a specific number of electrons.
Article outline
- Part 1: 30 Atomic Structure quiz questions & answers
- Part 2: Download Atomic Structure questions & answers for free
- Part 3: Free online quiz creator – OnlineExamMaker
Part 1: 30 Atomic Structure quiz questions & answers
1. What is the fundamental subatomic particle with a positive charge located in the nucleus of an atom?
a) Proton
b) Electron
c) Neutron
d) Positron
Answer: a) Proton
2. The number of protons in an atom determines its:
a) Atomic number
b) Mass number
c) Isotope
d) Electronegativity
Answer: a) Atomic number
3. Which subatomic particle has negligible mass and is responsible for the chemical properties of an element?
a) Proton
b) Electron
c) Neutron
d) Nucleon
Answer: b) Electron
4. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the:
a) Atomic number
b) Electron configuration
c) Mass number
d) Atomic mass
Answer: c) Mass number
5. What does the term “isotope” refer to in atomic structure?
a) Atoms with the same number of neutrons but different numbers of protons
b) Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of electrons
c) Atoms with the same number of electrons but different numbers of protons
d) Atoms with the same number of protons and neutrons
Answer: a) Atoms with the same number of neutrons but different numbers of protons
6. The energy levels of electrons in an atom are represented by:
a) Planetary model
b) Quantum numbers
c) Bohr model
d) Atomic orbitals
Answer: c) Bohr model
7. The maximum number of electrons that can occupy the third energy level of an atom is:
a) 2
b) 8
c) 18
d) 32
Answer: c) 18
8. What does the principal quantum number (n) represent in atomic orbitals?
a) Spin of an electron
b) Shape of the orbital
c) Size and energy level of the orbital
d) Orientation in space
Answer: c) Size and energy level of the orbital
9. The set of quantum numbers (n, l, m, s) describe:
a) The position of an electron in an atom
b) The charge of an electron
c) The mass of an electron
d) The speed of an electron
Answer: a) The position of an electron in an atom
10. The “s” and “p” orbitals are examples of:
a) Principal quantum numbers
b) Magnetic quantum numbers
c) Spin quantum numbers
d) Angular momentum quantum numbers
Answer: d) Angular momentum quantum numbers
11. How many quantum numbers are required to describe a single electron in an atom uniquely?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Answer: c) 3
12. The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that:
a) Electrons in the same orbital must have the same spin
b) Electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins
c) No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers
d) Electrons fill orbitals of the lowest energy first
Answer: c) No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers
13. Which of the following subshells can hold a maximum of 10 electrons?
a) 1s
b) 2p
c) 3d
d) 4f
Answer: c) 3d
14. What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy the “p” subshell?
a) 2
b) 6
c) 10
d) 14
Answer: c) 10
15. When writing electron configurations, the Aufbau principle states that electrons fill orbitals:
a) From highest to lowest energy
b) From lowest to highest energy
c) According to their respective principal quantum numbers
d) In pairs with opposite spins
Answer: b) From lowest to highest energy
Part 2: Download Atomic Structure questions & answers for free
Download questions & answers for free
16. The electron configuration of a chlorine atom (Cl) is:
a) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
b) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1
c) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 3p6 4s2
d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10
Answer: c) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2
17. The element with the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3 belongs to which group in the periodic table?
a) Group 13
b) Group 15
c) Group 17
d) Group 18
Answer: b) Group 15
18. An atom becomes an ion when it gains or loses:
a) Neutrons
b) Protons
c) Electrons
d) Nuclei
Answer: c) Electrons
19. A cation is formed when an atom:
a) Gains electrons
b) Loses protons
c) Loses electrons
d) Gains protons
Answer: c) Loses electrons
20. Which of the following elements has the highest electronegativity?
a) Hydrogen (H)
b) Carbon (C)
c) Oxygen (O)
d) Fluorine (F)
Answer: d) Fluorine (F)
21. The ionization energy of an atom refers to the energy required to:
a) Remove an electron from the atom in its gaseous state
b) Add an electron to the atom in its gaseous state
c) Split the nucleus of the atom
d) Convert the atom into an ion
Answer: a) Remove an electron from the atom in its gaseous state
Pro Tip
Want to assess your learners online? Create an online quiz for free!
22. Which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius?
a) Sodium (Na)
b) Aluminum (Al)
c) Silicon (Si)
d) Phosphorus (P)
Answer: a) Sodium (Na)
23. The shielding effect in atoms refers to:
a) The repulsion between electrons in the same orbital
b) The attraction between protons and electrons
c) The reduction of nuclear charge experienced by outer electrons due to inner electron repulsion
d) The energy levels occupied by electrons
in the atom
Answer: c) The reduction of nuclear charge experienced by outer electrons due to inner electron repulsion
24. The phenomenon of “quantum tunneling” in atomic particles is a result of:
a) Electrons jumping between energy levels
b) Electrons sharing energy levels
c) Electrons passing through potential energy barriers even when they do not have enough energy to overcome them
d) Electrons releasing photons of light
Answer: c) Electrons passing through potential energy barriers even when they do not have enough energy to overcome them
25. What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy the “d” subshell?
a) 2
b) 6
c) 10
d) 14
Answer: c) 10
26. The element with the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p3 belongs to which group in the periodic table?
a) Group 13
b) Group 15
c) Group 17
d) Group 18
Answer: a) Group 13
27. The electron configuration for a neutral oxygen atom (O) is:
a) 1s2 2s2 2p4
b) 1s2 2s2 2p6
c) 1s2 2s1 2p7
d) 1s2 2s2 2p5
Answer: d) 1s2 2s2 2p4
28. The element with the symbol “K” has an atomic number of 19. How many electrons does a neutral K atom have in its outermost shell?
a) 1
b) 8
c) 9
d) 19
Answer: c) 9
29. The electron configuration of a silver ion (Ag+) is:
a) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6
b) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9
c) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s1
d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10
Answer: b) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9
30. The element with the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 belongs to which period in the periodic table?
a) Period 5
b) Period 6
c) Period 7
d) Period 8
Answer: c) Period 7
Part 3: Free online quiz creator – OnlineExamMaker
With OnlineExamMaker software, you can easily enhance your assessment procedures, save time on grading, and gain valuable insights into learner performance. OnlineExamMaker grades quizzes automatically, and gives you access to detailed exam reports and statistics instantly. The insightful analytics help teachers and trainers gain valuable insights, enabling them to optimize their teaching methods.
Create Your Next Quiz/Exam with OnlineExamMaker