Work and energy are fundamental concepts in physics that describe the interactions between objects and the forces acting upon them. They play a crucial role in understanding the motion and behavior of various systems in the physical world.
Work:
Work, in physics, is defined as the transfer of energy that results from the application of a force over a certain distance. When a force is applied to an object, and the object moves in the direction of the force, work is said to be done on the object. The amount of work done is calculated as the product of the force and the displacement of the object in the direction of the force. Work is measured in joules (J) in the International System of Units (SI).
Energy:
Energy is a fundamental property of matter that allows it to perform work or cause changes in the environment. It comes in various forms, such as kinetic energy (the energy of motion), potential energy (stored energy due to position or configuration), thermal energy, and more. The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another. Therefore, the total energy in a closed system remains constant.
Pro Tip
You can build engaging online quizzes with our free online quiz maker.
Table of content
- Part 1: 30 work and energy quiz questions & answers
- Part 2: Download work and energy questions & answers for free
- Part 3: Free online quiz creator – OnlineExamMaker
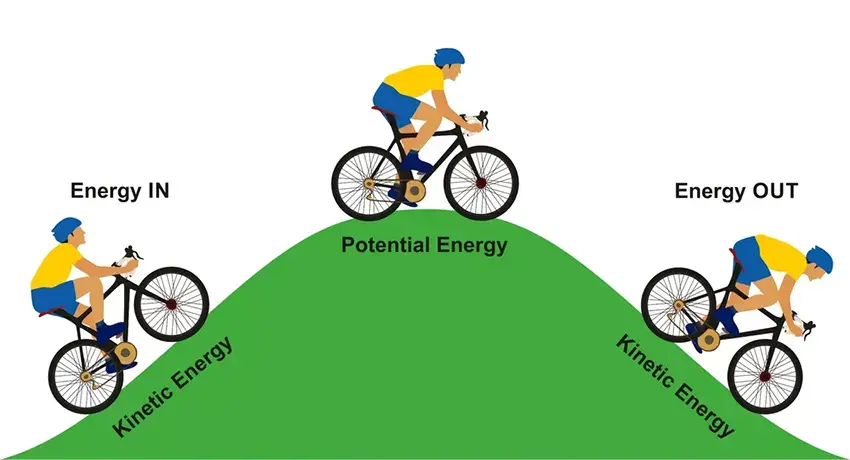
Part 1: 30 work and energy quiz questions & answers
1. What is the definition of work in physics?
a) The transfer of mass from one object to another
b) The transfer of energy due to the application of a force over a distance
c) The change in velocity of an object
d) The conversion of energy into mass
Answer: b) The transfer of energy due to the application of a force over a distance
2. Which unit is used to measure work in the International System of Units (SI)?
a) Meters per second (m/s)
b) Newtons (N)
c) Joules (J)
d) Watts (W)
Answer: c) Joules (J)
3. When is work considered to be done on an object?
a) When a force is applied to the object
b) When the object is at rest
c) When the object moves in the opposite direction of the force
d) When the object moves in the direction of the force
Answer: d) When the object moves in the direction of the force
4. The work-energy theorem states that work done on an object is equal to:
a) The force applied to the object
b) The change in the object’s position
c) The object’s acceleration
d) The change in the object’s kinetic energy
Answer: d) The change in the object’s kinetic energy
5. What is the formula for calculating work?
a) Work = Force * Time
b) Work = Mass * Acceleration
c) Work = Force * Displacement * Cos(θ)
d) Work = Power * Time
Answer: c) Work = Force * Displacement * Cos(θ)
6. When the angle between the force and displacement vectors is 0 degrees, the work done is:
a) Maximum
b) Minimum
c) Zero
d) Negative
Answer: a) Maximum
7. Which type of energy is associated with an object’s motion?
a) Potential energy
b) Thermal energy
c) Kinetic energy
d) Mechanical energy
Answer: c) Kinetic energy
8. What is the formula for calculating kinetic energy?
a) KE = m * v
b) KE = m * g * h
c) KE = (1/2) * m * v^2
d) KE = F * d
Answer: c) KE = (1/2) * m * v^2
9. What is the gravitational potential energy of an object at a certain height h near the Earth’s surface?
a) PE = m * v
b) PE = (1/2) * m * v^2
c) PE = m * g * h
d) PE = F * d
Answer: c) PE = m * g * h
10. The law of conservation of energy states that:
a) Energy can be created but not destroyed
b) Energy can be destroyed but not created
c) Energy can be converted from one form to another, but the total energy remains constant
d) Energy is neither created nor destroyed
Answer: c) Energy can be converted from one form to another, but the total energy remains constant
11. The potential energy of a stretched spring is an example of:
a) Gravitational potential energy
b) Elastic potential energy
c) Kinetic energy
d) Thermal energy
Answer: b) Elastic potential energy
12. In a closed system with no external forces acting, the total mechanical energy is:
a) Decreasing
b) Increasing
c) Constant
d) Zero
Answer: c) Constant
13. Which type of energy is associated with the position of an object relative to its surroundings?
a) Thermal energy
b) Kinetic energy
c) Potential energy
d) Mechanical energy
Answer: c) Potential energy
14. The work done on an object will be negative when:
a) The displacement is in the direction of the force
b) The displacement is opposite to the direction of the force
c) The object is at rest
d) The object has maximum kinetic energy
Answer: b) The displacement is opposite to the direction of the force
15. The unit of power, equivalent to one joule of work done per second, is called:
a) Newton (N)
b) Watt (W)
c) Volt (V)
d) Ampere (A)
Answer: b) Watt (W)
Part 2: Download work and energy questions & answers for free
Download questions & answers for free
16. If an object is lifted vertically upwards, its change in potential energy will be equal to the:
a) Work done on the object
b) Change in its velocity
c) Time taken to lift the object
d) Force applied to lift the object
Answer: a) Work done on the object
17. A car traveling at a constant speed along a straight road has a certain amount of kinetic energy. If the car’s speed is doubled, how will its kinetic energy change?
a) It will be halved
b) It will remain the same
c) It will be quadrupled
d) It will be doubled
Answer: c) It will be quadrupled
18. When an object is stationary and no work is being done on it, what is its kinetic energy?
a) Zero
b) Maximum
c) Constant
d) Impossible to determine without more information
Answer: a) Zero
19. Which type of potential energy is associated with an object’s position above the ground?
a) Gravitational potential energy
b) Elastic potential energy
c) Chemical potential energy
d) Nuclear potential energy
Answer: a) Gravitational potential energy
20. Which of the following energy conversions occurs when you turn on a light bulb?
a) Electrical energy to thermal energy
b) Thermal energy to electrical energy
c) Chemical energy to electrical energy
d) Nuclear energy to electrical energy
Answer: c) Chemical energy to electrical energy
21. An object moving with a constant velocity has:
a) Zero kinetic energy
b) Zero potential energy
c) Non-zero kinetic energy and non-zero potential energy
d) Non-zero kinetic energy and zero potential energy
Answer: d) Non-zero kinetic energy and zero potential energy
22. Which type of energy is associated with the motion of particles in a substance?
a) Thermal energy
b) Mechanical energy
c) Chemical energy
d) Gravitational potential energy
Answer: a) Thermal energy
23. What is the total work done on an object if it moves a distance of 5 meters against a constant force of 10 Newtons applied in the opposite direction of motion?
a) 10 J
b) 25 J
c) -50 J
d) -25 J
Answer: c) -50 J
Just to let you know
Sign up for a free OnlineExamMaker account to create an interactive online quiz in minutes – automatic grading & mobile friendly.
24. The unit of gravitational acceleration, often used in calculating potential energy, is expressed in:
a) Newtons (N)
b) Watts (W)
c) Meters per second (m/s)
d) Meters per second squared (m/s^2)
Answer: d) Meters per second squared (m/s^2)
25. Which type of energy is associated with the motion of charged particles and is used to power electrical devices?
a) Mechanical energy
b) Thermal energy
c) Chemical energy
d) Electrical energy
Answer: d) Electrical energy
26. The total mechanical energy of an object is the sum of its:
a) Kinetic energy and potential energy
b) Potential energy and thermal energy
c) Kinetic energy and thermal energy
d) Potential energy and electrical energy
Answer: a) Kinetic energy and potential energy
27. The work-energy theorem is a direct consequence of which fundamental law in physics?
a) Newton’s first law of motion
b) Newton’s second law of motion
c) The law of conservation of energy
d) The law of conservation of momentum
Answer: c) The law of conservation of energy
28. A rock is dropped from a height, and its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy as it falls. At the bottom, just before it hits the ground, the potential energy will be:
a) Zero
b) At its maximum
c) Equal to the kinetic energy
d) Impossible to determine without more information
Answer: a) Zero
29. In which scenario is work not done on an object?
a) Pushing a box across a floor
b) Lifting a box against gravity
c) Holding a box motionless in your hands
d) Sliding a box down a ramp
Answer: c) Holding a box motionless in your hands
30. Which factor does not affect the amount of work done on an object?
a) The displacement of the object
b) The angle between the force and displacement vectors
c) The mass of the object
d) The magnitude of the force applied
Answer: c) The mass of the object
Part 3: Free online quiz maker – OnlineExamMaker
Save time and effort with automated grading, instantly generating scores and results for each respondent. OnlineExamMaker grades your quizzes automatically, and provides valuable insights for performance evaluation. Whether you are an educator looking to engage students or a business professional seeking effective training methods, OnlineExamMaker quiz maker is a reliable and efficient solution that streamlines the assessment process for improved learning outcomes.
Create Your Next Quiz/Exam with OnlineExamMaker