Wave mechanics, also known as wave theory or wave physics, is a branch of physics that deals with the study of waves and their behavior. Waves are disturbances that transfer energy from one place to another without the physical movement of matter. Wave mechanics provides a mathematical framework to describe and understand the properties, behavior, and interactions of waves in various physical systems.
Wave mechanics has broad applications in various areas of physics, engineering, and technology. It is used to understand and analyze phenomena like sound propagation, light diffraction, radio transmission, earthquake behavior, and more. The principles of wave mechanics have also played a crucial role in the development of quantum mechanics, which is a fundamental theory in modern physics.
Just to let you know
Sign up for a free OnlineExamMaker account to create an interactive online quiz in minutes – automatic grading & mobile friendly.
Article overview
- Part 1: 30 Wave Mechanics quiz questions & answers
- Part 2: Download Wave Mechanics questions & answers for free
- Part 3: Free online quiz software – OnlineExamMaker
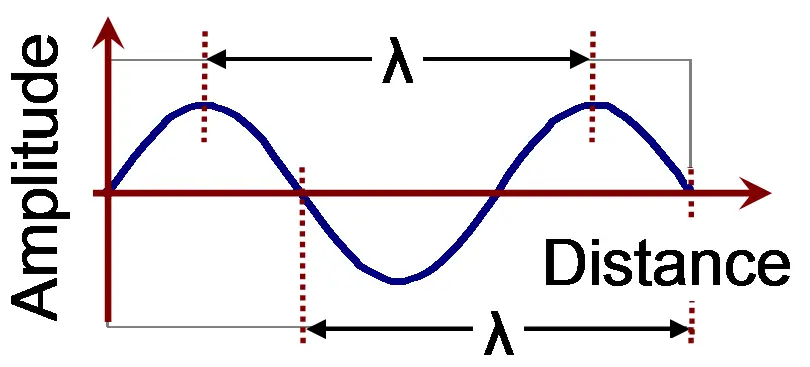
Part 1: 30 Wave Mechanics quiz questions & answers
1. What does wave mechanics study?
a) The behavior of particles in motion
b) The properties of electromagnetic waves
c) The properties and behavior of waves
d) The principles of quantum mechanics
Answer: c) The properties and behavior of waves
2. Waves transfer energy from one place to another without:
a) Changing the medium
b) The physical movement of matter
c) Interference
d) Displacement
Answer: b) The physical movement of matter
3. What is the maximum displacement of a wave from its equilibrium position called?
a) Frequency
b) Wavelength
c) Amplitude
d) Phase
Answer: c) Amplitude
4. Which type of waves require a medium for propagation?
a) Electromagnetic waves
b) Mechanical waves
c) Transverse waves
d) Longitudinal waves
Answer: b) Mechanical waves
5. The number of wave cycles per unit time is known as:
a) Frequency
b) Amplitude
c) Wavelength
d) Speed
Answer: a) Frequency
6. Which wave property is the distance between two consecutive points in phase?
a) Speed
b) Amplitude
c) Frequency
d) Wavelength
Answer: d) Wavelength
7. Which type of waves can travel through a vacuum?
a) Electromagnetic waves
b) Mechanical waves
c) Sound waves
d) Seismic waves
Answer: a) Electromagnetic waves
8. The propagation of waves through a medium is described by which type of equation?
a) Newton’s equation
b) Kepler’s equation
c) Wave equation
d) Einstein’s equation
Answer: c) Wave equation
9. According to the superposition principle, what happens when two waves meet at a point in space?
a) The waves disappear
b) The waves change direction
c) The waves combine to form a resultant wave
d) The waves change frequency
Answer: c) The waves combine to form a resultant wave
10. What is wave interference?
a) The bending of waves around obstacles
b) The bouncing of waves off a surface
c) The interaction of two or more waves at the same point in space
d) The spreading out of waves after passing through a small opening
Answer: c) The interaction of two or more waves at the same point in space
11. When two waves interfere constructively, what happens to the resulting wave?
a) The amplitude is reduced
b) The amplitude is increased
c) The wavelength is reduced
d) The wavelength is increased
Answer: b) The amplitude is increased
12. When two waves interfere destructively, what happens to the resulting wave?
a) The amplitude is reduced to zero
b) The amplitude is increased
c) The wavelength is reduced to zero
d) The wavelength is increased
Answer: a) The amplitude is reduced to zero
13. What term describes the phenomenon where waves of different wavelengths travel at different speeds through a medium?
a) Wave diffraction
b) Wave dispersion
c) Wave reflection
d) Wave refraction
Answer: b) Wave dispersion
14. Which type of waves are responsible for earthquakes?
a) Sound waves
b) Electromagnetic waves
c) Mechanical waves
d) Longitudinal waves
Answer: c) Mechanical waves
15. What is the principle that describes particles’ behavior using wave-like functions?
a) Wave-particle duality
b) Superposition principle
c) Quantum mechanics
d) Wave mechanics
Answer: a) Wave-particle duality
Part 2: Download Wave Mechanics questions & answers for free
Download questions & answers for free
16. In wave mechanics, what are the points where two waves meet and interfere constructively called?
a) Nodes
b) Crests
c) Antinodes
d) Troughs
Answer: c) Antinodes
17. In which type of wave, the particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation?
a) Transverse waves
b) Longitudinal waves
c) Mechanical waves
d) Electromagnetic waves
Answer: a) Transverse waves
18. Which property of a wave is measured in Hertz (Hz)?
a) Amplitude
b) Frequency
c) Wavelength
d) Speed
Answer: b) Frequency
19. What is the equation that describes the propagation of waves through a medium?
a) Einstein’s equation
b) Newton’s equation
c) Kepler’s equation
d) Wave equation
Answer: d) Wave equation
20. Which type of waves can travel through a vacuum?
a) Mechanical waves
b) Electromagnetic waves
c) Sound waves
d) Longitudinal waves
Answer: b) Electromagnetic waves
21. What does the superposition principle state regarding the interaction of waves?
a) Waves add up and become bigger
b) Waves cancel each other out
c) Waves travel in straight lines
d) Waves change their frequency
Answer: a) Waves add up and become bigger
22. What is the distance between two consecutive points in phase called?
a) Wavelength
b) Frequency
c) Amplitude
d) Speed
Answer: a) Wavelength
23. Which type of waves require a medium for their propagation?
a) Electromagnetic waves
b) Mechanical waves
c) Sound waves
d) Transverse waves
Answer: b) Mechanical waves
24. The number of wave cycles per unit time is known as:
a) Frequency
b) Amplitude
c) Wavelength
d) Speed
Answer: a) Frequency
25. The maximum displacement of a wave from its equilibrium position is called:
a) Frequency
b) Wavelength
c) Amplitude
d) Phase
Answer: c) Amplitude
26. What is the principle that describes particles’ behavior using wave-like functions?
a) Wave-particle duality
b) Superposition principle
c) Quantum mechanics
d) Wave mechanics
Answer: a) Wave-particle duality
You might like to know
Create an auto-grading quiz/assessment without any coding – try OnlineExamMaker today!
27. In which type of wave, the particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation?
a) Transverse waves
b) Longitudinal waves
c) Mechanical waves
d) Electromagnetic waves
Answer: a) Transverse waves
28. What term describes the phenomenon where waves of different wavelengths travel at different speeds through a medium?
a) Wave diffraction
b) Wave dispersion
c) Wave reflection
d) Wave refraction
Answer: b) Wave dispersion
29. When two waves interfere destructively, what happens to the resulting wave?
a) The amplitude is reduced to zero
b) The amplitude is increased
c) The wavelength is reduced to zero
d) The wavelength is increased
Answer: a) The amplitude is reduced to zero
30. The propagation of waves through a medium is described by which type of equation?
a) Newton’s equation
b) Kepler’s equation
c) Wave equation
d) Einstein’s equation
Answer: c) Wave equation
Part 3: Best online quiz making platform – OnlineExamMaker
OnlineExamMaker is a powerful and user-friendly software tool that allows educators, trainers, and businesses to create interactive online quizzes and assessments. With OnlineExamMaker quiz software, you can easily design and distribute quizzes to evaluate knowledge, gather feedback, and measure performance.
Create Your Next Quiz/Exam with OnlineExamMaker