Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology and set of tools and techniques used to improve processes and reduce defects in various industries. Originally developed by Motorola in the 1980s, Six Sigma has become a widely adopted quality management approach used by organizations around the world.
The primary goal of Six Sigma is to identify and eliminate the causes of defects, errors, or variations in processes, thereby improving overall efficiency, reducing waste, and enhancing customer satisfaction. It emphasizes the importance of data analysis and measurement to make informed decisions and drive continuous improvement.
The term “Six Sigma” refers to a statistical concept that represents a process that operates with a very low defect rate, aiming for a maximum of 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO). Achieving Six Sigma performance implies a high level of process capability and consistency.
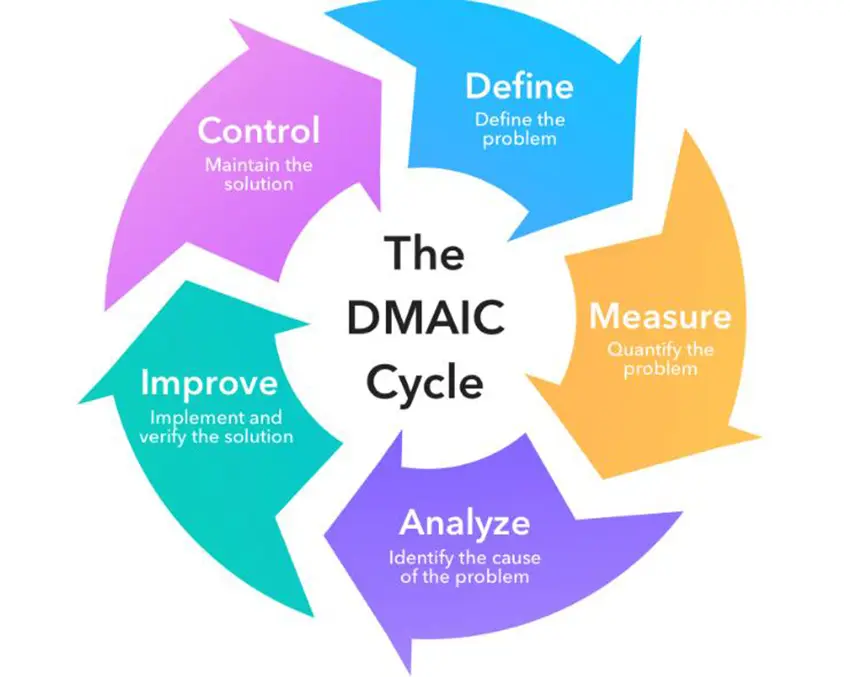
The Six Sigma methodology follows a structured approach known as DMAIC, which stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. Each phase of DMAIC involves specific activities and tools to systematically address process issues and make improvements.
You might like to know
Create an auto-grading quiz/assessment without any coding – try OnlineExamMaker today!
In this article
- Part 1: 30 Six Sigma quiz questions & answers
- Part 2: Download Six Sigma questions & answers for free
- Part 3: Free online quiz creator – OnlineExamMaker
Part 1: 30 Six Sigma quiz questions & answers
1. What is the primary goal of Six Sigma?
a) Reducing customer complaints
b) Reducing process variation and defects
c) Increasing the number of employees trained in statistical analysis
d) Increasing production output
Answer: b) Reducing process variation and defects
2. What does the term “Six Sigma” represent in the context of process performance?
a) A process with six steps
b) A process that requires six individuals to implement
c) A process that operates with 100% efficiency
d) A process with a low defect rate of 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO)
Answer: d) A process with a low defect rate of 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO)
3. What does DMAIC stand for in Six Sigma methodology?
a) Define, Measure, Analyze, Implement, Control
b) Develop, Manage, Assess, Improve, Communicate
c) Determine, Monitor, Assess, Improve, Correct
d) Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control
Answer: d) Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control
4. During which phase of DMAIC is the current performance of the process measured and data collected?
a) Define
b) Measure
c) Analyze
d) Improve
Answer: b) Measure
5. What is the role of a Six Sigma Black Belt?
a) Assist in the Define phase of DMAIC
b) Lead and manage improvement projects
c) Analyze data and create control charts
d) Train Green Belts in statistical analysis
Answer: b) Lead and manage improvement projects
6. What is the role of a Six Sigma Green Belt?
a) Provide statistical analysis for improvement projects
b) Assist in the Control phase of DMAIC
c) Lead and manage improvement projects
d) Train Yellow Belts in process mapping
Answer: a) Provide statistical analysis for improvement projects
7. Which Six Sigma tool is used to graphically display the frequency distribution of data?
a) Pareto Chart
b) Control Chart
c) Histogram
d) Fishbone Diagram
Answer: c) Histogram
8. What is the first step in the Define phase of DMAIC?
a) Develop the project charter
b) Analyze process data
c) Identify potential improvement opportunities
d) Establish process baselines
Answer: a) Develop the project charter
9. What is the primary purpose of the Measure phase in Six Sigma?
a) Analyzing the root causes of defects
b) Implementing process improvements
c) Defining project scope and objectives
d) Quantifying the current performance of the process
Answer: d) Quantifying the current performance of the process
10. What does the term “SIPOC” stand for in Six Sigma?
a) Start, Input, Process, Output, Close
b) Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers
c) Scope, Information, Process, Output, Control
d) Source, Input, Procedure, Output, Control
Answer: b) Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers
11. Which type of data is used to measure the number of defects in a process?
a) Continuous data
b) Discrete data
c) Attribute data
d) Nominal data
Answer: c) Attribute data
12. What is the purpose of the Analyze phase in Six Sigma?
a) Develop potential solutions to improve the process
b) Identify process improvement opportunities
c) Collect baseline process data
d) Develop a control plan for sustaining improvements
Answer: a) Develop potential solutions to improve the process
13. Which Six Sigma tool is used to prioritize improvement opportunities based on their impact?
a) Control Chart
b) Ishikawa Diagram
c) Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
d) Pareto Chart
Answer: d) Pareto Chart
14. Which phase of DMAIC focuses on implementing and verifying the effectiveness of process improvements?
a) Define
b) Measure
c) Analyze
d) Improve
Answer: d) Improve
15. What is the primary goal of the Control phase in Six Sigma?
a) Identify potential sources of variation in a process
b) Define project scope and objectives
c) Implement solutions and monitor process performance
d) Analyze process data to find root causes of defects
Answer: c) Implement solutions and monitor process performance
Part 2: Download Six Sigma questions & answers for free
Download questions & answers for free
16. Which Six Sigma tool is used to display the relationship between two variables?
a) Scatter Diagram
b) Control Chart
c) Fishbone Diagram
d) Histogram
Answer: a) Scatter Diagram
17. What is the main focus of the Improve phase in Six Sigma?
a) Identifying potential process improvement opportunities
b) Collecting process data for analysis
c) Implementing and verifying process improvements
d) Defining project scope and objectives
Answer: c) Implementing and verifying process improvements
18. What does the term “DFSS” stand for in Six Sigma?
a) Define, Focus, Standardize, Sustain
b) Design for Six Sigma
c) Data Focus for Statistical Solutions
d) Determining Factors for Systematic Success
Answer: b) Design for Six Sigma
19. Which Six Sigma tool is used to identify and prioritize potential causes of a problem?
a) Control Chart
b) Pareto Chart
c) Histogram
d) Fishbone Diagram
Answer: d) Fishbone Diagram
20. What is the primary purpose of the SIPOC diagram in Six Sigma?
a) Displaying the frequency distribution of data
b) Identifying potential root causes of defects
c) Defining the process inputs and outputs
d) Prioritizing improvement opportunities
Answer: c) Defining the process inputs and outputs
21. Which type of data is used to measure the weight of a product or the time taken to complete a task?
a) Continuous data
b) Discrete data
c) Attribute data
d) Nominal data
Answer: a) Continuous data
22. Which phase of DMAIC involves validating the stability and capability of the improved process?
a) Define
b) Measure
c) Analyze
d) Control
Answer: d) Control
23. Which Six Sigma tool is used to monitor process stability and identify potential sources of variation?
a) Control Chart
b) Scatter Diagram
c) Histogram
d) Pareto Chart
Answer: a) Control Chart
Pro Tip
Want to assess your learners online? Create an online quiz for free!
24. In the DMAIC methodology, what is the purpose of the Analyze phase?
a) To define the project scope and objectives
b) To identify potential improvement opportunities
c) To implement and verify process improvements
d) To collect baseline process data
Answer: b) To identify potential improvement opportunities
25. Which phase of DMAIC involves creating a detailed plan to maintain the improvements made in the process?
a) Define
b) Measure
c) Analyze
d) Control
Answer: d) Control
26. What is the primary goal of the Measure phase in Six Sigma?
a) To define the project scope and objectives
b) To identify potential improvement opportunities
c) To implement and verify process improvements
d) To quantify the current performance of the process
Answer: d) To quantify the current performance of the process
27. What does the term “CTQ” stand for in Six Sigma?
a) Critical To Quality
b) Control To Quality
c) Critical To Quantity
d) Control To Quantity
Answer: a) Critical To Quality
28. In Six Sigma, what is the role of the Project Champion?
a) Lead and manage improvement projects
b) Provide statistical analysis for improvement projects
c) Support and sponsor improvement initiatives
d) Train Green Belts in process improvement tools
Answer: c) Support and sponsor improvement initiatives
29. Which Six Sigma tool is used to identify the root causes of defects or variations in a process?
a) Control Chart
b) Scatter Diagram
c) Cause and Effect Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram)
d) Pareto Chart
Answer: c) Cause and Effect Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram)
30. What is the primary purpose of the Control phase in Six Sigma?
a) To identify potential improvement opportunities
b) To define the project scope and objectives
c) To implement and verify process improvements
d) To sustain the improvements made in the process
Answer: d) To sustain the improvements made in the process
Part 3: Best online quiz making platform – OnlineExamMaker
With OnlineExamMaker software, you can easily enhance your assessment procedures, save time on grading, and gain valuable insights into learner performance. OnlineExamMaker grades quizzes automatically, and gives you access to detailed exam reports and statistics instantly. The insightful analytics help teachers and trainers gain valuable insights, enabling them to optimize their teaching methods.
Create Your Next Quiz/Exam with OnlineExamMaker