Design Thinking is a problem-solving and innovation methodology that focuses on creating human-centered solutions to complex challenges. It was popularized and formalized by the design consultancy firm IDEO but has roots in design processes that have been used for many years.
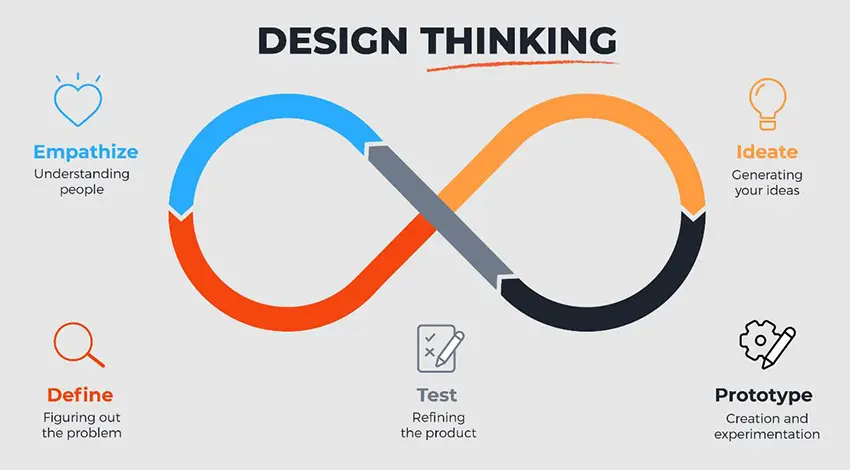
At its core, Design Thinking involves a deep understanding of the needs and perspectives of the end-users or customers. It encourages empathy, creativity, and iterative prototyping to develop innovative solutions that meet those needs effectively. The process typically consists of several stages, which may be fluid and non-linear, depending on the specific approach or framework used.
Pro Tip
Want to assess your learners online? Create an online quiz for free!
Table of content
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and share Design Thinking quiz with AI automatically
- Part 2: 30 Design Thinking quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Download Design Thinking questions & answers for free
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and share Design Thinking quiz with AI automatically
OnlineExamMaker is a powerful AI-powered assessment platform to create auto-grading Design Thinking skills assessments. It’s designed for educators, trainers, businesses, and anyone looking to generate engaging quizzes without spending hours crafting questions manually. The AI Question Generator feature allows you to input a topic or specific details, and it generates a variety of question types automatically.
Top features for assessment organizers:
● Prevent cheating by randomizing questions or changing the order of questions, so learners don’t get the same set of questions each time.
● AI Exam Grader for efficiently grading quizzes and assignments, offering inline comments, automatic scoring, and “fudge points” for manual adjustments.
● Embed quizzes on websites, blogs, or share via email, social media (Facebook, Twitter), or direct links.
● Handles large-scale testing (thousands of exams/semester) without internet dependency, backed by cloud infrastructure.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 30 Design Thinking quiz questions & answers
1. What is the main goal of Design Thinking?
a) To maximize profits
b) To create innovative solutions for complex problems
c) To reduce product development time
d) To increase customer satisfaction
Answer: b
2. Design Thinking is an iterative process that consists of how many stages?
a) 2
b) 4
c) 5
d) 7
Answer: c
3. Which stage of Design Thinking involves understanding the needs and wants of the end-users?
a) Ideation
b) Prototyping
c) Empathize
d) Define
Answer: c
4. Which design thinking technique involves generating a large number of ideas in a short amount of time?
a) Brainstorming
b) Mind mapping
c) SWOT analysis
d) Six Thinking Hats
Answer: a
5. In Design Thinking, the process of creating a tangible representation of ideas is known as:
a) Ideation
b) Prototyping
c) Testing
d) Refinement
Answer: b
6. What is the primary purpose of the “Empathize” stage in Design Thinking?
a) To identify potential risks
b) To analyze data and research
c) To understand the users and their needs
d) To finalize the design concept
Answer: c
7. Which of the following is not a characteristic of Design Thinking?
a) Linear process
b) Human-centered
c) Collaborative
d) Iterative
Answer: a
8. Which stage in the Design Thinking process involves defining the problem statement based on the user’s needs?
a) Empathize
b) Ideate
c) Prototype
d) Define
Answer: d
9. What is the purpose of user personas in Design Thinking?
a) To identify potential flaws in the product
b) To define the project timeline
c) To represent the needs and behaviors of the target users
d) To prioritize features for development
Answer: c
10. The “Diverge” phase in Design Thinking is related to:
a) Analyzing data
b) Narrowing down ideas
c) Generating multiple ideas
d) Testing prototypes
Answer: c
11. In Design Thinking, what does the “Prototype” stage involve?
a) Finalizing the design for production
b) Developing a working model of the solution
c) Conducting user testing
d) Collecting feedback from stakeholders
Answer: b
12. What is the purpose of conducting user testing during the Design Thinking process?
a) To identify potential risks
b) To refine and improve the prototype
c) To finalize the design concept
d) To document the design decisions
Answer: b
13. Which of the following is a core principle of Design Thinking?
a) Analysis paralysis
b) Focusing on the solution, not the problem
c) Emphasizing the status quo
d) Focusing on technology, not human needs
Answer: d
14. During the “Test” stage in Design Thinking, what should be evaluated?
a) The efficiency of the team
b) The project’s timeline and budget
c) The feasibility of the prototype
d) The performance of the product in the market
Answer: c
15. Which of the following is an essential characteristic of a Design Thinker?
a) Rigid thinking
b) Fear of failure
c) Bias towards action
d) Resistance to change
Answer: c
Part 3: Download Design Thinking questions & answers for free
Download questions & answers for free
16. What is the key benefit of using Design Thinking in problem-solving?
a) Faster decision-making process
b) Minimizing the importance of user feedback
c) Identifying the cheapest solution
d) Solving complex and ambiguous problems effectively
Answer: d
17. How does prototyping contribute to the Design Thinking process?
a) It helps to eliminate the need for user testing
b) It provides a detailed project plan
c) It allows for quick iteration and refinement of ideas
d) It ensures immediate implementation of the final design
Answer: c
18. What is the role of feedback in Design Thinking?
a) It helps in blaming individuals for failures
b) It provides assurance that the solution will work perfectly
c) It guides the improvement and evolution of the design
d) It is not essential in the design process
Answer: c
19. Which Design Thinking stage emphasizes converting ideas into actual solutions?
a) Ideate
b) Prototype
c) Test
d) Implement
Answer: d
20. Design Thinking encourages collaboration between which stakeholders?
a) Only designers and engineers
b) Designers, engineers, and project managers
c) Designers, engineers, and CEOs
d) All stakeholders, including end-users and clients
Answer: d
21. Why is the “Fail Fast” approach often recommended in Design Thinking?
a) To avoid spending resources on prototyping
b) To eliminate the need for user feedback
c) To test assumptions and ideas quickly and learn from failures
d) To avoid taking risks in the design process
Answer: c
22. What is the main purpose of the “Define” stage in Design Thinking?
a) To brainstorm potential solutions
b) To identify the root cause of the problem
c) To create a detailed project plan
d) To gain insights into user needs and pain points
Answer: d
23. Which Design Thinking stage involves prioritizing and selecting ideas for further development?
a) Ideate
b) Prototype
c) Test
d) Refine
Answer: a
24. What does the term “Design Thinking” imply?
a) A thinking process exclusive to designers
b) A process limited to graphical design projects
c) A way of thinking that can be applied across various disciplines
d) A linear problem-solving approach
Answer: c
25. Which stage of Design Thinking focuses on creating a visual representation of the user’s journey?
a) Empathize
b) Ideate
c) Define
d) Journey Map
Answer: d
26. Why is the “Empathize” stage crucial in the Design Thinking process?
a) To identify potential roadblocks
b) To analyze competitor products
c) To understand the needs and emotions of users
d) To determine the project budget
Answer: c
Just so you know
With OnlineExamMaker quiz software, anyone can create & share professional online assessments easily.
27. Design Thinking is often considered a human-centered approach. What does this mean?
a) The focus is solely on business goals and profits
b) The design process is automated and driven by AI
c) The needs and experiences of users are prioritized
d) The design team has full authority over decisions
Answer: c
28. How does prototyping support the overall design process in Design Thinking?
a) It helps to develop the final product version directly
b) It allows users to test the solution
c) It reduces the need for user feedback
d) It is only used for promotional purposes
Answer: b
29. What distinguishes Design Thinking from traditional problem-solving methods?
a) Rigid adherence to predefined steps
b) Focus on tangible results only
c) Continuous iteration and learning from failures
d) Limited involvement of end-users
Answer: c
30. Why is the “Ideate” stage often referred to as “Diverge” in Design Thinking?
a) The team focuses on narrowing down ideas
b) It involves generating a wide range of diverse ideas
c) It marks the end of the design process
d) The team converges on a single solution
Answer: b