Coulomb’s Law is a fundamental principle in physics that describes the electrostatic force between charged particles. It is named after Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, a French physicist who first formulated this law in the late 18th century. Coulomb’s Law is an essential concept in the study of electricity and magnetism, and it plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of charged particles and electric fields.
Pro Tip
You can build engaging online quizzes with our free online quiz maker.
Article outline
- Part 1: Create a Coulomb’s Law quiz in minutes using AI with OnlineExamMaker
- Part 2: 30 Coulomb’s Law quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Download Coulomb’s Law questions & answers for free
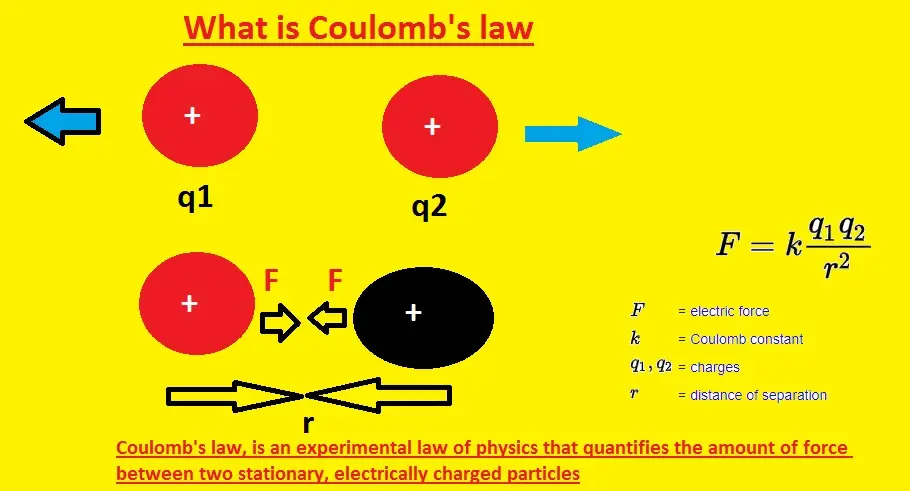
Part 1: Create a Coulomb’s Law quiz in minutes using AI with OnlineExamMaker
When it comes to ease of creating a Coulomb’s Law skills assessment, OnlineExamMaker is one of the best AI-powered quiz making software for your institutions or businesses. With its AI Question Generator, just upload a document or input keywords about your assessment topic, you can generate high-quality quiz questions on any topic, difficulty level, and format.
Overview of its key assessment-related features:
● AI Question Generator to help you save time in creating quiz questions automatically.
● Share your online exam with audiences on social platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Reddit and more.
● Instantly scores objective questions and subjective answers use rubric-based scoring for consistency.
● Simply copy and insert a few lines of embed codes to display your online exams on your website or WordPress blog.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 30 Coulomb’s Law quiz questions & answers
Sure! Here are 30 multiple-choice questions about Coulomb’s Law:
1. Coulomb’s Law describes the force between:
a) Electric charges and magnetic fields
b) Electric charges and gravitational fields
c) Electric charges
d) Electric charges and electric fields
Answer: d) Electric charges
2. Who formulated Coulomb’s Law?
a) Isaac Newton
b) Albert Einstein
c) James Clerk Maxwell
d) Charles-Augustin de Coulomb
Answer: d) Charles-Augustin de Coulomb
3. Coulomb’s Law states that the force between two point charges is:
a) Directly proportional to the product of their masses
b) Inversely proportional to the distance between them
c) Inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
d) Directly proportional to the distance between them
Answer: c) Inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
4. The SI unit of charge is:
a) Coulomb (C)
b) Newton (N)
c) Ohm (Ω)
d) Ampere (A)
Answer: a) Coulomb (C)
5. Coulomb’s constant, denoted by ‘k’, is approximately equal to:
a) 8.99 x 10^9 N m²/C²
b) 6.67 x 10^-11 N m²/kg²
c) 3.00 x 10^8 m/s
d) 1.60 x 10^-19 C
Answer: a) 8.99 x 10^9 N m²/C²
6. If the distance between two point charges is halved, the electrostatic force between them becomes:
a) Four times stronger
b) Two times stronger
c) Half as strong
d) One-fourth as strong
Answer: a) Four times stronger
7. Two positive point charges are brought closer together. The force between them:
a) Becomes more repulsive
b) Becomes more attractive
c) Remains the same
d) Becomes zero
Answer: a) Becomes more repulsive
8. Two negative point charges are brought closer together. The force between them:
a) Becomes more repulsive
b) Becomes more attractive
c) Remains the same
d) Becomes zero
Answer: b) Becomes more attractive
9. The force between two charges is 18 N. If the distance between them is doubled, the new force will be:
a) 9 N
b) 18 N
c) 36 N
d) 72 N
Answer: a) 9 N
10. The electrostatic force between two point charges is directly proportional to:
a) The magnitude of one charge
b) The magnitude of both charges
c) The distance between the charges
d) The square of the distance between the charges
Answer: b) The magnitude of both charges
11. What happens to the electrostatic force between two charges if they are moved three times farther apart?
a) It becomes one-third as strong
b) It becomes nine times stronger
c) It becomes one-ninth as strong
d) It remains the same
Answer: c) It becomes one-ninth as strong
12. If two charges of +2C and -4C are separated by a distance of 3 meters, what is the force between them?
a) 2 N
b) 8 N
c) 12 N
d) 24 N
Answer: d) 24 N
13. When a positive charge is brought near an uncharged conductor, the conductor acquires a:
a) Positive charge
b) Negative charge
c) Neutral charge
d) Variable charge
Answer: a) Positive charge
14. When two positive charges are placed close to each other, the force between them is:
a) Attractive
b) Repulsive
c) Zero
d) Variable
Answer: b) Repulsive
15. What happens to the force between two charges if the distance between them is tripled?
a) It becomes three times stronger
b) It becomes one-third as strong
c) It becomes nine times weaker
d) It remains the same
Answer: b) It becomes one-third as strong
Part 3: Download Coulomb’s Law questions & answers for free
Download questions & answers for free
16. If two charges of +5C and -3C are separated by a distance of 4 meters, what is the force between them?
a) 20 N
b) 60 N
c) 12 N
d) 45 N
Answer: a) 20 N
17. A positive charge exerts an electrostatic force of 8 N on another positive charge. If the distance between the charges is halved, what is the new force?
a) 8 N
b) 32 N
c) 64 N
d) 16 N
Answer: b) 32 N
18. When two negative charges are placed close to each other, the force between them is:
a) Attractive
b) Repulsive
c) Zero
d) Variable
Answer: a) Attractive
19. Two point charges of +2C and -5C are separated by a distance of 2 meters. What is the force between them?
a) 4 N
b) 10 N
c) 20 N
d) 50 N
Answer: b) 10 N
20. If the distance between two point charges is increased by a factor of 4, the new electrostatic force will be:
a) Four times weaker
b) One-sixteenth as strong
c) Four times stronger
d) One-fourth as strong
Answer: b) One-sixteenth as strong
21. A negative charge exerts an electrostatic force of 6 N on a positive charge. If the distance between the charges is doubled, what is the new force?
a) 3 N
b) 6 N
c) 12 N
d) 24 N
Answer: a) 3 N
22. If the distance between two point charges is tripled, the electrostatic force between them becomes:
a) Three times stronger
b) Three times weaker
c) Nine times stronger
d) Nine times weaker
Answer: b) Three times weaker
23. Two positive point charges are placed 2 meters apart. If the magnitude of each charge is doubled, what will be the new force between them?
a) Four times stronger
b) Two times stronger
c) Half as strong
d) One-fourth as strong
Answer: a) Four times stronger
24. The electrostatic force between two charges is 12 N. If the distance between them is tripled, the new force will be:
a) 4 N
b) 12 N
c) 36 N
d) 48 N
Answer: a) 4 N
25. If two charges of +3C and -3C are separated by a distance of 2 meters, what is the force between them?
a) 3 N
b) 6 N
c) 9 N
d) 12 N
Answer: c) 9 N
26. The electrostatic force between two charges is inversely proportional to:
a) The square of their magnitudes
b) The product of their magnitudes
c) The distance between them
d) The square of the distance between them
Answer: d) The square of the distance between them
Just to let you know
Sign up for a free OnlineExamMaker account to create an interactive online quiz in minutes – automatic grading & mobile friendly.
27. Two negative charges are placed 3 meters apart. If the magnitude of each charge is halved, what will be the new force between them?
a) One-fourth as strong
b) Half as strong
c) Four times weaker
d) Twice as strong
Answer: c) Four times weaker
28. Two positive charges are separated by a distance of 5 meters. If the magnitude of one charge is doubled and the other is halved, what will be the new force between them?
a) Four times stronger
b) Two times stronger
c) Half as strong
d) One-fourth as strong
Answer: a) Four times stronger
29. The electrostatic force between two charges is 24 N. If the distance between them is halved, the new force will be:
a) 12 N
b) 48 N
c) 96 N
d) 6 N
Answer: b) 48 N
30. The electrostatic force between two charges is directly proportional to:
a) The magnitude of one charge
b) The magnitude of both charges
c) The distance between the charges
d) The square of the distance between the charges
Answer: b) The magnitude of both charges