Cellular transport, also known as cell transport, refers to the movement of substances across the cell membrane and within the cellular environment. It is a fundamental process that allows cells to exchange essential molecules, nutrients, and waste products to maintain their internal balance and perform various physiological functions.
Cellular transport is vital for various cellular functions, including nutrient uptake, waste elimination, maintaining osmotic balance, signal transduction, and nerve impulse transmission. It plays a crucial role in the overall health and survival of cells and, consequently, the proper functioning of tissues and organisms. Dysfunction in cellular transport processes can lead to various diseases and disorders. Studying cellular transport helps researchers and medical professionals understand cellular physiology and develop therapies to address transport-related health issues.
Just to let you know
Sign up for a free OnlineExamMaker account to create an interactive online quiz in minutes – automatic grading & mobile friendly.
Article overview
- Part 1: 30 cellular transport quiz questions & answers
- Part 2: Download cellular transport questions & answers for free
- Part 3: Free online quiz software – OnlineExamMaker
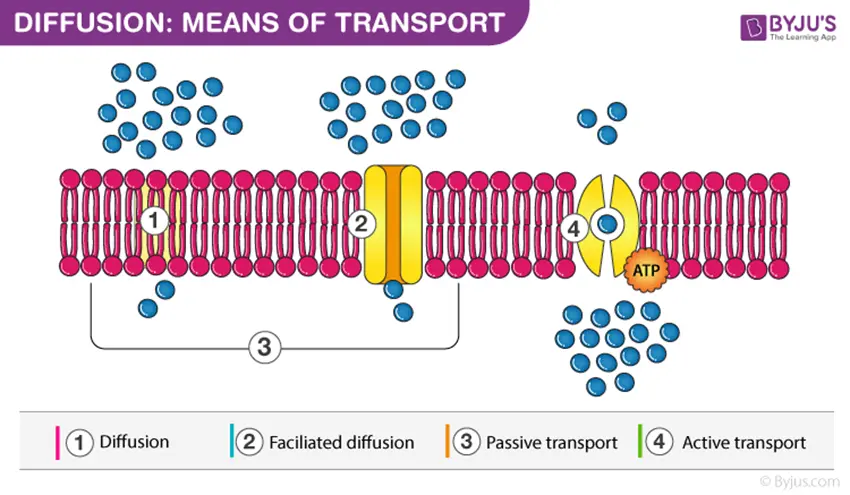
Part 1: 30 cellular transport quiz questions & answers
1. What is cellular transport?
a) The process of cell division
b) The movement of substances across the cell membrane
c) The synthesis of proteins within a cell
d) The breakdown of glucose in cellular respiration
Answer: b) The movement of substances across the cell membrane
2. Which type of cellular transport does not require energy?
a) Active transport
b) Facilitated diffusion
c) Osmosis
d) Endocytosis
Answer: c) Osmosis
3. What is the main driving force behind diffusion?
a) ATP hydrolysis
b) The concentration gradient
c) Cellular respiration
d) Enzyme activity
Answer: b) The concentration gradient
4. In which direction do molecules move during diffusion?
a) From areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration
b) From areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration
c) In a random pattern
d) They do not move during diffusion
Answer: b) From areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration
5. What is the movement of water molecules from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration across a selectively permeable membrane called?
a) Active transport
b) Endocytosis
c) Osmosis
d) Facilitated diffusion
Answer: c) Osmosis
6. Which cellular transport process involves the use of transport proteins to move specific molecules across the cell membrane?
a) Active transport
b) Facilitated diffusion
c) Exocytosis
d) Pinocytosis
Answer: b) Facilitated diffusion
7. What type of cellular transport is exemplified by the sodium-potassium pump?
a) Osmosis
b) Endocytosis
c) Facilitated diffusion
d) Primary active transport
Answer: d) Primary active transport
8. What is the role of ATP in primary active transport?
a) ATP is used to pump water molecules across the cell membrane.
b) ATP is used to transport molecules against their concentration gradient.
c) ATP provides energy for facilitated diffusion.
d) ATP is used to synthesize proteins.
Answer: b) ATP is used to transport molecules against their concentration gradient.
9. Which type of endocytosis involves the uptake of solid particles into the cell?
a) Pinocytosis
b) Phagocytosis
c) Exocytosis
d) Osmosis
Answer: b) Phagocytosis
10. Which of the following is an example of exocytosis?
a) A cell taking in small molecules from the external environment.
b) A cell expelling waste products into the extracellular space.
c) A cell releasing neurotransmitters to signal another cell.
d) A cell releasing water through a selectively permeable membrane.
Answer: c) A cell releasing neurotransmitters to signal another cell.
11. What is the net movement of molecules in a solution that is isotonic to the cytoplasm of a cell?
a) Molecules move into the cell.
b) Molecules move out of the cell.
c) No net movement of molecules occurs.
d) Molecules move randomly.
Answer: c) No net movement of molecules occurs.
12. In which cellular transport process are vesicles formed to transport substances into the cell?
a) Osmosis
b) Endocytosis
c) Facilitated diffusion
d) Active transport
Answer: b) Endocytosis
13. Which type of endocytosis involves the uptake of fluid and dissolved solutes into the cell?
a) Pinocytosis
b) Phagocytosis
c) Exocytosis
d) Osmosis
Answer: a) Pinocytosis
14. The sodium-potassium pump is essential for maintaining the ion balance in:
a) Nerve cells
b) Muscle cells
c) Red blood cells
d) Bone cells
Answer: a) Nerve cells
15. Which cellular transport process is used by white blood cells to engulf and digest foreign particles?
a) Phagocytosis
b) Exocytosis
c) Osmosis
d) Facilitated diffusion
Answer: a) Phagocytosis
Part 2: Download cellular transport questions & answers for free
Download questions & answers for free
16. Which of the following is NOT an example of passive transport?
a) Facilitated diffusion
b) Osmosis
c) Phagocytosis
d) Simple diffusion
Answer: c) Phagocytosis
17. What type of molecules can easily pass through the cell membrane via simple diffusion?
a) Large and charged molecules
b) Polar molecules
c) Small and nonpolar molecules
d) Water molecules
Answer: c) Small and nonpolar molecules
18. What is the name of the protein channels used in facilitated diffusion?
a) Glycoproteins
b) Ion channels
c) Enzymes
d) Carrier proteins
Answer: d) Carrier proteins
19. Which of the following is an example of secondary active transport?
a) Sodium-potassium pump
b) Sodium-glucose cotransporter
c) Endocytosis
d) Pinocytosis
Answer: b) Sodium-glucose cotransporter
20. Which type of cellular transport requires energy to move substances against their concentration gradient?
a) Active transport
b) Passive transport
c) Facilitated diffusion
d) Osmosis
Answer: a) Active transport
21. Which cellular transport process is used to expel waste products and secretory proteins from the cell?
a) Phagocytosis
b) Exocytosis
c) Osmosis
d) Facilitated diffusion
Answer: b) Exocytosis
22. What is the main function of the sodium-potassium pump in nerve cells?
a) To maintain the cell’s shape
b) To produce ATP for cellular energy
c) To generate an action potential
d) To maintain the ion balance for nerve impulse transmission
Answer: d) To maintain the ion balance for nerve impulse transmission
23. During which cellular transport process do molecules move with the help of protein channels but do not require energy?
a) Osmosis
b) Active transport
c) Facilitated diffusion
d) Endocytosis
Answer: c) Facilitated diffusion
24. Which of the following statements is true about facilitated diffusion?
a) It involves the movement of molecules from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration.
b) It requires ATP energy to move molecules across the cell membrane.
c) It is a form of active transport.
d) It uses protein channels or carriers to transport specific molecules.
Answer: d) It uses protein channels
or carriers to transport specific molecules.
25. Which cellular transport process involves the formation of a vesicle to transport substances out of the cell?
a) Exocytosis
b) Osmosis
c) Active transport
d) Phagocytosis
Answer: a) Exocytosis
26. What is the primary purpose of endocytosis in cells?
a) To export cellular waste products
b) To transport ions across the cell membrane
c) To bring extracellular substances into the cell
d) To maintain the cell’s shape
Answer: c) To bring extracellular substances into the cell
You might like to know
Create an auto-grading quiz/assessment without any coding – try OnlineExamMaker today!
27. Which of the following cellular transport processes relies on the hydrolysis of ATP to move substances?
a) Facilitated diffusion
b) Osmosis
c) Exocytosis
d) Active transport
Answer: d) Active transport
28. Which cellular transport process is primarily responsible for maintaining osmotic balance in cells?
a) Active transport
b) Phagocytosis
c) Osmosis
d) Facilitated diffusion
Answer: c) Osmosis
29. Which of the following cellular transport processes is responsible for the uptake of large particles, such as bacteria, into cells?
a) Osmosis
b) Active transport
c) Facilitated diffusion
d) Phagocytosis
Answer: d) Phagocytosis
30. Which of the following statements is true about active transport?
a) It does not require energy.
b) It moves substances along their concentration gradient.
c) It involves the movement of molecules from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration.
d) It relies on the hydrolysis of ATP to move substances.
Answer: d) It relies on the hydrolysis of ATP to move substances.
Part 3: Best online quiz making platform – OnlineExamMaker
OnlineExamMaker gives you everything you need to create interactive online quizzes to assess students and staffs, and engage potential customers. The online quiz platform offers options for adding multimedia elements, such as images and videos, to enhance the quiz-taking experience.
Create Your Next Quiz/Exam with OnlineExamMaker