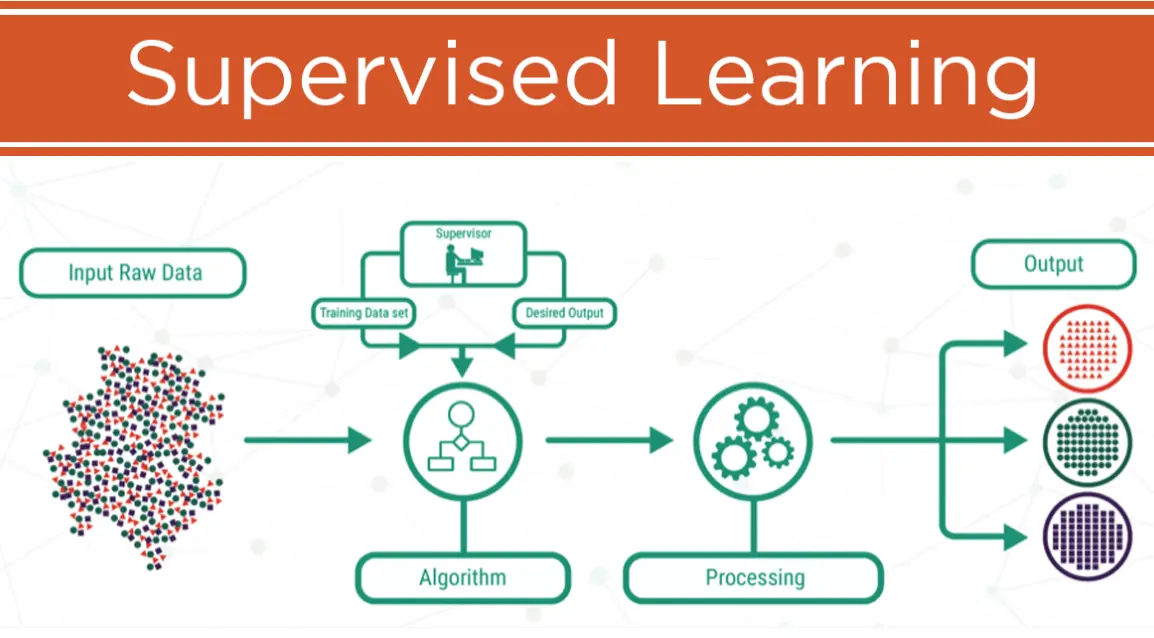
Supervised learning is a fundamental approach in machine learning where an algorithm is trained on a labeled dataset, meaning the data includes both input features and their corresponding output labels. The primary goal is to enable the model to learn a mapping function that predicts the output for new, unseen data based on the patterns identified during training.
This method involves two main types:
Regression: Used for predicting continuous values, such as estimating house prices based on features like size, location, and number of rooms.
Classification: Involves predicting discrete categories, for example, classifying emails as spam or not spam based on their content.
The process typically includes:
– Preparing a dataset with labeled examples.
– Training the model by adjusting its parameters to minimize the error between predicted and actual outputs.
– Evaluating the model using metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, or mean squared error.
– Deploying the model for real-world predictions.
Table of contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI quiz maker – Make a free quiz in minutes
- Part 2: 20 supervised learning quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically create questions for your next assessment
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI quiz maker – Make a free quiz in minutes
Still spend a lot of time in editing questions for your next supervised learning assessment? OnlineExamMaker is an AI quiz maker that leverages artificial intelligence to help users create quizzes, tests, and assessments quickly and efficiently. You can start by inputting a topic or specific details into the OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, and the AI will generate a set of questions almost instantly. It also offers the option to include answer explanations, which can be short or detailed, helping learners understand their mistakes.
What you may like:
● Automatic grading and insightful reports. Real-time results and interactive feedback for quiz-takers.
● The exams are automatically graded with the results instantly, so that teachers can save time and effort in grading.
● LockDown Browser to restrict browser activity during quizzes to prevent students searching answers on search engines or other software.
● Create certificates with personalized company logo, certificate title, description, date, candidate’s name, marks and signature.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 supervised learning quiz questions & answers
or
1. What is supervised learning primarily used for?
A. Finding hidden patterns in unlabeled data
B. Learning from labeled data to make predictions
C. Clustering similar data points without labels
D. Reducing the dimensionality of data
Answer: B
Explanation: Supervised learning involves training a model on labeled data, where the input and output are known, allowing the model to learn patterns for making predictions on new data.
2. In supervised learning, what does the term “target variable” refer to?
A. The input features used for training
B. The output or label that the model predicts
C. The algorithm used for learning
D. The testing dataset
Answer: B
Explanation: The target variable is the variable that the model aims to predict, based on the input features, making it central to supervised learning tasks.
3. Which of the following is an example of a regression problem in supervised learning?
A. Predicting whether an email is spam or not
B. Classifying images of cats and dogs
C. Forecasting house prices based on features
D. Grouping customers by shopping behavior
Answer: C
Explanation: Regression problems predict continuous values, such as house prices, whereas classification predicts discrete categories.
4. What is the main difference between classification and regression in supervised learning?
A. Classification uses labeled data, while regression does not
B. Classification predicts categorical outputs, while regression predicts continuous outputs
C. Classification is for unsupervised learning, while regression is for supervised
D. Regression requires more data than classification
Answer: B
Explanation: Classification assigns inputs to categories (e.g., yes/no), while regression predicts a numerical value (e.g., price), distinguishing the two supervised learning types.
5. Which algorithm is commonly used for binary classification problems?
A. K-means clustering
B. Logistic regression
C. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
D. Apriori algorithm
Answer: B
Explanation: Logistic regression is designed for binary classification, estimating probabilities to classify inputs into two classes.
6. In a supervised learning model, what happens during the training phase?
A. The model is tested on new data
B. The model learns from input features and their corresponding labels
C. The model evaluates its performance metrics
D. The model reduces noise in the dataset
Answer: B
Explanation: During training, the model adjusts its parameters based on the input features and labels to minimize errors and improve accuracy.
7. What is overfitting in the context of supervised learning?
A. When the model performs well on training data but poorly on new data
B. When the model is too simple and underperforms
C. When the model has no errors on any data
D. When the model uses unsupervised data
Answer: A
Explanation: Overfitting occurs when a model learns the noise in the training data, leading to poor generalization on unseen data.
8. Which evaluation metric is most appropriate for a binary classification problem?
A. Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
B. Accuracy
C. Silhouette Score
D. Root Mean Square Error (RMSE)
Answer: B
Explanation: Accuracy measures the proportion of correct predictions in binary classification, making it a straightforward metric for such tasks.
9. What role does the training set play in supervised learning?
A. It is used to fine-tune the model after deployment
B. It provides the data for the model to learn patterns
C. It evaluates the model’s final performance
D. It generates new features
Answer: B
Explanation: The training set contains labeled examples that the model uses to learn and adjust its parameters.
10. Which supervised learning algorithm is based on finding the hyperplane that best separates classes in a dataset?
A. Linear regression
B. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
C. Decision Tree
D. K-Nearest Neighbors
Answer: B
Explanation: SVM works by finding the optimal hyperplane that maximizes the margin between classes, making it effective for classification.
11. In supervised learning, how is the model’s performance typically measured on a test set?
A. By calculating the number of clusters formed
B. By comparing predicted outputs to actual labels
C. By visualizing data distributions
D. By reducing feature dimensions
Answer: B
Explanation: Performance is assessed by how well the model’s predictions match the actual labels in the test set, indicating generalization.
12. What is the purpose of cross-validation in supervised learning?
A. To increase the size of the dataset
B. To assess the model’s ability to generalize by using multiple subsets of data
C. To label unsupervised data
D. To select features automatically
Answer: B
Explanation: Cross-validation helps evaluate the model’s performance more reliably by splitting the data into folds and testing on each.
13. Which type of supervised learning is used when the output is a probability score?
A. Regression
B. Classification, such as logistic regression
C. Clustering
D. Dimensionality reduction
Answer: B
Explanation: Classification algorithms like logistic regression output probabilities, which can be thresholded to make decisions.
14. What does a confusion matrix help identify in supervised learning classification?
A. The distribution of features
B. True positives, false positives, true negatives, and false negatives
C. The mean error of predictions
D. The number of clusters
Answer: B
Explanation: A confusion matrix provides a detailed breakdown of correct and incorrect predictions, aiding in understanding model errors.
15. In linear regression, what does the coefficient represent?
A. The bias term in the model
B. The weight assigned to each feature’s impact on the target variable
C. The error rate of predictions
D. The number of data points
Answer: B
Explanation: Coefficients indicate how much each feature contributes to the predicted output, helping interpret the model’s behavior.
16. Why is feature scaling important in some supervised learning algorithms?
A. It labels the data automatically
B. It ensures features contribute equally to the model, especially in distance-based algorithms
C. It reduces the dataset size
D. It prevents overfitting entirely
Answer: B
Explanation: Feature scaling normalizes data ranges, preventing features with larger scales from dominating in algorithms like SVM or KNN.
17. What is the key assumption in simple linear regression?
A. There is a linear relationship between the independent and dependent variables
B. All data must be categorical
C. The model must use multiple algorithms
D. Data must be unlabeled
Answer: A
Explanation: Simple linear regression assumes a straight-line relationship between the input feature and the output, forming the basis of the model.
18. Which supervised learning technique is ensemble-based and combines multiple decision trees?
A. Neural Networks
B. Random Forest
C. K-means
D. Gradient Descent
Answer: B
Explanation: Random Forest builds multiple decision trees and aggregates their predictions to improve accuracy and reduce overfitting.
19. How does the holdout method work in supervised learning?
A. It splits data into training and testing sets for evaluation
B. It clusters data without labels
C. It trains the model on all data at once
D. It generates synthetic data
Answer: A
Explanation: The holdout method divides the dataset into subsets, using one for training and another for testing the model’s performance.
20. In supervised learning, what is the primary goal of hyperparameter tuning?
A. To increase the number of features
B. To optimize the model’s parameters for better performance
C. To convert data to unsupervised format
D. To visualize the data
Answer: B
Explanation: Hyperparameter tuning adjusts settings like learning rate to fine-tune the model and achieve optimal results on validation data.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically create questions for your next assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI