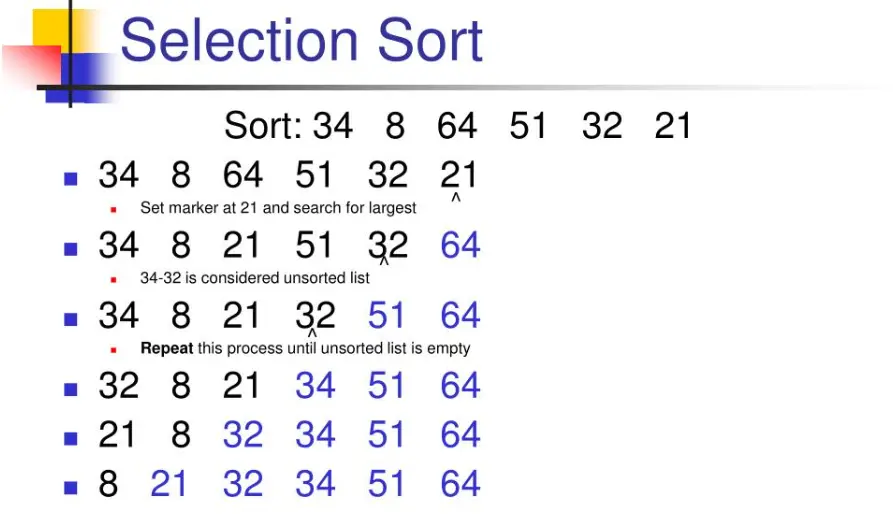
Selection Sort is a simple in-place comparison sorting algorithm that divides the input list into two parts: a sorted sublist at the beginning and an unsorted sublist at the end. The algorithm works by repeatedly finding the smallest element from the unsorted sublist and swapping it with the leftmost unsorted element, thereby expanding the sorted sublist one element at a time.
For example, consider the array: [64, 25, 12, 22, 11]
1. Find the minimum element in the entire array (11) and swap it with the first element: [11, 25, 12, 22, 64]
2. Find the minimum element in the subarray [25, 12, 22, 64] (12) and swap it with the second element: [11, 12, 25, 22, 64]
3. Find the minimum element in the subarray [25, 22, 64] (22) and swap it with the third element: [11, 12, 22, 25, 64]
4. Find the minimum element in the subarray [25, 64] (25) and swap it with the fourth element: [11, 12, 22, 25, 64]
5. The subarray [64] is already sorted.
The process continues until the entire array is sorted. Selection Sort has a time complexity of O(n²), making it less efficient for large datasets but useful for educational purposes or small arrays.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Maker – Make A Free Quiz in Minutes
- Part 2: 20 Selection Sort Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Maker – Make A Free Quiz in Minutes
Still spend a lot of time in editing questions for your next Selection Sort assessment? OnlineExamMaker is an AI quiz maker that leverages artificial intelligence to help users create quizzes, tests, and assessments quickly and efficiently. You can start by inputting a topic or specific details into the OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, and the AI will generate a set of questions almost instantly. It also offers the option to include answer explanations, which can be short or detailed, helping learners understand their mistakes.
What you may like:
● Automatic grading and insightful reports. Real-time results and interactive feedback for quiz-takers.
● The exams are automatically graded with the results instantly, so that teachers can save time and effort in grading.
● LockDown Browser to restrict browser activity during quizzes to prevent students searching answers on search engines or other software.
● Create certificates with personalized company logo, certificate title, description, date, candidate’s name, marks and signature.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Selection Sort Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is the primary operation in Selection Sort?
A) Swapping elements after each comparison
B) Dividing the array into halves
C) Selecting the smallest element from the unsorted portion and swapping it with the first unsorted element
D) Merging sorted subarrays
Answer: C
Explanation: Selection Sort works by repeatedly finding the minimum element from the unsorted part and placing it at the beginning of the unsorted portion, which involves selecting and swapping.
2. Question: How many passes does Selection Sort make on an array of n elements?
A) n-1
B) n
C) n/2
D) 1
Answer: A
Explanation: For an array of n elements, Selection Sort performs n-1 passes to sort the array, as each pass places one element in its correct position.
3. Question: What is the time complexity of Selection Sort in the worst case?
A) O(n)
B) O(n log n)
C) O(n^2)
D) O(1)
Answer: C
Explanation: Selection Sort always requires O(n^2) time due to its nested loops: one for each element and another to find the minimum in the unsorted subarray.
4. Question: In Selection Sort, how many swaps are performed for a sorted array of n elements?
A) 0
B) n-1
C) n
D) n^2
Answer: B
Explanation: Even for a sorted array, Selection Sort will perform n-1 swaps because it checks and swaps the minimum element each pass, though the array is already sorted.
5. Question: Which of the following best describes Selection Sort?
A) It is a divide-and-conquer algorithm
B) It builds the sorted array one element at a time by selecting the minimum
C) It compares adjacent elements and swaps them if needed
D) It uses recursion to sort elements
Answer: B
Explanation: Selection Sort constructs the sorted array incrementally by selecting the smallest unsorted element and moving it to its correct position.
6. Question: What is the space complexity of Selection Sort?
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(n log n)
D) O(n^2)
Answer: A
Explanation: Selection Sort is an in-place sorting algorithm, using only a constant amount of extra space regardless of the input size.
7. Question: For an array [4, 2, 7, 1, 3], what is the array after the first pass of Selection Sort?
A) [1, 2, 7, 4, 3]
B) [1, 2, 4, 7, 3]
C) [4, 2, 7, 1, 3]
D) [1, 4, 2, 7, 3]
Answer: A
Explanation: In the first pass, the smallest element (1) is selected from the array and swapped with the first element, resulting in [1, 2, 7, 4, 3].
8. Question: Is Selection Sort stable?
A) Yes
B) No
C) It depends on the implementation
D) Only for even-sized arrays
Answer: B
Explanation: Selection Sort is not stable because it may swap elements that are equal, potentially changing their relative order.
9. Question: What is the best-case time complexity of Selection Sort?
A) O(n)
B) O(n log n)
C) O(n^2)
D) O(1)
Answer: C
Explanation: Selection Sort has a time complexity of O(n^2) in all cases, including the best case, because it always performs the full nested loop operations.
10. Question: How does Selection Sort compare to Bubble Sort in terms of performance?
A) Selection Sort is always faster
B) Bubble Sort is always faster
C) Both have the same worst-case time complexity
D) Selection Sort uses more space
Answer: C
Explanation: Both Selection Sort and Bubble Sort have a worst-case time complexity of O(n^2), though their approaches differ.
11. Question: In Selection Sort, what happens during each iteration?
A) The largest element is moved to the end
B) The smallest element from the unsorted part is moved to the sorted part
C) All elements are compared pairwise
D) The array is reversed
Answer: B
Explanation: Each iteration of Selection Sort finds and moves the smallest element from the unsorted subarray to the end of the sorted subarray.
12. Question: For an array of 5 elements, how many comparisons does Selection Sort make in the worst case?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 15
D) 25
Answer: C
Explanation: Selection Sort makes n + (n-1) + … + 1 comparisons, which for n=5 is 5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1 = 15.
13. Question: Which of the following arrays will require the most swaps in Selection Sort?
A) Already sorted array
B) Reverse sorted array
C) Array with all identical elements
D) Randomly ordered array
Answer: B
Explanation: A reverse sorted array will require the maximum swaps because the smallest element is always at the opposite end each time.
14. Question: Can Selection Sort be used for linked lists?
A) Yes, efficiently
B) No, it requires random access
C) Only for singly linked lists
D) Only for doubly linked lists
Answer: B
Explanation: Selection Sort assumes array-like access for finding minimum elements, making it inefficient for linked lists without additional structures.
15. Question: What is a key disadvantage of Selection Sort?
A) It is not in-place
B) It has poor performance for large datasets due to O(n^2) complexity
C) It requires extra memory
D) It is not stable
Answer: B
Explanation: The O(n^2) time complexity makes Selection Sort inefficient for large arrays compared to algorithms like Quick Sort or Merge Sort.
16. Question: In Selection Sort, after sorting an array of n elements, how many elements are in the sorted portion?
A) n-1
B) n
C) 0
D) 1
Answer: B
Explanation: After all passes, the entire array of n elements is sorted.
17. Question: Which algorithm is similar to Selection Sort in terms of selecting elements?
A) Insertion Sort
B) Heap Sort
C) Merge Sort
D) Quick Sort
Answer: B
Explanation: Heap Sort also involves selecting the maximum or minimum element repeatedly, similar to how Selection Sort operates.
18. Question: For the array [3, 1, 4, 2], what is the minimum number of swaps Selection Sort will perform?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Answer: C
Explanation: Selection Sort will perform 3 swaps: one for each of the first three elements to place them in order.
19. Question: Is Selection Sort adaptive?
A) Yes
B) No
C) Only for sorted arrays
D) Only for reverse sorted arrays
Answer: B
Explanation: Selection Sort is not adaptive because its performance does not improve even if the array is partially sorted; it always runs in O(n^2) time.
20. Question: When might you choose Selection Sort over other sorting algorithms?
A) For very small arrays
B) For large datasets
C) When stability is required
D) For external sorting
Answer: A
Explanation: Selection Sort is simple and works well for small arrays or educational purposes, despite its inefficiency for larger ones.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI