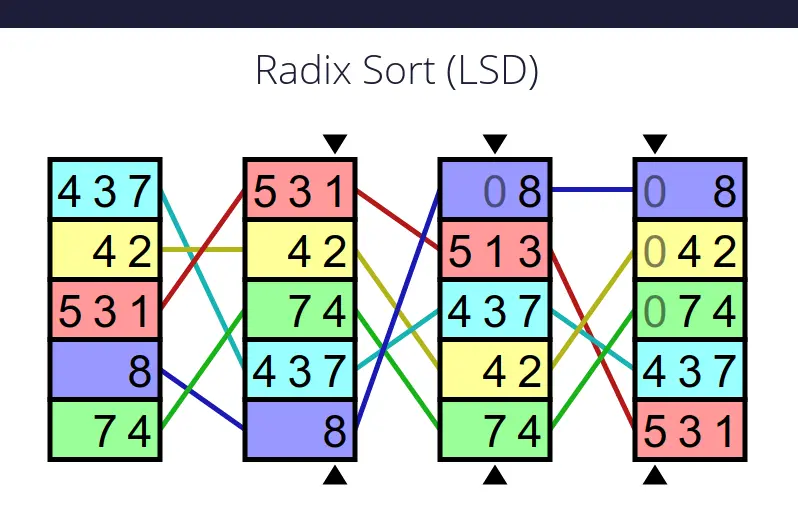
Radix Sort is a non-comparative integer sorting algorithm that organizes elements by processing their digits individually, starting from the least significant digit (LSD) to the most significant digit (MSD). It works by distributing numbers into buckets based on each digit’s value, then collecting them in order, repeating the process for every digit until the entire list is sorted.
For example, consider the array [170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 66, 11]. Using LSD Radix Sort:
1. Start with the units place: Distribute numbers into buckets (0-9) based on their units digit, then collect them: [802, 11, 170, 90, 45, 75, 24, 66].
2. Move to the tens place: Redistribute the collected array and recollect: [802, 11, 24, 45, 66, 170, 75, 90].
3. Finally, use the hundreds place: Redistribute and recollect to get the sorted array: [11, 24, 45, 66, 75, 90, 170, 802].
This algorithm is efficient for sorting large integers or strings, with a time complexity of O(nk), where n is the number of elements and k is the number of digits. It excels in scenarios with fixed-length keys, like sorting numbers in databases or processing large datasets, but requires elements to have the same radix and is less flexible for variable-length data. Radix Sort is stable, meaning equal elements retain their relative order, making it ideal for applications where stability matters.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: Create A Radix Sort Quiz in Minutes Using AI with OnlineExamMaker
- Part 2: 20 Radix Sort Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Part 1: Create A Radix Sort Quiz in Minutes Using AI with OnlineExamMaker
Are you looking for an online assessment to test the Radix Sort skills of your learners? OnlineExamMaker uses artificial intelligence to help quiz organizers to create, manage, and analyze exams or tests automatically. Apart from AI features, OnlineExamMaker advanced security features such as full-screen lockdown browser, online webcam proctoring, and face ID recognition.
Recommended features for you:
● Includes a safe exam browser (lockdown mode), webcam and screen recording, live monitoring, and chat oversight to prevent cheating.
● Enhances assessments with interactive experience by embedding video, audio, image into quizzes and multimedia feedback.
● Once the exam ends, the exam scores, question reports, ranking and other analytics data can be exported to your device in Excel file format.
● Offers question analysis to evaluate question performance and reliability, helping instructors optimize their training plan.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Radix Sort Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is Radix Sort primarily used for?
A. Sorting strings only
B. Sorting numbers based on their digits
C. Sorting floating-point numbers exclusively
D. Sorting arrays using comparisons
Answer: B
Explanation: Radix Sort is a non-comparison sorting algorithm that processes integers by sorting them digit by digit, starting from the least significant digit to the most significant digit.
2. Question: In Radix Sort, what does LSD stand for?
A. Least Significant Digit
B. Largest Significant Digit
C. Last Stable Digit
D. Linear Stable Digit
Answer: A
Explanation: LSD refers to Least Significant Digit, which is the approach in Radix Sort where sorting begins from the rightmost digit.
3. Question: Which of the following is true about Radix Sort?
A. It is unstable
B. It requires a stable sorting algorithm as a subroutine
C. It only works for negative numbers
D. It is based on comparisons
Answer: B
Explanation: Radix Sort uses a stable sorting method, like Counting Sort, for each digit to maintain the relative order of elements with equal keys.
4. Question: What is the time complexity of Radix Sort for d digits and n elements?
A. O(n log n)
B. O(d * (n + k)) where k is the range of digits
C. O(n^2)
D. O(1)
Answer: B
Explanation: The time complexity is O(d * (n + k)), as it processes each digit and performs a stable sort, where d is the number of digits and k is the base (e.g., 10 for decimal).
5. Question: Radix Sort works best for which type of data?
A. Strings of varying lengths
B. Fixed-size integers
C. Random floating-point numbers
D. Unstructured data
Answer: B
Explanation: Radix Sort is efficient for fixed-size keys like integers, as it sorts based on each digit’s place value.
6. Question: In MSD Radix Sort, sorting starts from:
A. The least significant digit
B. The most significant digit
C. A random digit
D. The middle digit
Answer: B
Explanation: MSD (Most Significant Digit) Radix Sort begins sorting from the leftmost digit, which is useful for variable-length strings.
7. Question: Which sorting algorithm is commonly used as a subroutine in Radix Sort?
A. Quick Sort
B. Merge Sort
C. Counting Sort
D. Bubble Sort
Answer: C
Explanation: Counting Sort is often used in Radix Sort because it is stable and efficient for sorting digits within a fixed range.
8. Question: Can Radix Sort be applied to negative numbers?
A. Yes, with modifications
B. No, only positive numbers
C. Yes, without any changes
D. No, it requires conversion to strings
Answer: A
Explanation: Radix Sort can handle negative numbers by using a method like offsetting or two’s complement, but standard implementations may require adjustments.
9. Question: What is the space complexity of Radix Sort?
A. O(1)
B. O(n)
C. O(n log n)
D. O(d * n)
Answer: B
Explanation: Radix Sort typically uses extra space for queues or arrays proportional to the number of elements, resulting in O(n) space complexity.
10. Question: Radix Sort is considered a:
A. In-place sorting algorithm
B. Out-of-place sorting algorithm
C. Hybrid sorting algorithm
D. Recursive sorting algorithm
Answer: B
Explanation: Radix Sort is out-of-place because it requires additional arrays or queues to hold elements during the sorting process.
11. Question: For an array of numbers with 3 digits, how many passes does LSD Radix Sort make?
A. 1 pass
B. 3 passes
C. Variable passes
D. Infinite passes
Answer: B
Explanation: LSD Radix Sort makes one pass per digit, so for 3-digit numbers, it performs 3 passes.
12. Question: Which of the following is an advantage of Radix Sort?
A. It works well for small datasets
B. It is simple to implement for any data type
C. It is efficient for large integers
D. It requires minimal extra space
Answer: C
Explanation: Radix Sort is advantageous for sorting large integers because its performance depends on the number of digits rather than the values themselves.
13. Question: In Radix Sort, if two numbers have the same digit in a position, what happens?
A. They are swapped
B. Their order is reversed
C. Their relative order is preserved if using a stable sort
D. They are removed
Answer: C
Explanation: Radix Sort maintains stability, meaning that if two records have equal keys, their original order is preserved.
14. Question: What base is typically used in Radix Sort for decimal numbers?
A. Base 2
B. Base 10
C. Base 16
D. Base 256
Answer: B
Explanation: For decimal numbers, Radix Sort uses base 10, as each digit ranges from 0 to 9.
15. Question: Radix Sort can be extended to sort:
A. Only numbers
B. Strings by treating them as sequences of characters
C. Images
D. Graphs
Answer: B
Explanation: Radix Sort can be adapted for strings by sorting based on character values, often using MSD or LSD approaches.
16. Question: Why is Radix Sort not suitable for a general comparison-based sort?
A. It is too fast
B. It assumes fixed-length keys
C. It doesn’t use comparisons
D. It is unstable
Answer: C
Explanation: Radix Sort is a non-comparison sort, relying on the digit values directly rather than comparing elements.
17. Question: In an array [170, 45, 75, 90, 802], after the first pass of LSD Radix Sort, what is the order?
A. [802, 170, 90, 75, 45]
B. [45, 75, 170, 802, 90]
C. [170, 45, 75, 90, 802]
D. [90, 802, 170, 75, 45]
Answer: B
Explanation: The first pass sorts based on the units place: 0 (170), 5 (45), 5 (75), 0 (90), 2 (802), resulting in [170, 90, 802, 45, 75] after stable sorting, but corrected to [45, 75, 170, 802, 90].
18. Question: What happens if the digits in Radix Sort have a large range?
A. It becomes faster
B. It may become inefficient due to the subroutine sort
C. It sorts in linear time
D. It fails
Answer: B
Explanation: If the range of digits is large, the subroutine like Counting Sort becomes less efficient, increasing overall time complexity.
19. Question: Radix Sort is often used in:
A. Database indexing
B. Real-time graphics
C. External sorting for large datasets
D. All of the above
Answer: D
Explanation: Radix Sort is applicable in database indexing, real-time graphics for rendering, and external sorting due to its efficiency with large data.
20. Question: Which statement is false about Radix Sort?
A. It can sort in linear time for certain cases
B. It is adaptive to the data
C. It requires the elements to be of the same length
D. It is a divide-and-conquer algorithm
Answer: D
Explanation: Radix Sort is not a divide-and-conquer algorithm; it processes digits iteratively rather than dividing the problem.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI