Prefabrication is a modern construction technique where building components, such as walls, floors, and modules, are manufactured in a controlled factory environment before being transported to the site for quick assembly. This method enhances efficiency by reducing on-site labor, minimizing material waste, and improving quality control through precise manufacturing processes. It is widely applied in residential, commercial, and industrial projects, allowing for faster completion times, cost savings, and greater adaptability to various designs, while also promoting sustainability by optimizing resource use and reducing environmental impact.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Generator – Save Time and Efforts
- Part 2: 20 Prefabrication Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: Save Time and Energy: Generate Quiz Questions with AI Technology
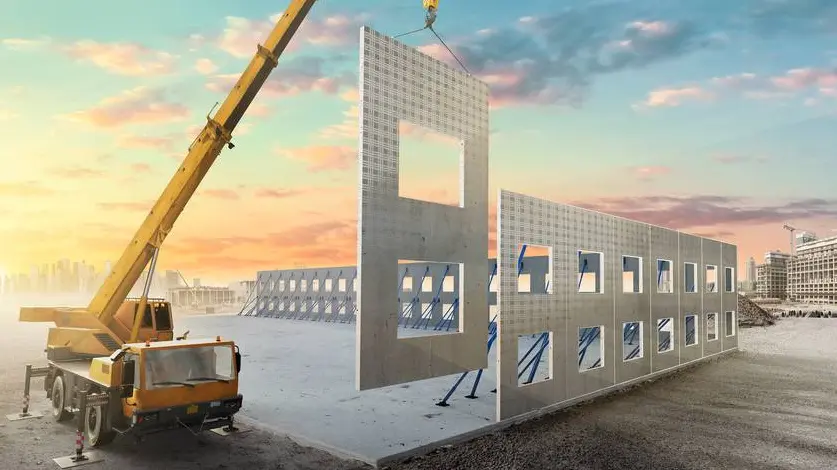
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Generator – Save Time and Efforts
What’s the best way to create a Prefabrication quiz online? OnlineExamMaker is the best AI quiz making software for you. No coding, and no design skills required. If you don’t have the time to create your online quiz from scratch, you are able to use OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to create question automatically, then add them into your online assessment. What is more, the platform leverages AI proctoring and AI grading features to streamline the process while ensuring exam integrity.
Key features of OnlineExamMaker:
● Combines AI webcam monitoring to capture cheating activities during online exam.
● Allow the quiz taker to answer by uploading video or a Word document, adding an image, and recording an audio file.
● Automatically scores multiple-choice, true/false, and even open-ended/audio responses using AI, reducing manual work.
● OnlineExamMaker API offers private access for developers to extract your exam data back into your system automatically.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Prefabrication Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is prefabrication in the context of construction?
Options:
A) Building structures entirely on-site
B) Assembling components off-site and transporting them for final assembly
C) Demolishing old buildings to create new ones
D) Using only natural materials in construction
Answer: B
Explanation: Prefabrication involves manufacturing building components in a controlled factory environment, which reduces on-site time and improves efficiency.
2. Question: Which of the following is a primary advantage of prefabrication?
Options:
A) Increased waste on construction sites
B) Faster project completion times
C) Higher costs due to custom on-site work
D) Dependency on weather conditions
Answer: B
Explanation: Prefabrication allows for simultaneous factory production and site preparation, leading to quicker overall project timelines.
3. Question: In prefabrication, what role does modular construction play?
Options:
A) It involves only decorative elements
B) It creates repeatable units that can be stacked or combined
C) It focuses solely on foundation work
D) It is limited to small-scale projects
Answer: B
Explanation: Modular construction in prefabrication uses standardized modules that can be easily transported and assembled, enhancing scalability.
4. Question: What material is commonly used in prefabrication for structural components?
Options:
A) Wood only
B) Steel, concrete, and wood
C) Glass exclusively
D) Plastic polymers
Answer: B
Explanation: Steel, concrete, and wood are versatile materials in prefabrication due to their strength, durability, and ease of factory manipulation.
5. Question: How does prefabrication impact labor requirements on a construction site?
Options:
A) It increases the need for skilled on-site workers
B) It reduces on-site labor by shifting work to factories
C) It eliminates the need for any labor
D) It requires more manual assembly on-site
Answer: B
Explanation: Prefabrication minimizes on-site assembly, thereby reducing the demand for extensive labor at the construction location.
6. Question: What is a potential disadvantage of prefabrication?
Options:
A) Lower initial costs
B) Transportation challenges for large components
C) Immediate availability of materials
D) Enhanced customization options
Answer: B
Explanation: Large prefabricated elements can be difficult and costly to transport, potentially delaying projects if logistics are not managed properly.
7. Question: In prefabrication, what does “just-in-time” delivery mean?
Options:
A) Delaying delivery until the project is complete
B) Supplying components exactly when needed to minimize storage
C) Using outdated materials
D) Overstocking materials on-site
Answer: B
Explanation: Just-in-time delivery in prefabrication ensures components arrive precisely when required, reducing inventory costs and site clutter.
8. Question: Which industry commonly uses prefabrication for housing?
Options:
A) Automotive
B) Aerospace
C) Residential construction
D) Textile manufacturing
Answer: C
Explanation: Residential construction benefits from prefabrication through factory-built homes that are quicker to erect and often more cost-effective.
9. Question: What quality control benefit does prefabrication offer?
Options:
A) It relies on on-site inspections only
B) Factory settings allow for precise and consistent quality checks
C) It eliminates the need for standards
D) Quality is harder to monitor due to off-site work
Answer: B
Explanation: Controlled factory environments in prefabrication enable better monitoring and adherence to quality standards compared to traditional sites.
10. Question: How does prefabrication contribute to sustainability?
Options:
A) By increasing material waste
B) Through reduced energy consumption in manufacturing
C) By promoting single-use materials
D) It has no environmental impact
Answer: B
Explanation: Prefabrication often uses efficient manufacturing processes that minimize waste and energy use, supporting sustainable practices.
11. Question: What is the difference between prefabrication and traditional construction?
Options:
A) Prefabrication uses no planning
B) Traditional construction assembles everything on-site, while prefabrication uses off-site assembly
C) They are identical processes
D) Prefabrication is always more expensive
Answer: B
Explanation: Prefabrication shifts much of the assembly to factories, contrasting with traditional methods that handle most work on-site.
12. Question: In prefabrication, what is a panelized system?
Options:
A) A method for demolishing walls
B) Pre-built wall or floor panels assembled on-site
C) Only for roof structures
D) A type of foundation
Answer: B
Explanation: Panelized systems involve creating flat components like walls in a factory for quick on-site installation.
13. Question: Why might prefabrication be unsuitable for certain projects?
Options:
A) It is always suitable
B) Due to site-specific irregularities or custom designs
C) It speeds up all projects equally
D) It requires no adaptation
Answer: B
Explanation: Projects with unique site conditions or highly customized designs may not align well with standardized prefabrication methods.
14. Question: What technology is often integrated into prefabrication processes?
Options:
A) Manual tools only
B) Building Information Modeling (BIM) for design and planning
C) Paper-based blueprints
D) No technology is used
Answer: B
Explanation: BIM enhances prefabrication by providing digital models that improve accuracy and coordination in manufacturing.
15. Question: How does prefabrication affect project costs?
Options:
A) It always increases costs
B) It can lower costs through reduced labor and material waste
C) Costs remain unchanged
D) It eliminates all budgeting needs
Answer: B
Explanation: Efficient factory production in prefabrication often leads to savings in labor, materials, and time, reducing overall expenses.
16. Question: What is a key step in the prefabrication process?
Options:
A) On-site fabrication only
B) Designing components for easy transport and assembly
C) Ignoring safety standards
D) Using improvised materials
Answer: B
Explanation: Effective prefabrication requires designing elements that are modular and easy to handle during transportation and installation.
17. Question: In prefabrication, what does “off-site construction” refer to?
Options:
A) Building away from the final site
B) All work done on-site
C) Only finishing touches off-site
D) Demolition activities
Answer: A
Explanation: Off-site construction means manufacturing building parts in a separate location before transporting them to the main site.
18. Question: Which factor influences the success of a prefabrication project?
Options:
A) Poor coordination between factory and site
B) Strong supply chain management
C) Ignoring timelines
D) Using incompatible materials
Answer: B
Explanation: Effective supply chain management ensures timely delivery and integration of prefabricated components, crucial for project success.
19. Question: How has prefabrication evolved with modern techniques?
Options:
A) It has remained unchanged
B) Incorporation of automation and 3D printing for precision
C) Only manual methods are used now
D) It is phasing out technology
Answer: B
Explanation: Advances like automation and 3D printing have made prefabrication more accurate and efficient in contemporary applications.
20. Question: What is the global impact of prefabrication on the construction industry?
Options:
A) It has decreased productivity
B) It promotes standardization and global trade in building components
C) It limits international collaboration
D) It is irrelevant to global trends
Answer: B
Explanation: Prefabrication facilitates the export and import of standardized modules, enhancing global construction efficiency and collaboration.
or
Part 3: Save Time and Energy: Generate Quiz Questions with AI Technology
Automatically generate questions using AI