Muscle tissue is a specialized type of soft tissue in animals that enables movement, maintains posture, and generates force through contraction. It is composed of elongated cells known as muscle fibers, which contain proteins like actin and myosin that slide past each other to produce motion.
There are three primary types of muscle tissue:
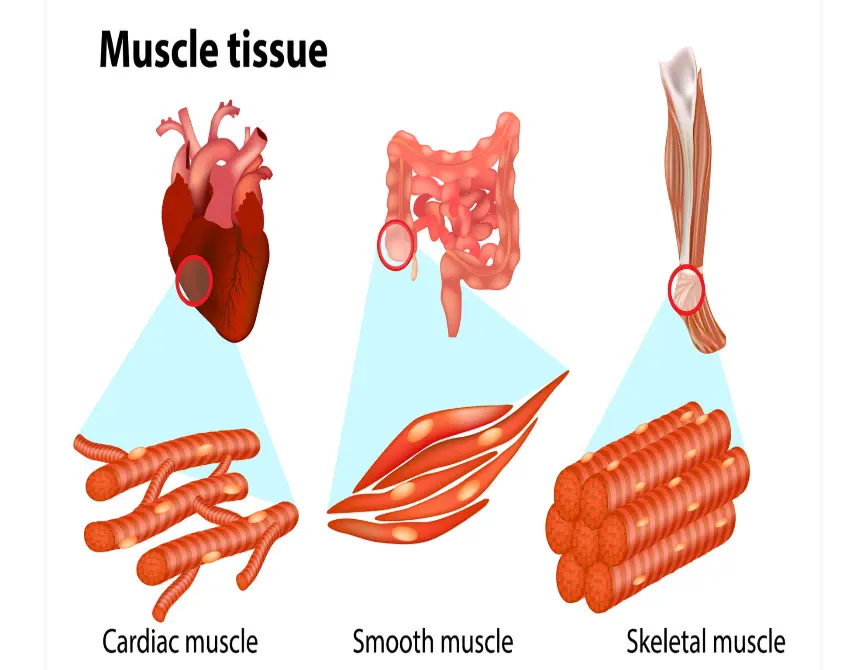
1. Skeletal muscle: Attached to bones via tendons, it is voluntary and responsible for conscious movements, such as walking or lifting objects. It appears striated under a microscope and consists of multinucleated fibers.
2. Cardiac muscle: Found exclusively in the heart, it is involuntary and pumps blood throughout the body. It has a striated appearance but features interconnected cells with intercalated discs for synchronized contractions.
3. Smooth muscle: Located in the walls of internal organs like the stomach, blood vessels, and intestines, it is involuntary and non-striated. It facilitates functions such as peristalsis and blood flow regulation, with spindle-shaped cells that contract slowly and sustainably.
Overall, muscle tissue is essential for locomotion, heat production, and maintaining bodily functions, adapting through exercise or injury to support overall health.
Table of contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI quiz maker – Make a free quiz in minutes
- Part 2: 20 muscle tissue quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically create questions for your next assessment
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI quiz maker – Make a free quiz in minutes
Still spend a lot of time in editing questions for your next muscle tissue assessment? OnlineExamMaker is an AI quiz maker that leverages artificial intelligence to help users create quizzes, tests, and assessments quickly and efficiently. You can start by inputting a topic or specific details into the OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, and the AI will generate a set of questions almost instantly. It also offers the option to include answer explanations, which can be short or detailed, helping learners understand their mistakes.
What you may like:
● Automatic grading and insightful reports. Real-time results and interactive feedback for quiz-takers.
● The exams are automatically graded with the results instantly, so that teachers can save time and effort in grading.
● LockDown Browser to restrict browser activity during quizzes to prevent students searching answers on search engines or other software.
● Create certificates with personalized company logo, certificate title, description, date, candidate’s name, marks and signature.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 muscle tissue quiz questions & answers
or
1. Question: What type of muscle tissue is responsible for voluntary movements?
Options:
A) Smooth muscle
B) Cardiac muscle
C) Skeletal muscle
D) Adipose tissue
Answer: C) Skeletal muscle
Explanation: Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and controlled by the somatic nervous system, enabling voluntary actions like walking or lifting weights.
2. Question: Which protein is primarily responsible for muscle contraction?
Options:
A) Actin
B) Myosin
C) Collagen
D) Keratin
Answer: B) Myosin
Explanation: Myosin interacts with actin filaments during the sliding filament mechanism, using ATP to generate force and cause muscle contraction.
3. Question: What is the functional unit of a muscle fiber?
Options:
A) Sarcomere
B) Myofibril
C) T-tubule
D) Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Answer: A) Sarcomere
Explanation: The sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of striated muscle, consisting of actin and myosin filaments that shorten during contraction.
4. Question: Which muscle tissue is found in the walls of blood vessels?
Options:
A) Skeletal muscle
B) Cardiac muscle
C) Smooth muscle
D) Connective tissue
Answer: C) Smooth muscle
Explanation: Smooth muscle lines the walls of blood vessels and organs, allowing for involuntary contractions that regulate blood flow and digestion.
5. Question: What ion is essential for muscle contraction to occur?
Options:
A) Sodium
B) Potassium
C) Calcium
D) Magnesium
Answer: C) Calcium
Explanation: Calcium ions bind to troponin, which moves tropomyosin and exposes actin binding sites, initiating the cross-bridge cycle in muscle contraction.
6. Question: Which characteristic distinguishes cardiac muscle from skeletal muscle?
Options:
A) Striated appearance
B) Involuntary control
C) Multinucleated cells
D) Rapid fatigue
Answer: B) Involuntary control
Explanation: Cardiac muscle is involuntarily controlled by the autonomic nervous system, unlike skeletal muscle which is under voluntary control.
7. Question: What is the role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle tissue?
Options:
A) Stores calcium ions
B) Produces ATP
C) Transmits nerve impulses
D) Forms the cell membrane
Answer: A) Stores calcium ions
Explanation: The sarcoplasmic reticulum acts as a calcium reservoir, releasing it into the cytoplasm to trigger muscle contraction.
8. Question: Which type of muscle tissue has intercalated discs?
Options:
A) Smooth muscle
B) Skeletal muscle
C) Cardiac muscle
D) Tendons
Answer: C) Cardiac muscle
Explanation: Intercalated discs in cardiac muscle facilitate electrical communication between cells, allowing synchronized heart contractions.
9. Question: What causes muscle fatigue?
Options:
A) Excess oxygen
B) Depletion of ATP and glycogen
C) Increased blood flow
D) High calcium levels
Answer: B) Depletion of ATP and glycogen
Explanation: Muscle fatigue occurs due to the buildup of lactic acid and the depletion of energy sources like ATP and glycogen during prolonged activity.
10. Question: Which muscle type is multinucleated?
Options:
A) Smooth muscle
B) Cardiac muscle
C) Skeletal muscle
D) Epithelial muscle
Answer: C) Skeletal muscle
Explanation: Skeletal muscle fibers are formed by the fusion of myoblasts, resulting in long, multinucleated cells for powerful contractions.
11. Question: What is the sliding filament theory?
Options:
A) Actin and myosin filaments slide past each other
B) Muscles elongate during contraction
C) Filaments dissolve and reform
D) Only myosin moves
Answer: A) Actin and myosin filaments slide past each other
Explanation: The sliding filament theory describes how actin thin filaments slide over myosin thick filaments, shortening the sarcomere and causing contraction.
12. Question: Which neurotransmitter stimulates skeletal muscle contraction?
Options:
A) Acetylcholine
B) Dopamine
C) Serotonin
D) Norepinephrine
Answer: A) Acetylcholine
Explanation: Acetylcholine is released at the neuromuscular junction, binding to receptors on the muscle fiber to initiate an action potential and contraction.
13. Question: What is the primary energy source for muscle contraction?
Options:
A) Glucose
B) ATP
C) Oxygen
D) Fatty acids
Answer: B) ATP
Explanation: ATP provides the direct energy for the cross-bridge cycling between actin and myosin during muscle contraction.
14. Question: Which muscle tissue regenerates the least?
Options:
A) Skeletal muscle
B) Smooth muscle
C) Cardiac muscle
D) All regenerate equally
Answer: C) Cardiac muscle
Explanation: Cardiac muscle has limited regenerative capacity due to its terminally differentiated cells, relying on existing cells for function.
15. Question: What structure anchors muscle to bone?
Options:
A) Ligament
B) Tendon
C) Fascia
D) Aponeurosis
Answer: B) Tendon
Explanation: Tendons are tough connective tissues that connect skeletal muscle to bones, transmitting the force of contraction.
16. Question: How does smooth muscle differ from striated muscle?
Options:
A) Lacks striations
B) Faster contraction
C) Voluntary control
D) Multinucleated
Answer: A) Lacks striations
Explanation: Smooth muscle appears non-striated under a microscope due to its disorganized actin and myosin arrangement, unlike the banded pattern in striated muscles.
17. Question: What is rigor mortis?
Options:
A) Muscle relaxation after death
B) Stiffening of muscles due to ATP depletion
C) Increased flexibility post-mortem
D) Swelling of muscle tissue
Answer: B) Stiffening of muscles due to ATP depletion
Explanation: Rigor mortis occurs after death when ATP is unavailable, preventing myosin from detaching from actin, leading to rigid muscles.
18. Question: Which enzyme breaks down ATP in muscle contraction?
Options:
A) ATPase
B) Amylase
C) Kinase
D) Phosphatase
Answer: A) ATPase
Explanation: Myosin ATPase hydrolyzes ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate, providing energy for the power stroke in muscle contraction.
19. Question: What is the function of T-tubules in muscle tissue?
Options:
A) Store calcium
B) Conduct action potentials into the cell interior
C) Produce ATP
D) Anchor actin filaments
Answer: B) Conduct action potentials into the cell interior
Explanation: T-tubules are invaginations of the sarcolemma that propagate electrical impulses deep into the muscle fiber, triggering calcium release.
20. Question: Which disease is associated with muscle tissue degeneration?
Options:
A) Muscular dystrophy
B) Diabetes
C) Hypertension
D) Osteoporosis
Answer: A) Muscular dystrophy
Explanation: Muscular dystrophy involves genetic mutations leading to progressive weakening and degeneration of muscle fibers, particularly skeletal muscle.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically create questions for your next assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI