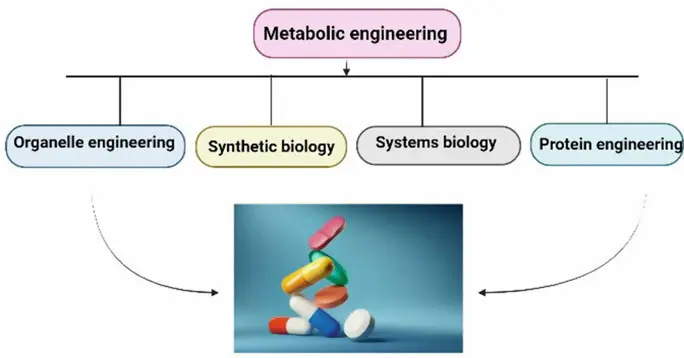
Metabolic engineering is a multidisciplinary field that applies principles of biochemistry, genetics, and systems biology to redesign metabolic pathways in organisms for enhanced production of desired compounds or improved cellular functions. At its core, it involves the targeted modification of genes, enzymes, and regulatory networks to optimize the flux of metabolites, thereby increasing yields of biofuels, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and other valuable products.
Key techniques include pathway engineering, where genes are introduced, deleted, or overexpressed; flux analysis to measure and balance metabolic flows; and synthetic biology tools like CRISPR for precise genome editing. For instance, engineers might redirect carbon flow in microorganisms like E. coli or yeast to produce bio-based chemicals such as ethanol or artemisinin.
Applications span industries: in biotechnology, it enables sustainable production of biofuels and bioplastics; in medicine, it facilitates the synthesis of therapeutic proteins and vaccines; and in agriculture, it enhances crop resilience and nutritional value through engineered plants.
Historically, the field emerged in the 1990s with foundational work by researchers like Gregory Stephanopoulos and Jay Keasling, building on earlier metabolic studies. Challenges include managing unintended side effects, such as metabolic burden or instability, and scaling up processes for industrial use.
Future directions involve integrating machine learning for predictive design, expanding to non-model organisms, and addressing global issues like climate change through carbon-neutral bioprocesses. As tools advance, metabolic engineering promises to revolutionize sustainable manufacturing and bioeconomy.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: Best AI Quiz Making Software for Creating A Metabolic Engineering Quiz
- Part 2: 20 Metabolic Engineering Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: Try OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to Create Quiz Questions
Part 1: Best AI Quiz Making Software for Creating A Metabolic Engineering Quiz
Nowadays more and more people create Metabolic Engineering quizzes using AI technologies, OnlineExamMaker a powerful AI-based quiz making tool that can save you time and efforts. The software makes it simple to design and launch interactive quizzes, assessments, and surveys. With the Question Editor, you can create multiple-choice, open-ended, matching, sequencing and many other types of questions for your tests, exams and inventories. You are allowed to enhance quizzes with multimedia elements like images, audio, and video to make them more interactive and visually appealing.
Take a product tour of OnlineExamMaker:
● Create a question pool through the question bank and specify how many questions you want to be randomly selected among these questions.
● Build and store questions in a centralized portal, tagged by categories and keywords for easy reuse and organization.
● Simply copy a few lines of codes, and add them to a web page, you can present your online quiz in your website, blog, or landing page.
● Randomize questions or change the order of questions to ensure exam takers don’t get the same set of questions each time.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Metabolic Engineering Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is the primary goal of metabolic engineering?
a) To increase the yield of a specific metabolite
b) To study protein structures
c) To analyze gene expression patterns
d) To develop new antibiotics
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Metabolic engineering focuses on modifying metabolic pathways to enhance the production of desired compounds, such as increasing metabolite yield through genetic and enzymatic interventions.
2. Question: Which enzyme is commonly targeted in metabolic engineering to redirect carbon flux towards a product like ethanol?
a) Pyruvate dehydrogenase
b) Pyruvate decarboxylase
c) Citrate synthase
d) ATP synthase
Correct Answer: b
Explanation: Pyruvate decarboxylase converts pyruvate to acetaldehyde, a key step in ethanol production, allowing engineers to reroute metabolic flux away from other pathways.
3. Question: In metabolic engineering, what does the term “flux” refer to?
a) The rate of metabolite flow through a pathway
b) The total number of enzymes in a cell
c) The DNA sequence of a gene
d) The pH level in the cell
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Flux represents the quantitative measure of metabolite movement through enzymatic reactions, which is crucial for optimizing pathway efficiency.
4. Question: Which technique is often used to knock out genes in metabolic engineering?
a) CRISPR-Cas9
b) PCR amplification
c) Gel electrophoresis
d) Mass spectrometry
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: CRISPR-Cas9 allows precise gene editing, including knockouts, enabling the removal of unwanted genes to alter metabolic pathways.
5. Question: What role does ATP play in metabolic engineering?
a) It provides energy for cellular reactions
b) It acts as a structural protein
c) It serves as a signaling molecule
d) It is a primary carbon source
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: ATP is essential for driving energy-dependent reactions in engineered pathways, ensuring that metabolic modifications are energetically feasible.
6. Question: How can metabolic engineering improve biofuel production?
a) By enhancing the conversion of sugars to alcohols
b) By increasing photosynthesis rates
c) By reducing water usage in plants
d) By altering soil composition
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Engineering microbes to efficiently convert sugars into biofuels like ethanol improves yield and reduces costs in production processes.
7. Question: What is a common host organism in metabolic engineering for pharmaceutical production?
a) Escherichia coli
b) Humans
c) Plants
d) Viruses
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: E. coli is widely used due to its fast growth, well-understood genetics, and ease of genetic manipulation for producing compounds like insulin.
8. Question: In the TCA cycle, which intermediate is often engineered for amino acid production?
a) Oxaloacetate
b) Glucose
c) NADH
d) ATP
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Oxaloacetate serves as a precursor for aspartate-derived amino acids, making it a key target for flux redirection in metabolic engineering.
9. Question: What is the purpose of cofactor engineering in metabolic pathways?
a) To balance redox states for efficient reactions
b) To increase cell membrane permeability
c) To enhance DNA replication
d) To reduce enzyme stability
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Cofactor engineering, such as manipulating NADH/NAD+ ratios, ensures that redox balances support the flow through engineered pathways.
10. Question: Which analytical tool is used to measure metabolic fluxes in vivo?
a) 13C metabolic flux analysis
b) X-ray crystallography
c) Fluorescence microscopy
d) Gas chromatography
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: 13C metabolic flux analysis tracks isotope-labeled carbons to quantify flux rates, providing data for pathway optimization.
11. Question: How does overexpression of a rate-limiting enzyme affect a metabolic pathway?
a) It increases the flux through the pathway
b) It decreases enzyme activity
c) It causes pathway shutdown
d) It has no effect
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Overexpressing a rate-limiting enzyme removes bottlenecks, allowing for higher throughput and increased product formation.
12. Question: What is synthetic biology’s role in metabolic engineering?
a) Designing new pathways from modular parts
b) Only studying natural pathways
c) Focusing on protein folding
d) Analyzing environmental impacts
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Synthetic biology provides tools to assemble and test artificial pathways, expanding the capabilities of metabolic engineering.
13. Question: In metabolic engineering, what does “dynamic regulation” involve?
a) Controlling gene expression in response to conditions
b) Keeping pathways static
c) Random gene mutations
d) External chemical additions
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Dynamic regulation uses sensors and feedback loops to adjust pathway activity based on cellular needs, improving efficiency and yield.
14. Question: Which pathway is frequently engineered for lactic acid production?
a) Glycolytic pathway
b) Photosynthetic pathway
c) Fatty acid synthesis
d) Nitrogen fixation
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: The glycolytic pathway converts glucose to pyruvate, which can be further modified to produce lactic acid in engineered organisms.
15. Question: What challenge does metabolic burden pose in engineered strains?
a) It reduces growth due to resource demands
b) It enhances enzyme activity
c) It increases mutation rates
d) It stabilizes DNA
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Metabolic burden from overexpressed genes can divert resources from growth, necessitating balanced engineering strategies.
16. Question: How is pathway balancing achieved in metabolic engineering?
a) By adjusting enzyme levels to match flux rates
b) By ignoring enzyme kinetics
c) By increasing substrate availability only
d) By reducing all enzyme expressions
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Balancing involves fine-tuning enzyme expressions to prevent accumulation of intermediates and ensure smooth flux.
17. Question: What is the significance of heterologous expression in metabolic engineering?
a) Introducing genes from other organisms to create new capabilities
b) Expressing only native genes
c) Deleting all foreign DNA
d) Focusing on RNA interference
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Heterologous expression allows the incorporation of pathways from different species, enabling production of novel compounds.
18. Question: In metabolic engineering, what does “yield” measure?
a) The amount of product per unit of substrate
b) The total biomass produced
c) The enzyme concentration
d) The reaction time
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Yield quantifies efficiency by comparing product output to input substrate, a key metric for process optimization.
19. Question: Which factor is critical for scaling up metabolic engineering processes?
a) Fermentation conditions and bioreactor design
b) Laboratory glassware only
c) Genetic sequencing alone
d) Manual cell counting
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: Scaling requires optimizing conditions like pH, temperature, and oxygen in bioreactors to maintain engineered pathway performance.
20. Question: How can metabolic engineering contribute to sustainable chemistry?
a) By producing chemicals from renewable resources
b) By increasing fossil fuel use
c) By polluting waterways
d) By ignoring environmental impacts
Correct Answer: a
Explanation: It enables the use of microbes to convert biomass into valuable chemicals, reducing reliance on non-renewable resources and minimizing waste.
or
Part 3: Try OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to Create Quiz Questions
Automatically generate questions using AI