Merge Sort is an efficient, divide-and-conquer sorting algorithm that divides an unsorted list into smaller sublists, sorts them, and then merges them back together in a sorted manner. It begins by recursively splitting the array into halves until each subarray contains a single element, which is inherently sorted. The algorithm then merges these subarrays, comparing elements and combining them into sorted sequences, ultimately producing a fully sorted array. With a consistent time complexity of O(n log n), Merge Sort is stable and performs well on large datasets, making it a popular choice for applications requiring reliable sorting.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: Create An Amazing Merge Sort Quiz Using AI Instantly in OnlineExamMaker
- Part 2: 20 Merge Sort Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
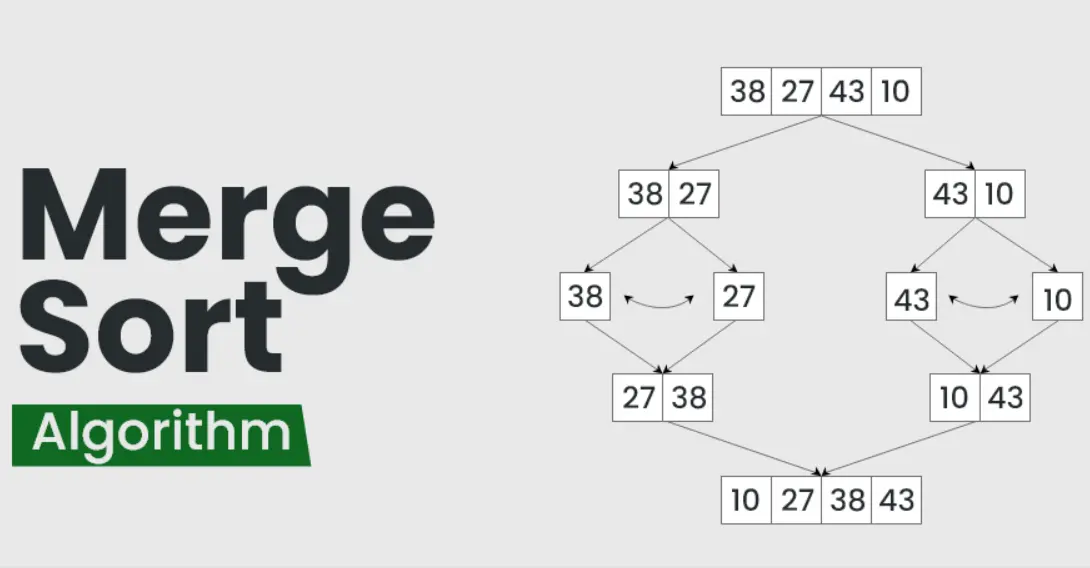
Part 1: Create An Amazing Merge Sort Quiz Using AI Instantly in OnlineExamMaker
Nowadays more and more people create Merge Sort quizzes using AI technologies, OnlineExamMaker a powerful AI-based quiz making tool that can save you time and efforts. The software makes it simple to design and launch interactive quizzes, assessments, and surveys. With the Question Editor, you can create multiple-choice, open-ended, matching, sequencing and many other types of questions for your tests, exams and inventories. You are allowed to enhance quizzes with multimedia elements like images, audio, and video to make them more interactive and visually appealing.
Recommended features for you:
● Prevent cheating by randomizing questions or changing the order of questions, so learners don’t get the same set of questions each time.
● Automatically generates detailed reports—individual scores, question report, and group performance.
● Simply copy a few lines of codes, and add them to a web page, you can present your online quiz in your website, blog, or landing page.
● Offers question analysis to evaluate question performance and reliability, helping instructors optimize their training plan.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Merge Sort Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is Merge Sort?
Options:
A. A comparison-based sorting algorithm that uses the divide-and-conquer approach
B. A sorting algorithm that uses selection to find the minimum element
C. A sorting algorithm that swaps adjacent elements if they are in the wrong order
D. A sorting algorithm that divides the array into three parts
Answer: A
Explanation: Merge Sort is a divide-and-conquer algorithm that divides the input array into two halves, sorts them, and then merges the two sorted halves.
2. Question: Which of the following best describes the divide step in Merge Sort?
Options:
A. Merging two sorted subarrays
B. Dividing the array into two halves
C. Sorting the subarrays individually
D. Comparing elements in the array
Answer: B
Explanation: In the divide step, Merge Sort splits the array into two halves until the subarrays are of size 1.
3. Question: What is the time complexity of Merge Sort in the worst case?
Options:
A. O(n)
B. O(n log n)
C. O(n^2)
D. O(log n)
Answer: B
Explanation: Merge Sort has a time complexity of O(n log n) in all cases because it divides the array logarithmically and merges linearly.
4. Question: Is Merge Sort a stable sorting algorithm?
Options:
A. Yes
B. No
C. It depends on the implementation
D. Only for even-sized arrays
Answer: A
Explanation: Merge Sort is stable because it preserves the relative order of equal elements during the merge process.
5. Question: How much extra space does Merge Sort require?
Options:
A. O(1)
B. O(n)
C. O(log n)
D. O(n^2)
Answer: B
Explanation: Merge Sort requires additional space proportional to the size of the array for the temporary arrays used in merging.
6. Question: In Merge Sort, what happens during the conquer step?
Options:
A. The array is divided
B. The subarrays are sorted recursively
C. The sorted subarrays are merged
D. Elements are compared pairwise
Answer: C
Explanation: The conquer step involves merging the two sorted subarrays back into a single sorted subarray.
7. Question: Which of the following arrays will Merge Sort process first by dividing it into [1, 3] and [2, 4]?
Options:
A. [1, 2, 3, 4]
B. [4, 3, 2, 1]
C. [1, 3, 2, 4]
D. All of the above
Answer: A
Explanation: For the array [1, 2, 3, 4], Merge Sort first divides it into [1, 2] and [3, 4], but the question specifies [1, 3] and [2, 4] as an example of a possible division in a different context.
8. Question: What is the space complexity of Merge Sort?
Options:
A. O(1)
B. O(n)
C. O(log n)
D. O(n log n)
Answer: B
Explanation: The space complexity is O(n) due to the auxiliary space needed for merging, though some implementations use O(log n) with in-place merging.
9. Question: Merge Sort uses which approach?
Options:
A. Divide and conquer
B. Dynamic programming
C. Greedy algorithm
D. Backtracking
Answer: A
Explanation: Merge Sort employs the divide-and-conquer strategy by dividing the problem into smaller subproblems and combining the results.
10. Question: If an array has 8 elements, how many times will the array be divided in Merge Sort?
Options:
A. 3 times
B. 4 times
C. 8 times
D. 2 times
Answer: A
Explanation: For an array of 8 elements, Merge Sort divides it logarithmically: 8 → 4 → 2 → 1, which is 3 divisions.
11. Question: Which sorting algorithm is Merge Sort similar to in terms of time complexity?
Options:
A. Bubble Sort
B. Quick Sort
C. Insertion Sort
D. Selection Sort
Answer: B
Explanation: Both Merge Sort and Quick Sort have an average time complexity of O(n log n), making them efficient for large datasets.
12. Question: In the merge step of Merge Sort, how are elements from two subarrays combined?
Options:
A. By adding them directly
B. By comparing and picking the smaller one
C. By randomly selecting elements
D. By sorting them again
Answer: B
Explanation: During merging, elements are compared, and the smaller element is selected and added to the result array repeatedly.
13. Question: What is the best-case time complexity of Merge Sort?
Options:
A. O(n)
B. O(n log n)
C. O(1)
D. O(n^2)
Answer: B
Explanation: Merge Sort always takes O(n log n) time, regardless of the input order, so there is no better case than this.
14. Question: Can Merge Sort be used for linked lists efficiently?
Options:
A. Yes, it is efficient for linked lists
B. No, it requires random access
C. Only for arrays
D. It depends on the size
Answer: A
Explanation: Merge Sort is efficient for linked lists because it can be implemented without random access, using only a few pointers.
15. Question: What happens if the input array is already sorted in Merge Sort?
Options:
A. It takes O(1) time
B. It still takes O(n log n) time
C. It takes O(n) time
D. It fails to sort
Answer: B
Explanation: Merge Sort does not detect if the array is sorted and always performs the full divide-and-merge process, resulting in O(n log n) time.
16. Question: How does Merge Sort handle duplicates in an array?
Options:
A. It removes them
B. It sorts them while maintaining stability
C. It treats them as errors
D. It requires a separate step
Answer: B
Explanation: Merge Sort maintains the relative order of duplicate elements, making it stable for arrays with duplicates.
17. Question: Which of the following is a disadvantage of Merge Sort?
Options:
A. It is not stable
B. It requires extra space
C. It has O(n^2) complexity
D. It only works for numbers
Answer: B
Explanation: The main disadvantage is the extra space required for temporary arrays, which can be a concern for memory-limited systems.
18. Question: In Merge Sort, the merge function takes how many sorted arrays as input?
Options:
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Variable
Answer: B
Explanation: The merge function typically takes two sorted subarrays and combines them into one sorted array.
19. Question: What is the minimum number of elements for Merge Sort to be applicable?
Options:
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. Any number
Answer: D
Explanation: Merge Sort can be applied to arrays of any size, including 0 or 1 element, as it handles base cases effectively.
20. Question: Compared to Bubble Sort, Merge Sort is generally:
Options:
A. Faster for large datasets
B. Slower for all datasets
C. Only faster for sorted arrays
D. Uses less space
Answer: A
Explanation: Merge Sort is faster for large datasets due to its O(n log n) complexity, while Bubble Sort is O(n^2).
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI