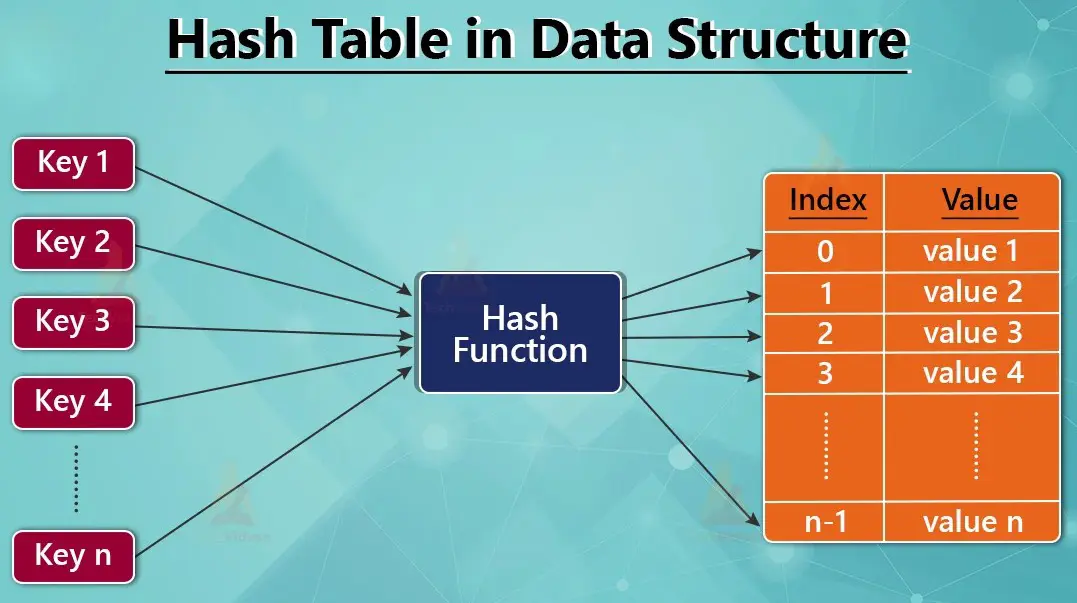
Hash-based structures are efficient data structures that utilize a hash function to map keys to values, enabling fast access, insertion, and deletion operations. In a hash table, for instance, the hash function computes an index in an array where the data is stored, allowing average-case O(1) time complexity for lookups. This makes them ideal for applications like databases, caches, and symbol tables, where quick retrieval is essential. However, they must address potential collisions—when two keys hash to the same index—through methods such as chaining, where collided items form a linked list, or open addressing, which probes for the next available slot. Overall, hash-based structures balance speed and space efficiency, making them a cornerstone of modern computing for handling large datasets.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Generator – Save Time and Efforts
- Part 2: 20 Hash-Based Structures Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Generator – Save Time and Efforts
What’s the best way to create a Hash-Based Structures quiz online? OnlineExamMaker is the best AI quiz making software for you. No coding, and no design skills required. If you don’t have the time to create your online quiz from scratch, you are able to use OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to create question automatically, then add them into your online assessment. What is more, the platform leverages AI proctoring and AI grading features to streamline the process while ensuring exam integrity.
Key features of OnlineExamMaker:
● Combines AI webcam monitoring to capture cheating activities during online exam.
● Allow the quiz taker to answer by uploading video or a Word document, adding an image, and recording an audio file.
● Automatically scores multiple-choice, true/false, and even open-ended/audio responses using AI, reducing manual work.
● OnlineExamMaker API offers private access for developers to extract your exam data back into your system automatically.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Hash-Based Structures Quiz Questions & Answers
or
Question 1:
What is the primary purpose of a hash function in a hash table?
A) To sort the elements in ascending order
B) To compute an index into an array of buckets
C) To encrypt data for security
D) To link elements in a chain
Answer: B
Explanation: A hash function takes a key and returns an index in the hash table array, allowing for fast access to data by mapping keys to array positions.
Question 2:
Which of the following is a common method for resolving hash collisions?
A) Binary search
B) Open addressing
C) Quick sort
D) Depth-first search
Answer: B
Explanation: Open addressing handles collisions by probing for the next available slot in the hash table when a collision occurs.
Question 3:
In a hash table, what does the load factor represent?
A) The total number of elements divided by the table size
B) The speed of the hash function
C) The memory usage of the entire program
D) The number of collisions per insertion
Answer: A
Explanation: The load factor is the ratio of the number of elements to the number of slots in the hash table, which influences performance and the need for resizing.
Question 4:
Which data structure is typically used in separate chaining for collision resolution?
A) Stack
B) Queue
C) Linked list
D) Binary tree
Answer: C
Explanation: Separate chaining uses a linked list (or another structure) at each hash table index to store multiple elements that hash to the same slot.
Question 5:
What happens when the load factor of a hash table exceeds a certain threshold?
A) The table is automatically deleted
B) Rehashing or resizing occurs to maintain efficiency
C) All elements are removed
D) The hash function is changed
Answer: B
Explanation: When the load factor is too high, the hash table may resize or rehash to reduce collisions and improve performance.
Question 6:
Which hashing technique uses linear probing for collision resolution?
A) Double hashing
B) Chaining
C) Open addressing
D) Perfect hashing
Answer: C
Explanation: Open addressing includes linear probing, where the algorithm searches linearly for the next open slot after a collision.
Question 7:
In a hash map, what is the key used for?
A) Storing the value directly
B) Mapping to a specific value in the table
C) Sorting the entries
D) Counting the number of elements
Answer: B
Explanation: In a hash map, the key is used by the hash function to determine the index where the associated value is stored.
Question 8:
What is a potential disadvantage of using a hash table?
A) It requires more memory than arrays
B) It does not handle duplicates well
C) Keys must be unique and collisions can degrade performance
D) It is slower for sequential access
Answer: C
Explanation: Hash tables require unique keys, and collisions can lead to longer search times, affecting overall efficiency.
Question 9:
Which of the following is an example of a good hash function property?
A) It should always produce the same output for different inputs
B) It should minimize collisions by distributing keys uniformly
C) It should use a lot of computation time
D) It should only work with strings
Answer: B
Explanation: A good hash function distributes keys evenly across the hash table to minimize collisions and ensure efficient operations.
Question 10:
What is the time complexity of a successful search in an average-case hash table?
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(log n)
D) O(n log n)
Answer: A
Explanation: In an average-case scenario with a good hash function and low load factor, hash table operations like search are constant time.
Question 11:
In quadratic probing, how does the algorithm probe for the next slot?
A) By adding a linear increment
B) By squaring the probe number and adding it to the index
C) By randomly selecting an index
D) By using a separate hash function
Answer: B
Explanation: Quadratic probing uses a quadratic function (e.g., i^2) to determine the next probe offset, helping to reduce clustering.
Question 12:
What is the main benefit of using a hash set?
A) It allows duplicate elements
B) It provides fast lookups for unique elements
C) It maintains elements in sorted order
D) It uses less memory than arrays
Answer: B
Explanation: A hash set stores unique elements and offers average O(1) time complexity for insertions, deletions, and lookups.
Question 13:
Which collision resolution technique is more memory-efficient in practice?
A) Chaining
B) Open addressing
C) Binary search
D) Heap sorting
Answer: B
Explanation: Open addressing stores elements directly in the table without additional structures, making it more memory-efficient than chaining.
Question 14:
What type of hash table uses a fixed size and does not resize?
A) Dynamic hash table
B) Static hash table
C) Extendible hash table
D) Linear hash table
Answer: B
Explanation: A static hash table has a fixed size, and if it becomes full, it may lead to more collisions without automatic resizing.
Question 15:
In double hashing, what is used to compute the probe sequence?
A) A single hash function
B) Two different hash functions
C) The key’s length
D) The table’s size only
Answer: B
Explanation: Double hashing uses two hash functions: one for the initial index and another to determine the increment for probing.
Question 16:
Why might a hash table experience clustering?
A) If the hash function is uniform
B) Due to primary clustering in linear probing
C) When keys are sorted
D) If the table is empty
Answer: B
Explanation: Primary clustering occurs in linear probing when colliding elements form clusters, leading to longer probe sequences.
Question 17:
What is a universal hash function?
A) A hash function that works for all data types
B) One that guarantees no collisions
C) A family of hash functions chosen randomly for better distribution
D) A function that hashes strings only
Answer: C
Explanation: A universal hash function is selected from a family of functions to minimize the probability of collisions across different inputs.
Question 18:
In a hash table with chaining, how are elements accessed?
A) By traversing the array linearly
B) By following pointers in the linked list at the hashed index
C) Using binary search on the keys
D) By sorting the chain first
Answer: B
Explanation: Elements at a hashed index are stored in a linked list, so access involves traversing that list to find the matching key.
Question 19:
What is the worst-case time complexity for operations in a hash table?
A) O(1)
B) O(log n)
C) O(n)
D) O(n^2)
Answer: C
Explanation: In the worst case, if all keys hash to the same index, operations like search or insert become linear time due to checking all elements.
Question 20:
Which application commonly uses hash tables?
A) Storing data in a database index
B) Implementing a priority queue
C) Performing graph traversals
D) Sorting algorithms
Answer: A
Explanation: Hash tables are widely used in database indexing for fast key-value lookups and retrieval of data.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI