The Google File System (GFS) is a scalable distributed file system designed by Google to manage large-scale data across commodity hardware. It was introduced in 2003 to address the challenges of storing and processing massive datasets for Google’s applications.
Key Features:
– Scalability: GFS is built to handle petabytes of data and thousands of servers, allowing seamless expansion as data grows.
– Fault Tolerance: It replicates data across multiple machines to ensure availability and reliability, even if hardware failures occur.
– High Performance: Optimized for large, streaming reads and writes, with features like append operations and chunk-based storage to support high-throughput workloads.
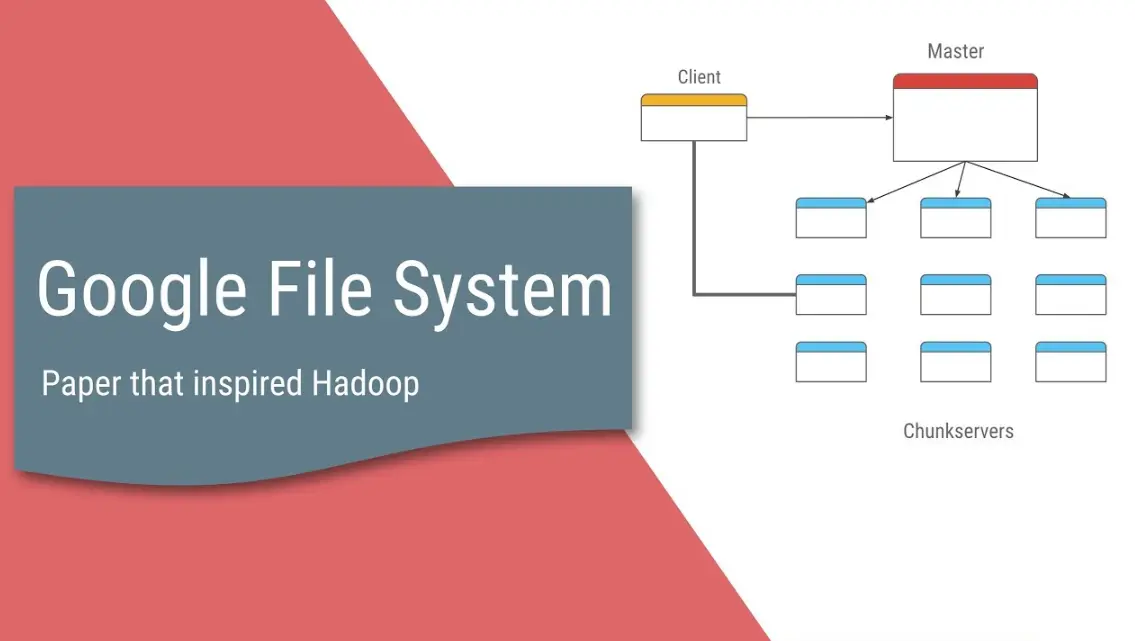
– Architecture: GFS uses a single master server to manage metadata and multiple chunk servers to store data in 64MB chunks. Clients interact directly with chunk servers for data access, reducing bottlenecks.
How It Works:
– Data Storage: Files are divided into fixed-size chunks (typically 64MB), and each chunk is replicated on three or more servers for redundancy.
– Metadata Management: The master server tracks file namespaces, chunk locations, and access control, while chunk servers handle the actual data storage.
– Consistency Model: GFS provides relaxed consistency guarantees, allowing for efficient writes and updates while maintaining data integrity through mechanisms like mutation ordering.
GFS served as the foundation for many big data technologies, influencing systems like Hadoop’s HDFS. It prioritizes throughput over low-latency access, making it ideal for batch processing and data-intensive applications.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: Create An Amazing Google File System Quiz Using AI Instantly in OnlineExamMaker
- Part 2: 20 Google File System Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: Try OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to Create Quiz Questions
Part 1: Create An Amazing Google File System Quiz Using AI Instantly in OnlineExamMaker
The quickest way to assess the Google File System knowledge of candidates is using an AI assessment platform like OnlineExamMaker. With OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, you are able to input content—like text, documents, or topics—and then automatically generate questions in various formats (multiple-choice, true/false, short answer). Its AI Exam Grader can automatically grade the exam and generate insightful reports after your candidate submit the assessment.
Overview of its key assessment-related features:
● Create up to 10 question types, including multiple-choice, true/false, fill-in-the-blank, matching, short answer, and essay questions.
● Automatically generates detailed reports—individual scores, question report, and group performance.
● Instantly scores objective questions and subjective answers use rubric-based scoring for consistency.
● API and SSO help trainers integrate OnlineExamMaker with Google Classroom, Microsoft Teams, CRM and more.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Google File System Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. What is the primary role of the Master in the Google File System?
A. To store user data directly
B. To manage the namespace and coordinate access to files
C. To handle all read operations from clients
D. To replicate chunks across servers
Answer: B
Explanation: The Master in GFS maintains the metadata, including the namespace and the locations of chunks, ensuring coordinated access and management of the file system.
2. How are files divided in the Google File System?
A. Into fixed-size blocks of 1KB
B. Into variable-size chunks managed by the client
C. Into fixed-size chunks typically 64MB
D. Into directories without chunking
Answer: C
Explanation: GFS divides files into chunks of a fixed size, usually 64MB, which are stored on chunk servers for efficient distribution and management.
3. What is the default replication factor for chunks in GFS?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 5
Answer: C
Explanation: GFS replicates each chunk three times by default across different chunk servers to ensure fault tolerance and data availability.
4. Which component in GFS handles the actual storage of file chunks?
A. The Master
B. The client
C. Chunk servers
D. The namespace manager
Answer: C
Explanation: Chunk servers store the actual data chunks and serve read and write requests from clients, while the Master oversees their management.
5. What type of consistency does GFS provide for mutations?
A. Strict consistency for all operations
B. Eventual consistency only
C. At-least-once consistency
D. Weak consistency with relaxed models for writes
Answer: D
Explanation: GFS uses a weak consistency model for mutations, allowing for efficient writes and appends while ensuring data integrity through mechanisms like leases.
6. How does GFS ensure fault tolerance?
A. By using a single central server
B. Through chunk replication and automatic recovery
C. By avoiding network failures entirely
D. By storing all data in memory
Answer: B
Explanation: GFS achieves fault tolerance by replicating chunks across multiple chunk servers and using the Master to monitor and re-replicate data as needed.
7. What is a lease in the context of GFS mutations?
A. A permanent lock on a file
B. A temporary exclusive lock granted by the Master
C. A replication agreement between servers
D. A client-side caching mechanism
Answer: B
Explanation: A lease is a temporary lock that the Master grants to a primary replica for a chunk, allowing it to coordinate mutations and ensure consistency.
8. Which operation in GFS is designed to append data atomically?
A. Regular write
B. Record append
C. Snapshot
D. Garbage collection
Answer: B
Explanation: Record append ensures that data is appended atomically and consistently across replicas, making it suitable for log-structured applications.
9. What happens when a chunk server fails in GFS?
A. The system shuts down
B. The Master re-replicates the chunks from other replicas
C. Clients are notified to stop operations
D. Data is lost permanently
Answer: B
Explanation: The Master detects chunk server failures and initiates re-replication of the affected chunks from available replicas to maintain the desired replication factor.
10. How does GFS handle large files efficiently?
A. By storing them as a single chunk
B. By splitting them into multiple chunks
C. By compressing them on the client side
D. By using external storage devices
Answer: B
Explanation: GFS splits large files into multiple chunks, allowing for parallel access and distribution across chunk servers for better performance.
11. What is the purpose of snapshots in GFS?
A. To delete old data
B. To create a copy of a file or directory at a point in time
C. To replicate data in real-time
D. To manage user access
Answer: B
Explanation: Snapshots allow users to create point-in-time copies of files or directories, enabling efficient versioning and backup without duplicating data immediately.
12. In GFS, who is responsible for choosing which chunk servers to use for a new chunk?
A. The client
B. The Master
C. The chunk servers themselves
D. A secondary coordinator
Answer: B
Explanation: The Master selects the chunk servers for storing new chunks based on factors like load balancing and proximity to maintain system efficiency.
13. What consistency level is guaranteed for reads in GFS after a mutation?
A. Always the latest version
B. At least one replica has the latest version
C. No consistency is guaranteed
D. Eventual consistency across all replicas
Answer: B
Explanation: GFS ensures that at least one replica has the latest version after a mutation, but reads might access stale data from other replicas depending on the configuration.
14. How does GFS manage metadata?
A. Stored entirely in memory on chunk servers
B. Kept in a centralized database
C. Maintained by the Master in memory and on disk
D. Distributed across all clients
Answer: C
Explanation: The Master keeps metadata in memory for fast access and periodically checkpoints it to disk to ensure persistence and recovery.
15. What is the main advantage of GFS over traditional file systems?
A. Smaller file support
B. High scalability for large-scale data
C. Faster single-server performance
D. Simplified single-user access
Answer: B
Explanation: GFS is designed for scalability, handling petabytes of data across thousands of servers, making it ideal for distributed, data-intensive applications.
16. In GFS, what mechanism is used to handle concurrent writes to the same chunk?
A. First-come, first-served
B. The Master serializes all writes
C. Leases to designate a primary writer
D. Random selection of writers
Answer: C
Explanation: Leases allow the Master to designate a primary replica for writes, ensuring that concurrent writes are serialized to maintain consistency.
17. What is garbage collection in GFS used for?
A. To remove unused chunks and reclaim space
B. To replicate data automatically
C. To handle user authentication
D. To optimize read operations
Answer: A
Explanation: Garbage collection in GFS identifies and deletes unreferenced chunks, freeing up storage space on chunk servers.
18. How do clients interact with GFS for file operations?
A. Directly with chunk servers only
B. Through the Master for all operations
C. By communicating with the Master for metadata and chunk servers for data
D. Via a separate proxy server
Answer: C
Explanation: Clients contact the Master to get metadata and chunk locations, then interact directly with chunk servers for reading or writing data.
19. What limitation does GFS have regarding small files?
A. It cannot store files smaller than 1MB
B. Overhead from chunking makes it inefficient for very small files
C. Small files are not replicated
D. Small files require special handling by the Master
Answer: B
Explanation: The fixed chunk size in GFS introduces overhead for small files, as each file still requires at least one chunk, making it less efficient for such cases.
20. Why is GFS designed with a single Master?
A. To simplify the architecture and reduce costs
B. To ensure all operations are processed sequentially
C. For better fault tolerance with multiple Masters
D. To handle all data storage directly
Answer: A
Explanation: A single Master simplifies metadata management and coordination, though it introduces a potential single point of failure mitigated by other mechanisms like backups.
or
Part 3: Try OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to Create Quiz Questions
Automatically generate questions using AI