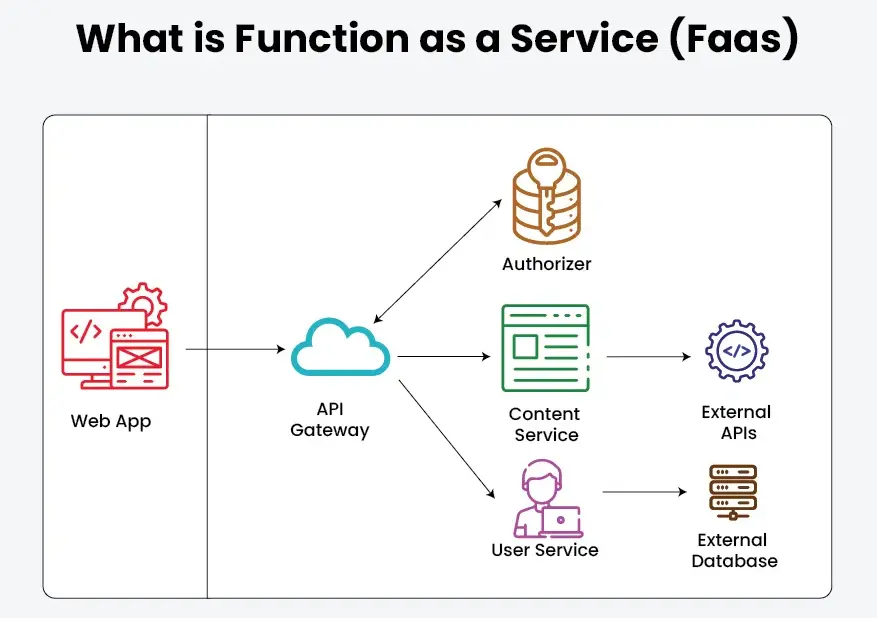
Function as a Service (FaaS) is a cloud computing model that enables developers to execute individual functions or pieces of code in response to events, without managing the underlying infrastructure. This serverless architecture allows for automatic scaling, where resources are allocated dynamically based on demand, and users only pay for the actual compute time used.
Key features of FaaS include:
– Event-driven execution: Functions are triggered by specific events, such as HTTP requests, database changes, or file uploads.
– Stateless operations: Each function invocation is independent, making it ideal for microservices and scalable applications.
– Automatic scaling: The platform handles load balancing and resource allocation, eliminating the need for manual server management.
– Rapid deployment: Developers can deploy code quickly, often in seconds, using lightweight containers or virtual environments.
Benefits of FaaS include cost efficiency, as it reduces operational overhead and optimizes resource usage; faster time-to-market for applications; and enhanced flexibility for building modular, event-based systems. It is particularly useful for scenarios like real-time data processing, API backends, automated workflows, and IoT applications.
Popular FaaS providers include AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, Azure Functions, and IBM Cloud Functions. As part of the broader serverless paradigm, FaaS is transforming how organizations develop and deploy applications, fostering innovation and efficiency in modern cloud environments.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and Share Function As A Service Quiz with AI Automatically
- Part 2: 20 Function As A Service Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: Try OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to Create Quiz Questions
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and Share Function As A Service Quiz with AI Automatically
OnlineExamMaker is a powerful AI-powered assessment platform to create auto-grading Function As A Service skills assessments. It’s designed for educators, trainers, businesses, and anyone looking to generate engaging quizzes without spending hours crafting questions manually. The AI Question Generator feature allows you to input a topic or specific details, and it generates a variety of question types automatically.
Top features for assessment organizers:
● Prevent cheating by randomizing questions or changing the order of questions, so learners don’t get the same set of questions each time.
● AI Exam Grader for efficiently grading quizzes and assignments, offering inline comments, automatic scoring, and “fudge points” for manual adjustments.
● Embed quizzes on websites, blogs, or share via email, social media (Facebook, Twitter), or direct links.
● Handles large-scale testing (thousands of exams/semester) without internet dependency, backed by cloud infrastructure.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Function As A Service Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is Function as a Service (FaaS)?
Options:
A) A cloud service where users manage their own servers and infrastructure.
B) A model that allows developers to execute code in response to events without managing servers.
C) A database service for storing functions.
D) A networking service for connecting applications.
Answer: B
Explanation: FaaS is a serverless computing model that enables developers to run individual functions in the cloud, automatically scaling and managing the underlying infrastructure, which reduces operational overhead.
2. Question: Which of the following is a key benefit of FaaS?
Options:
A) Full control over server hardware.
B) Automatic scaling based on demand.
C) Requirement for dedicated hardware purchases.
D) Manual code deployment for every function.
Answer: B
Explanation: FaaS automatically scales functions up or down based on incoming events or traffic, allowing for efficient resource use without manual intervention.
3. Question: How does FaaS differ from Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)?
Options:
A) IaaS provides virtual machines, while FaaS focuses on event-driven code execution.
B) FaaS requires managing operating systems, unlike IaaS.
C) Both are identical in terms of abstraction level.
D) IaaS is always more cost-effective than FaaS.
Answer: A
Explanation: IaaS offers virtual servers and infrastructure that users must manage, whereas FaaS abstracts away all infrastructure, allowing developers to focus solely on writing and deploying functions.
4. Question: What triggers a function in a FaaS environment?
Options:
A) Scheduled server reboots.
B) Events such as HTTP requests or database changes.
C) Manual user logins.
D) Hardware upgrades.
Answer: B
Explanation: FaaS functions are typically triggered by specific events like API calls, file uploads, or messages from queues, making it ideal for reactive applications.
5. Question: Which cloud provider offers a FaaS service named AWS Lambda?
Options:
A) Google Cloud.
B) Microsoft Azure.
C) Amazon Web Services.
D) IBM Cloud.
Answer: C
Explanation: AWS Lambda is Amazon’s FaaS offering, allowing users to run code without provisioning or managing servers, integrating seamlessly with other AWS services.
6. Question: What is a common challenge with FaaS known as “cold start”?
Options:
A) Overheating of servers during peak times.
B) Latency caused by initializing a function instance for the first time.
C) Excessive data storage requirements.
D) Network failures in distributed systems.
Answer: B
Explanation: Cold start refers to the delay in executing a function when it’s invoked for the first time after inactivity, as the environment must be set up, impacting performance in time-sensitive applications.
7. Question: In FaaS, who is responsible for managing the underlying servers?
Options:
A) The developer using the service.
B) The cloud provider.
C) Third-party vendors.
D) End-users of the application.
Answer: B
Explanation: FaaS shifts the responsibility of server management, including provisioning and scaling, to the cloud provider, allowing developers to focus on code.
8. Question: What pricing model is typically associated with FaaS?
Options:
A) Flat monthly fees regardless of usage.
B) Pay-per-use based on execution time and resources consumed.
C) Annual subscriptions only.
D) Free for all users.
Answer: B
Explanation: FaaS usually charges based on the actual number of function invocations and the compute resources used, making it cost-effective for variable workloads.
9. Question: Which of the following is NOT a typical use case for FaaS?
Options:
A) Real-time data processing.
B) Long-running batch jobs that take hours.
C) Webhook handlers for APIs.
D) Automated image resizing.
Answer: B
Explanation: FaaS is designed for short-lived, event-driven tasks, so it’s not ideal for long-running processes, which may exceed time limits and incur higher costs.
10. Question: How does FaaS promote microservices architecture?
Options:
A) By requiring monolithic applications.
B) By allowing individual functions to be developed and deployed independently.
C) By enforcing a single database for all services.
D) By limiting scalability options.
Answer: B
Explanation: FaaS enables the creation of small, independent functions that can be deployed separately, aligning with microservices principles for better modularity and scalability.
11. Question: What role do APIs play in FaaS?
Options:
A) They are not used in FaaS at all.
B) They serve as triggers or endpoints for functions.
C) They replace the need for functions entirely.
D) They only handle data storage.
Answer: B
Explanation: APIs often act as entry points or triggers for FaaS functions, allowing external systems to invoke and interact with them seamlessly.
12. Question: In FaaS, what happens to unused functions?
Options:
A) They are permanently deleted.
B) They are scaled down or terminated to save resources.
C) They continue running at full capacity.
D) They require manual shutdown.
Answer: B
Explanation: FaaS platforms automatically manage resources by spinning down idle functions, which helps in reducing costs and improving efficiency.
13. Question: Which programming languages are commonly supported in FaaS platforms?
Options:
A) Only low-level languages like C++.
B) A variety, including Python, Node.js, and Java.
C) Only assembly language.
D) Custom languages created by users.
Answer: B
Explanation: Most FaaS providers support multiple high-level languages like Python, Node.js, and Java to accommodate diverse development needs.
14. Question: What is vendor lock-in in the context of FaaS?
Options:
A) A feature that enhances portability.
B) Dependency on a specific provider’s ecosystem, making migration difficult.
C) A free service offered by vendors.
D) Automatic updates across all platforms.
Answer: B
Explanation: Vendor lock-in occurs when FaaS applications are tailored to a provider’s tools and services, complicating the process of switching to another provider.
15. Question: How does FaaS handle state management?
Options:
A) It maintains state within functions automatically.
B) Functions are stateless by design, requiring external services for state.
C) All state is stored locally on the user’s device.
D) State is managed through hardware connections.
Answer: B
Explanation: FaaS functions are typically stateless, meaning each invocation is independent, and persistent state must be handled via external databases or storage.
16. Question: What security measure is important in FaaS to protect functions?
Options:
A) Ignoring authentication for faster execution.
B) Implementing API keys and identity access management.
C) Leaving functions publicly accessible.
D) Disabling encryption.
Answer: B
Explanation: Proper security in FaaS involves using tools like API keys, IAM roles, and encryption to control access and protect sensitive data.
17. Question: Why is FaaS suitable for event-driven architectures?
Options:
A) It requires polling for events.
B) Functions can be triggered directly by events without constant servers.
C) It only supports scheduled tasks.
D) It demands pre-warmed servers.
Answer: B
Explanation: FaaS excels in event-driven setups by executing code only when events occur, eliminating the need for always-on infrastructure.
18. Question: What is the typical execution time limit for FaaS functions?
Options:
A) Unlimited, as long as needed.
B) Varies by provider, often a few minutes or less.
C) Exactly 24 hours.
D) Dependent on user hardware.
Answer: B
Explanation: Most FaaS platforms impose time limits (e.g., 15 minutes on AWS Lambda) to prevent abuse and ensure efficient resource allocation.
19. Question: How does FaaS integrate with other cloud services?
Options:
A) It cannot integrate with any other services.
B) Through event triggers, APIs, and direct service linkages.
C) Only via manual code edits.
D) By requiring a complete rewrite of services.
Answer: B
Explanation: FaaS functions can easily connect to other services like databases or storage via events and APIs, enhancing overall application ecosystems.
20. Question: What is a potential drawback of using FaaS for complex applications?
Options:
A) Overly high costs for simple tasks.
B) Difficulty in debugging and tracing function executions.
C) Excessive control over infrastructure.
D) Mandatory long-term commitments.
Answer: B
Explanation: In FaaS, the distributed and ephemeral nature of functions can make debugging and monitoring more challenging compared to traditional architectures.
or
Part 3: Try OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator to Create Quiz Questions
Automatically generate questions using AI