Excel Automation refers to the process of using scripting, macros, or external tools to automate repetitive tasks in Microsoft Excel, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and productivity.
Key Benefits:
– Time Savings: Automates routine operations like data entry, calculations, and formatting, allowing users to focus on analysis.
– Error Reduction: Minimizes human errors in large datasets by executing predefined steps consistently.
– Scalability: Handles complex tasks across multiple files or workbooks, ideal for businesses processing vast amounts of data.
– Integration: Seamlessly connects with other Microsoft tools, such as Power BI or Outlook, for advanced workflows.
Common Methods:
– VBA (Visual Basic for Applications): Built-in scripting language for creating macros. Example: Automate report generation by writing a script to filter and summarize data.
– Office Scripts: Cloud-based automation in Excel for Microsoft 365, using TypeScript for web-enabled tasks like data imports from APIs.
– Power Automate: No-code/low-code platform to trigger Excel actions based on events, such as sending emails when a spreadsheet updates.
– Add-ins and APIs: Third-party tools or Excel’s REST API for advanced integrations, like pulling real-time data from external sources.
Basic Steps to Get Started:
1. Identify Tasks: Pinpoint repetitive processes, such as updating formulas or generating charts.
2. Choose a Tool: Select based on complexity—VBA for desktop, Office Scripts for cloud.
3. Record or Write Code: Use Excel’s macro recorder for simple automations or write custom code in the Visual Basic Editor.
4. Test and Debug: Run the automation on sample data and troubleshoot errors.
5. Deploy and Schedule: Save macros in personal workbooks or set up triggers in Power Automate for automatic execution.
Best Practices:
– Security First: Enable macros only from trusted sources and use digital signatures to prevent malware.
– Modular Code: Write reusable scripts to avoid redundancy and ease maintenance.
– Documentation: Comment code thoroughly and maintain a log of changes for future reference.
– Performance Optimization: Avoid unnecessary loops in VBA to prevent slowdowns with large datasets.
– Backup Data: Always work on copies of files to safeguard original data during testing.
Excel Automation empowers users from beginners to experts, transforming static spreadsheets into dynamic, intelligent tools for data-driven decision-making.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: Best AI Quiz Making Software for Creating A Excel Automation Quiz
- Part 2: 20 Excel Automation Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate Questions for Any Topic
Part 1: Best AI Quiz Making Software for Creating A Excel Automation Quiz
Nowadays more and more people create Excel Automation quizzes using AI technologies, OnlineExamMaker a powerful AI-based quiz making tool that can save you time and efforts. The software makes it simple to design and launch interactive quizzes, assessments, and surveys. With the Question Editor, you can create multiple-choice, open-ended, matching, sequencing and many other types of questions for your tests, exams and inventories. You are allowed to enhance quizzes with multimedia elements like images, audio, and video to make them more interactive and visually appealing.
Take a product tour of OnlineExamMaker:
● Create a question pool through the question bank and specify how many questions you want to be randomly selected among these questions.
● Build and store questions in a centralized portal, tagged by categories and keywords for easy reuse and organization.
● Simply copy a few lines of codes, and add them to a web page, you can present your online quiz in your website, blog, or landing page.
● Randomize questions or change the order of questions to ensure exam takers don’t get the same set of questions each time.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Excel Automation Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. What is a macro in Excel?
A. A predefined function in Excel
B. A series of commands and functions that are stored and can be run to automate tasks
C. A type of chart
D. A formula for calculations
Answer: B
Explanation: A macro in Excel is a sequence of instructions that automates repetitive tasks, typically created using VBA to save time and reduce errors.
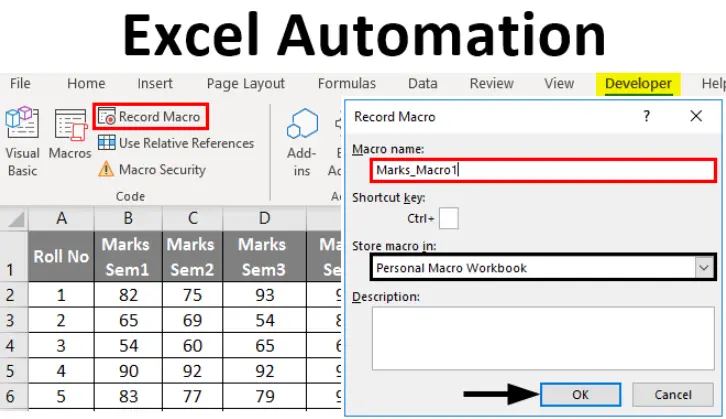
2. How do you start recording a macro in Excel?
A. Go to Insert > Macro
B. Go to View > Macros > Record Macro
C. Go to Developer > Record Macro
D. Go to File > Options > Macros
Answer: C
Explanation: In Excel, you access the macro recording feature through the Developer tab, which allows you to record actions for automation.
3. What programming language is primarily used for Excel automation?
A. Python
B. Java
C. Visual Basic for Applications (VBA)
D. C++
Answer: C
Explanation: VBA is the built-in language in Excel for creating macros and automating tasks, enabling users to write custom code.
4. Which of the following is NOT a type of reference used in Excel macros?
A. Absolute reference
B. Relative reference
C. Mixed reference
D. Dynamic reference
Answer: D
Explanation: Excel macros use absolute, relative, and mixed references, but “dynamic reference” is not a standard term; dynamics are handled through formulas or code.
5. What does the VBA command “Range(“A1″).Value = 10” do?
A. Selects cell A1
B. Sets the value of cell A1 to 10
C. Clears cell A1
D. Formats cell A1
Answer: B
Explanation: This VBA code directly assigns the value 10 to the cell in range A1, automating data entry.
6. How can you run a macro in Excel?
A. Only through the VBA editor
B. By assigning it to a button, keyboard shortcut, or via the Macro dialog box
C. By double-clicking the file
D. Through Excel’s Help menu
Answer: B
Explanation: Macros can be run in multiple ways for convenience, such as assigning them to form controls or using shortcuts, enhancing automation efficiency.
7. What is the purpose of the “Do Until” loop in VBA?
A. To repeat code until a condition is met
B. To execute code once
C. To skip code
D. To handle errors
Answer: A
Explanation: The “Do Until” loop in VBA continues executing code until a specified condition becomes true, useful for automating repetitive tasks.
8. Which event in VBA can trigger a macro when a workbook is opened?
A. Workbook_Open
B. Sheet_Activate
C. Button_Click
D. Macro_Run
Answer: A
Explanation: The Workbook_Open event automatically runs code when the workbook is opened, allowing for immediate automation upon startup.
9. What does the “Debug.Print” statement do in VBA?
A. Prints output to the Immediate window
B. Displays a message box
C. Saves the file
D. Deletes data
Answer: A
Explanation: Debug.Print outputs information to the Immediate window in the VBA editor, helping in debugging and testing automated scripts.
10. How do you declare a variable in VBA?
A. var x = 5
B. Dim x As Integer
C. Set x = 5
D. Define x As 5
Answer: B
Explanation: In VBA, variables are declared using the “Dim” statement followed by the variable name and data type, which is essential for structured automation.
11. What is the function of the “On Error GoTo” statement in VBA?
A. To handle errors by jumping to a specific line
B. To create a loop
C. To format cells
D. To insert data
Answer: A
Explanation: “On Error GoTo” directs the code to a labeled section when an error occurs, improving the robustness of automated processes.
12. Which of the following is a way to automate data import in Excel?
A. Using Power Query
B. Manually copying and pasting
C. Only through formulas
D. Via the Help menu
Answer: A
Explanation: Power Query is a tool in Excel that automates the import, transformation, and loading of data from various sources.
13. What does the VBA method “Worksheets(“Sheet1″).Activate” do?
A. Deletes Sheet1
B. Makes Sheet1 the active sheet
C. Renames Sheet1
D. Hides Sheet1
Answer: B
Explanation: This code activates the specified worksheet, allowing subsequent automation commands to target that sheet.
14. How can you protect VBA code from being viewed?
A. By locking the project and setting a password
B. By hiding the sheet
C. By encrypting the file
D. By deleting the code
Answer: A
Explanation: In the VBA editor, you can lock the project with a password to prevent unauthorized viewing, securing automated scripts.
15. What is the role of the “For Next” loop in VBA?
A. To iterate through a range of values
B. To run code once
C. To check conditions
D. To exit the program
Answer: A
Explanation: The “For Next” loop automates repetitive tasks by executing code a specific number of times, such as looping through cells.
16. Which Excel feature allows you to automate reports using dynamic data?
A. PivotTables
B. Simple formulas
C. Charts only
D. Conditional formatting
Answer: A
Explanation: PivotTables enable automated summarization and analysis of large datasets, making report generation more efficient.
17. What is the purpose of the “MsgBox” function in VBA?
A. To display a message to the user
B. To calculate values
C. To format cells
D. To save files
Answer: A
Explanation: MsgBox is used in VBA to show pop-up messages, which can be part of user-interactive automation workflows.
18. How do you automate sending emails from Excel?
A. Using VBA to interact with Outlook
B. Manually via the Send button
C. Through Excel’s email options
D. By exporting to Word
Answer: A
Explanation: VBA can automate email sending by integrating with Microsoft Outlook, allowing for scripted communication.
19. What does the “Application.ScreenUpdating = False” statement do in VBA?
A. Speeds up macro execution by hiding screen changes
B. Updates the screen immediately
C. Deletes the screen content
D. Formats the screen
Answer: A
Explanation: This statement turns off screen updates during code execution, making automation faster and more efficient.
20. Which of the following is a best practice for Excel automation?
A. Always use absolute references
B. Comment your code for clarity
C. Avoid using loops
D. Run macros without testing
Answer: B
Explanation: Commenting code in VBA improves readability and maintainability, which is crucial for effective and collaborative automation.
or
Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate Questions for Any Topic
Automatically generate questions using AI