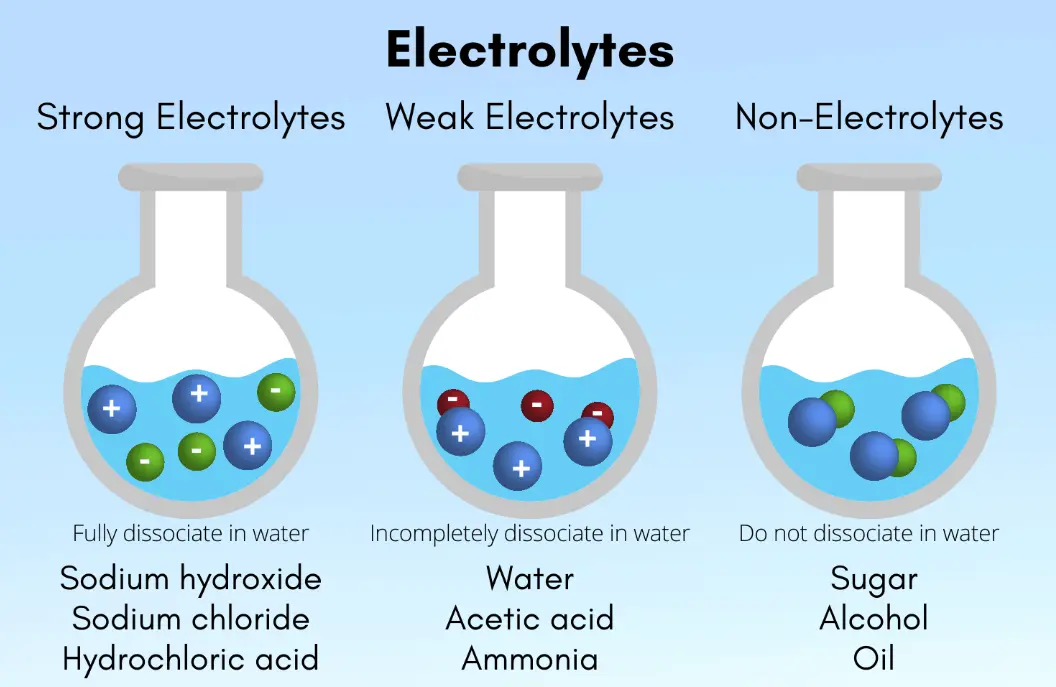
Electrolytes are essential minerals in the body that carry an electric charge when dissolved in fluids, playing a critical role in maintaining various physiological functions. They include sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, magnesium, phosphate, and bicarbonate, among others.
These substances help regulate fluid balance, nerve impulses, muscle contractions, and pH levels in the blood. For instance, sodium and chloride maintain hydration and blood pressure, while potassium supports heart rhythm and muscle function.
Imbalances in electrolytes can occur due to dehydration, illness, or poor diet, leading to symptoms like fatigue, cramps, or irregular heartbeats. Common sources include fruits, vegetables, dairy, and sports drinks, with daily intake varying based on age, activity level, and health needs.
To maintain optimal levels, monitor intake through a balanced diet, and consult a healthcare professional if imbalances are suspected. Regular testing via blood work can help identify issues early.
Table of contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and share electrolytes quiz with AI automatically
- Part 2: 20 electrolytes quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker – Generate and share electrolytes quiz with AI automatically
OnlineExamMaker is a powerful AI-powered assessment platform to create auto-grading electrolytes assessments. It’s designed for educators, trainers, businesses, and anyone looking to generate engaging quizzes without spending hours crafting questions manually. The AI Question Generator feature allows you to input a topic or specific details, and it generates a variety of question types automatically.
Top features for assessment organizers:
● Prevent cheating by randomizing questions or changing the order of questions, so learners don’t get the same set of questions each time.
● AI Exam Grader for efficiently grading quizzes and assignments, offering inline comments, automatic scoring, and “fudge points” for manual adjustments.
● Embed quizzes on websites, blogs, or share via email, social media (Facebook, Twitter), or direct links.
● Handles large-scale testing (thousands of exams/semester) without internet dependency, backed by cloud infrastructure.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 electrolytes quiz questions & answers
or
1. What is the primary role of sodium (Na+) in the human body?
A. Regulating blood pH
B. Maintaining fluid balance
C. Facilitating oxygen transport
D. Promoting bone health
Answer: B
Explanation: Sodium is the main electrolyte responsible for maintaining fluid balance inside and outside cells, as well as aiding in nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction.
2. Which electrolyte is most commonly associated with muscle contractions and heart rhythm?
A. Calcium (Ca2+)
B. Potassium (K+)
C. Magnesium (Mg2+)
D. Chloride (Cl-)
Answer: B
Explanation: Potassium plays a critical role in regulating muscle contractions, including the heart’s rhythm, by influencing electrical impulses in cells.
3. What happens to the body during hyperkalemia?
A. Low potassium levels leading to weakness
B. High potassium levels causing cardiac arrhythmias
C. Low sodium levels causing dehydration
D. High calcium levels causing bone pain
Answer: B
Explanation: Hyperkalemia, or elevated potassium levels, can disrupt normal heart function, potentially leading to arrhythmias and cardiac arrest.
4. Which electrolyte is essential for nerve signal transmission and is often lost through sweating?
A. Sodium (Na+)
B. Phosphate (PO43-)
C. Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
D. Iron (Fe2+)
Answer: A
Explanation: Sodium is crucial for generating nerve impulses and maintaining hydration, and it is commonly depleted during physical activity due to sweat.
5. What is a common symptom of hypocalcemia?
A. Muscle cramps and spasms
B. High blood pressure
C. Excessive urination
D. Weight gain
Answer: A
Explanation: Hypocalcemia, or low calcium levels, can lead to neuromuscular irritability, resulting in symptoms like muscle cramps, spasms, and tingling sensations.
6. Which electrolyte helps buffer acids in the blood to maintain pH balance?
A. Chloride (Cl-)
B. Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
C. Sodium (Na+)
D. Potassium (K+)
Answer: B
Explanation: Bicarbonate acts as a base in the blood, helping to neutralize acids and maintain the body’s pH within a narrow range.
7. What condition results from severe magnesium deficiency?
A. Osteoporosis
B. Arrhythmias and muscle weakness
C. Dehydration
D. Anemia
Answer: B
Explanation: Magnesium deficiency can cause neuromuscular issues, including arrhythmias, muscle weakness, and cramps, due to its role in enzyme function and nerve signaling.
8. Which electrolyte imbalance is linked to edema (swelling due to fluid retention)?
A. Hyponatremia
B. Hypernatremia
C. Hypokalemia
D. Hypercalcemia
Answer: A
Explanation: Hyponatremia, or low sodium levels, can lead to water retention in cells, causing edema, as the body tries to dilute the low sodium concentration.
9. What is the main function of phosphate (PO43-) in the body?
A. Energy storage and bone formation
B. Fluid regulation
C. Blood clotting
D. Hormone production
Answer: A
Explanation: Phosphate is vital for forming bones and teeth, as well as storing and transferring energy in cells through compounds like ATP.
10. Which electrolyte is primarily responsible for maintaining osmotic pressure in blood vessels?
A. Chloride (Cl-)
B. Sodium (Na+)
C. Calcium (Ca2+)
D. Magnesium (Mg2+)
Answer: B
Explanation: Sodium helps regulate osmotic pressure, which controls the movement of water in and out of cells and blood vessels.
11. What are the risks of hypernatremia?
A. Confusion and seizures
B. Muscle paralysis
C. Bone fractures
D. Anemia
Answer: A
Explanation: Hypernatremia, or high sodium levels, can cause dehydration of cells, leading to neurological symptoms like confusion, irritability, and seizures.
12. Which electrolyte is involved in blood clotting and enzyme activation?
A. Calcium (Ca2+)
B. Potassium (K+)
C. Sodium (Na+)
D. Chloride (Cl-)
Answer: A
Explanation: Calcium is essential for blood clotting processes, muscle function, and activating various enzymes in the body.
13. What symptom is commonly associated with hypokalemia?
A. Fatigue and arrhythmias
B. Hypertension
C. Diarrhea
D. Fever
Answer: A
Explanation: Hypokalemia, or low potassium, often results in fatigue, muscle weakness, and heart arrhythmias due to impaired cellular function.
14. Which pair of electrolytes works together to maintain acid-base balance?
A. Sodium and chloride
B. Potassium and magnesium
C. Bicarbonate and chloride
D. Calcium and phosphate
Answer: C
Explanation: Bicarbonate and chloride help regulate acid-base balance through processes like the chloride shift in red blood cells.
15. What is a key role of chloride (Cl-) in the body?
A. Producing stomach acid
B. Building muscle tissue
C. Synthesizing proteins
D. Storing energy
Answer: A
Explanation: Chloride is a major component of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, aiding digestion, and it also helps maintain fluid and electrolyte balance.
16. Which electrolyte deficiency can lead to rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown)?
A. Magnesium (Mg2+)
B. Phosphate (PO43-)
C. Sodium (Na+)
D. Potassium (K+)
Answer: B
Explanation: Phosphate deficiency can cause muscle weakness and breakdown, as it is necessary for energy production and cell membrane integrity.
17. What is the effect of excessive bicarbonate in the blood?
A. Metabolic alkalosis
B. Metabolic acidosis
C. Respiratory distress
D. Hypovolemia
Answer: A
Explanation: High bicarbonate levels can lead to metabolic alkalosis, where the blood becomes too alkaline, affecting organ function.
18. Which electrolyte is crucial for ATP production and DNA synthesis?
A. Magnesium (Mg2+)
B. Calcium (Ca2+)
C. Sodium (Na+)
D. Potassium (K+)
Answer: A
Explanation: Magnesium is a cofactor for enzymes involved in ATP production, DNA synthesis, and over 300 biochemical reactions.
19. What condition might arise from an imbalance of sodium and water?
A. Dehydration or overhydration
B. Bone density loss
C. Liver failure
D. Skin disorders
Answer: A
Explanation: Imbalances in sodium levels can lead to dehydration (high sodium) or overhydration (low sodium), affecting overall fluid balance.
20. Which electrolyte is often monitored in patients with kidney disease?
A. Potassium (K+)
B. Iron (Fe2+)
C. Vitamin D
D. Glucose
Answer: A
Explanation: Potassium levels are closely monitored in kidney disease because the kidneys regulate its excretion, and imbalances can lead to serious cardiac issues.
or
Part 3: Save time and energy: generate quiz questions with AI technology
Automatically generate questions using AI