El Niño is a climate phenomenon characterized by the periodic warming of the ocean surface in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific, which disrupts normal weather patterns worldwide. It typically occurs every 2 to 7 years and is part of a larger climate cycle known as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), which includes its counterpart, La Niña.
Causes
El Niño develops when trade winds in the Pacific weaken or reverse, allowing warm water from the western Pacific to flow eastward. This process is influenced by atmospheric pressure differences between the eastern and western Pacific, often triggered by oceanic and atmospheric interactions.
Effects
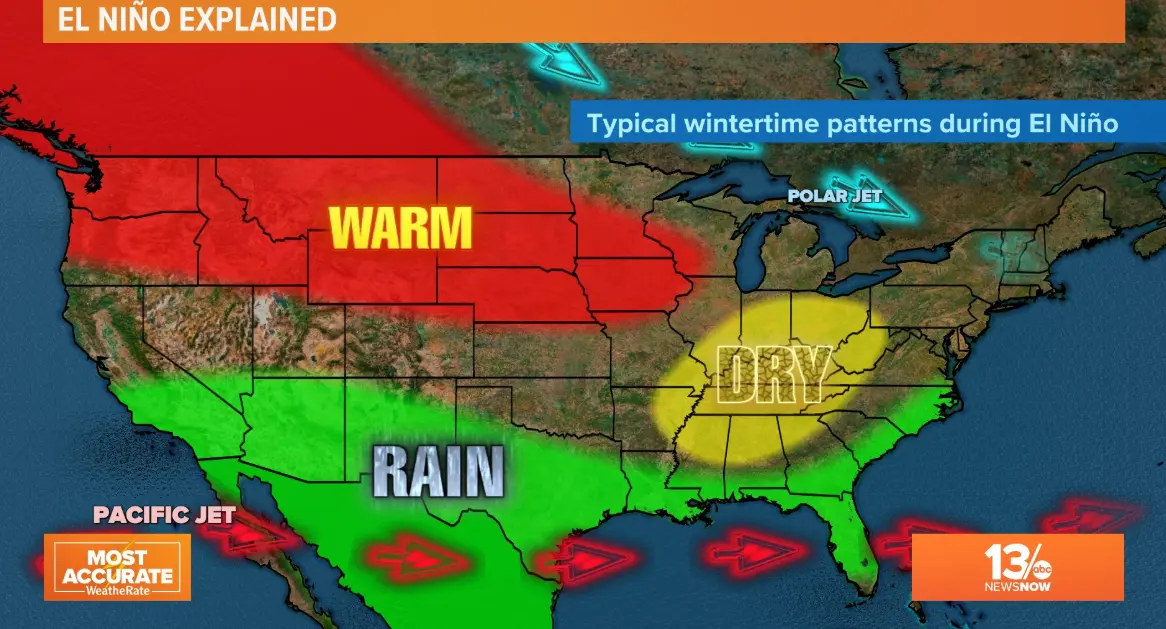
The warming disrupts global weather systems, leading to:
– Drier conditions in parts of Australia, Indonesia, and the southern United States.
– Increased rainfall in the western Americas, including flooding in Peru and Ecuador.
– Warmer temperatures globally, which can exacerbate droughts, wildfires, and coral bleaching in tropical regions.
– Economic impacts, such as reduced agricultural yields in affected areas and changes in fisheries due to altered ocean currents.
Historical Context
First recognized in the 19th century by Peruvian fishermen, El Niño has been linked to major weather events, such as the 1997-98 event, one of the strongest on record, which caused billions in damages. Scientists monitor it using tools like sea surface temperature data and satellite observations from organizations like NOAA and the World Meteorological Organization.
Monitoring and Prediction
El Niño is tracked through indices like the Oceanic Niño Index (ONI), which measures sea surface temperatures. Early predictions help mitigate impacts through preparedness measures, such as water resource management and disaster planning.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Best AI quiz making software for creating a El Niño quiz
- Part 2: 20 El Niño quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically create questions for your next assessment
Part 1: Best AI quiz making software for creating a El Niño quiz
Nowadays more and more people create El Niño quizzes using AI technologies, OnlineExamMaker a powerful AI-based quiz making tool that can save you time and efforts. The software makes it simple to design and launch interactive quizzes, assessments, and surveys. With the Question Editor, you can create multiple-choice, open-ended, matching, sequencing and many other types of questions for your tests, exams and inventories. You are allowed to enhance quizzes with multimedia elements like images, audio, and video to make them more interactive and visually appealing.
Take a product tour of OnlineExamMaker:
● Create a question pool through the question bank and specify how many questions you want to be randomly selected among these questions.
● Build and store questions in a centralized portal, tagged by categories and keywords for easy reuse and organization.
● Simply copy a few lines of codes, and add them to a web page, you can present your online quiz in your website, blog, or landing page.
● Randomize questions or change the order of questions to ensure exam takers don’t get the same set of questions each time.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 El Niño quiz questions & answers
or
1. Question: What is El Niño?
Options:
A) A cooling of ocean waters in the Pacific.
B) A warming of ocean waters in the central and eastern Pacific.
C) A storm system in the Atlantic Ocean.
D) A type of volcanic eruption.
Answer: B
Explanation: El Niño is a climate pattern involving the warming of the surface waters of the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean, which affects global weather.
2. Question: Which region is most directly affected by El Niño?
Options:
A) The Indian Ocean.
B) The Atlantic Ocean.
C) The Pacific Ocean.
D) The Arctic Ocean.
Answer: C
Explanation: El Niño originates in the Pacific Ocean, where warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures disrupt normal weather patterns.
3. Question: How does El Niño typically impact rainfall in Indonesia?
Options:
A) Increases it significantly.
B) Has no effect.
C) Decreases it, leading to droughts.
D) Causes extreme flooding.
Answer: C
Explanation: El Niño often shifts weather patterns, reducing rainfall in Indonesia and Southeast Asia, which can result in droughts.
4. Question: What is the Southern Oscillation associated with El Niño?
Options:
A) Changes in atmospheric pressure between the eastern and western Pacific.
B) Ocean currents in the Atlantic.
C) Temperature changes in the Arctic.
D) Wind patterns in the Indian Ocean.
Answer: A
Explanation: The Southern Oscillation is the atmospheric component of El Niño, involving pressure differences that influence global climate.
5. Question: Which of the following is a common effect of El Niño on the United States?
Options:
A) Increased snowfall in the Midwest.
B) Wetter conditions in the southern states.
C) Drought in the northern states.
D) Cooler temperatures nationwide.
Answer: B
Explanation: El Niño often brings increased precipitation to the southern U.S., while it can cause drier conditions in the northern areas.
6. Question: How often does El Niño typically occur?
Options:
A) Every 5-7 years.
B) Every year.
C) Every 20-30 years.
D) Every 2-3 years.
Answer: A
Explanation: El Niño events generally occur every 2 to 7 years, with an average cycle of about 3-5 years, though the exact timing varies.
7. Question: What role do trade winds play in El Niño?
Options:
A) They strengthen during El Niño.
B) They weaken or reverse, allowing warm water to move eastward.
C) They have no effect on El Niño.
D) They cause cooling in the Pacific.
Answer: B
Explanation: Normally, trade winds push warm water westward; during El Niño, these winds weaken, enabling warm water to spread eastward.
8. Question: Which organization monitors El Niño events?
Options:
A) NASA.
B) The World Health Organization.
C) The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
D) The United Nations.
Answer: C
Explanation: NOAA, along with other agencies, tracks El Niño through buoys and satellites to predict its impacts.
9. Question: How does El Niño affect marine life in the eastern Pacific?
Options:
A) It increases fish populations.
B) It has no significant impact.
C) It disrupts food chains by warming waters and reducing nutrients.
D) It cools waters, benefiting certain species.
Answer: C
Explanation: Warmer waters during El Niño reduce upwelling of nutrients, leading to declines in fish populations and affecting marine ecosystems.
10. Question: What is the difference between El Niño and La Niña?
Options:
A) El Niño is warmer, while La Niña is cooler.
B) They are the same phenomenon.
C) El Niño occurs in the Atlantic.
D) La Niña strengthens trade winds.
Answer: A
Explanation: El Niño involves warming of Pacific waters, whereas La Niña involves cooling, leading to opposite weather effects.
11. Question: Which year had one of the strongest El Niño events on record?
Options:
A) 1997-1998.
B) 1980.
C) 2005.
D) 2010.
Answer: A
Explanation: The 1997-1998 El Niño was one of the most intense, causing widespread global weather extremes.
12. Question: How does El Niño influence global temperatures?
Options:
A) It cools the planet.
B) It has no effect on temperatures.
C) It generally leads to warmer global temperatures.
D) It only affects ocean temperatures.
Answer: C
Explanation: El Niño releases stored heat from the ocean, contributing to higher global average temperatures during events.
13. Question: What is the ENSO cycle?
Options:
A) A cycle of earthquakes in the Pacific.
B) The El Niño-Southern Oscillation, including El Niño and La Niña.
C) A pattern of Atlantic hurricanes.
D) Seasonal changes in the Arctic.
Answer: B
Explanation: ENSO refers to the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, a cycle that includes both El Niño and La Niña phases.
14. Question: How does El Niño impact agriculture in Australia?
Options:
A) It improves crop yields with more rain.
B) It causes droughts and reduces yields.
C) It has no agricultural effects.
D) It leads to flooding in farming areas.
Answer: B
Explanation: El Niño often brings drier conditions to Australia, resulting in reduced rainfall and challenges for agriculture.
15. Question: What measurement is used to identify El Niño?
Options:
A) Sea surface temperature anomalies.
B) Atmospheric CO2 levels.
C) Wind speed in the Atlantic.
D) Ocean depth variations.
Answer: A
Explanation: El Niño is identified by sea surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific being at least 0.5°C warmer than average for several months.
16. Question: Which country is particularly vulnerable to El Niño-induced flooding?
Options:
A) Canada.
B) Peru.
C) Russia.
D) Saudi Arabia.
Answer: B
Explanation: Peru often experiences heavy rainfall and flooding during El Niño due to the warming of eastern Pacific waters.
17. Question: How does El Niño affect the jet stream?
Options:
A) It strengthens it globally.
B) It shifts it southward over North America.
C) It has no impact on the jet stream.
D) It eliminates it temporarily.
Answer: B
Explanation: El Niño can alter the jet stream’s position, leading to changes in weather patterns, such as milder winters in some regions.
18. Question: What economic impacts can El Niño cause?
Options:
A) Only positive effects on fishing.
B) Disruptions to agriculture, fisheries, and increased disaster costs.
C) No economic effects.
D) Boosts in global trade.
Answer: B
Explanation: El Niño can lead to crop failures, fishery declines, and higher costs from weather-related disasters, affecting economies worldwide.
19. Question: How is El Niño predicted?
Options:
A) Using computer models and ocean monitoring.
B) By observing lunar cycles.
C) Through satellite images alone.
D) By tracking bird migrations.
Answer: A
Explanation: Scientists use computer models, buoys, and satellite data to forecast El Niño events months in advance.
20. Question: What is a long-term effect of frequent El Niño events?
Options:
A) Permanent cooling of oceans.
B) Changes in global climate patterns and potential links to climate change.
C) Increased volcanic activity.
D) Stable weather worldwide.
Answer: B
Explanation: Repeated El Niño events can contribute to shifts in long-term climate trends, exacerbating issues like global warming.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically create questions for your next assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI