Data structures are specialized formats for organizing and storing data in a computer to enable efficient access and modification. They are fundamental in computer science and programming, as they impact the performance and scalability of algorithms.
Key Types of Data Structures
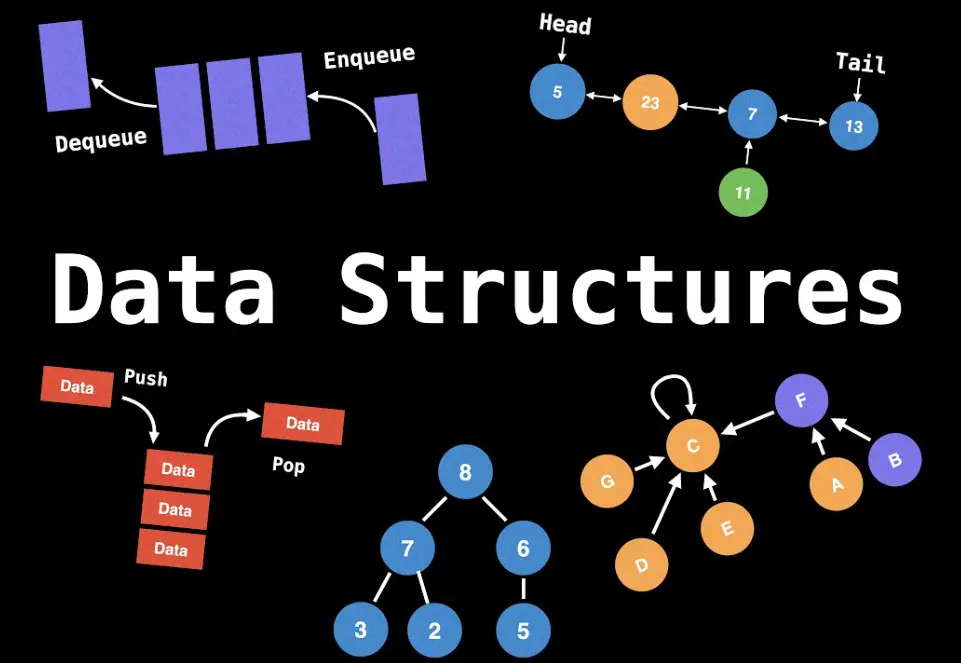
1. Arrays: A collection of elements of the same type stored in contiguous memory locations. They allow fast access via indices but have fixed sizes in some languages.
2. Linked Lists: A sequence of nodes where each node contains data and a reference to the next node (or previous in doubly linked lists). They are dynamic and efficient for insertions and deletions but slower for access.
3. Stacks: A Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) structure that operates like a stack of plates. Common operations include push (add) and pop (remove). Used in function calls and undo mechanisms.
4. Queues: A First-In-First-Out (FIFO) structure, like a line of people. Operations include enqueue (add) and dequeue (remove). Useful in scheduling and buffering.
5. Trees: A hierarchical structure with a root node and child nodes. Binary trees, for example, have at most two children per node. Variants include binary search trees (BST) for efficient searching and AVL trees for balanced operations.
6. Graphs: A collection of nodes connected by edges, representing networks. Types include directed, undirected, weighted, and unweighted graphs. Used in social networks, routing, and pathfinding algorithms like Dijkstra’s.
7. Hash Tables: Structures that use a hash function to map keys to values for fast retrieval. They handle collisions and are ideal for dictionaries and caches, though they can have variable performance based on load factors.
Importance and Applications
Data structures optimize memory usage and processing speed, making them essential for tasks like sorting, searching, and data management. For instance:
– Arrays and lists are used in arrays-based algorithms.
– Trees and graphs power database indexing and network analysis.
– Choosing the right structure depends on operations like insertion, deletion, and traversal.
In summary, understanding data structures helps in designing efficient software systems, from simple applications to complex systems like operating systems and databases.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Generator – Save Time and Efforts
- Part 2: 20 Data Structures Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate Questions for Any Topic
Part 1: OnlineExamMaker AI Quiz Generator – Save Time and Efforts
Still spend a lot of time in editing questions for your next Data Structures assessment? OnlineExamMaker is an AI quiz maker that leverages artificial intelligence to help users create quizzes, tests, and assessments quickly and efficiently. You can start by inputting a topic or specific details into the OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, and the AI will generate a set of questions almost instantly. It also offers the option to include answer explanations, which can be short or detailed, helping learners understand their mistakes.
What you may like:
● Automatic grading and insightful reports. Real-time results and interactive feedback for quiz-takers.
● The exams are automatically graded with the results instantly, so that teachers can save time and effort in grading.
● LockDown Browser to restrict browser activity during quizzes to prevent students searching answers on search engines or other software.
● OnlineExamMaker API offers private access for developers to extract your exam data back into your system automatically.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Data Structures Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is the primary characteristic of a stack data structure?
A) First In, First Out (FIFO)
B) Last In, First Out (LIFO)
C) Random access
D) Sorted order
Answer: B
Explanation: A stack operates on the LIFO principle, meaning the last element added is the first one to be removed, similar to a stack of plates.
2. Question: Which data structure uses the First In, First Out (FIFO) principle?
A) Stack
B) Queue
C) Array
D) Linked List
Answer: B
Explanation: A queue adds elements at one end (rear) and removes them from the other end (front), following FIFO, like a line of people.
3. Question: What is the main advantage of a linked list over an array?
A) Faster random access
B) Dynamic size adjustment
C) Better cache performance
D) Fixed memory allocation
Answer: B
Explanation: Linked lists can grow or shrink as needed during runtime, unlike arrays which require a fixed size to be declared in advance.
4. Question: In a singly linked list, how many links does each node have?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
Answer: B
Explanation: Each node in a singly linked list contains data and a single pointer to the next node, allowing traversal in one direction.
5. Question: What operation is performed by the pop() function in a stack?
A) Adds an element
B) Removes the top element
C) Searches for an element
D) Sorts the elements
Answer: B
Explanation: The pop() operation removes and returns the topmost element from the stack, adhering to the LIFO principle.
6. Question: Which of the following is a self-balancing binary search tree?
A) Binary Tree
B) AVL Tree
C) Linked List
D) Hash Table
Answer: B
Explanation: An AVL Tree maintains balance by ensuring that the height difference of child subtrees for any node is at most one, keeping search operations efficient.
7. Question: In a binary search tree, where is a new value inserted?
A) At the root
B) At the leftmost leaf
C) In a position that maintains the BST property
D) At the rightmost leaf
Answer: C
Explanation: A new value is inserted by traversing the tree and placing it in a leaf node where it fits the BST rule: left subtree values less than the node, right greater.
8. Question: What is the time complexity of accessing an element in an array by index?
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(log n)
D) O(n log n)
Answer: A
Explanation: Array elements are stored in contiguous memory, allowing direct access by index in constant time.
9. Question: Which traversal method visits nodes level by level in a binary tree?
A) Inorder
B) Preorder
C) Postorder
D) Level Order
Answer: D
Explanation: Level Order traversal uses a queue to visit nodes from left to right, level by level, starting from the root.
10. Question: What is a hash table primarily used for?
A) Storing hierarchical data
B) Fast insertion and lookup
C) Sorting elements
D) Graph representation
Answer: B
Explanation: Hash tables use a hash function to map keys to values, enabling average-case O(1) time complexity for insertions and lookups.
11. Question: In a doubly linked list, what does each node contain?
A) Data and one pointer
B) Data and two pointers
C) Only data
D) Data and an array
Answer: B
Explanation: Each node in a doubly linked list has data, a pointer to the next node, and a pointer to the previous node, allowing bidirectional traversal.
12. Question: Which data structure is best for implementing a priority queue?
A) Stack
B) Heap
C) Array
D) Queue
Answer: B
Explanation: A heap, particularly a min-heap or max-heap, efficiently maintains elements based on priority, making it ideal for priority queues.
13. Question: What is the worst-case time complexity for inserting an element into a sorted array?
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(log n)
D) O(n^2)
Answer: B
Explanation: Inserting into a sorted array requires shifting elements, which takes O(n) time in the worst case due to the linear search and shift.
14. Question: In graph theory, what does a cycle represent?
A) A path that starts and ends at the same vertex
B) A straight line between nodes
C) A tree structure
D) A disconnected graph
Answer: A
Explanation: A cycle in a graph is a path that begins and ends at the same vertex, forming a loop without repeating edges except the starting one.
15. Question: Which sorting algorithm is commonly used with heaps?
A) Bubble Sort
B) Heap Sort
C) Quick Sort
D) Merge Sort
Answer: B
Explanation: Heap Sort uses a binary heap to sort elements by building a max heap and then extracting elements one by one.
16. Question: What is the purpose of a sentinel node in a linked list?
A) To mark the end of the list
B) To store data
C) To speed up insertions
D) To simplify boundary condition checks
Answer: D
Explanation: A sentinel node acts as a dummy node at the head or tail, reducing the need for special cases when adding or removing nodes.
17. Question: In a binary tree, what is the maximum number of nodes at level k?
A) 2^k
B) k^2
C) 2^(k-1)
D) k
Answer: A
Explanation: A binary tree can have up to 2^k nodes at level k, as each level doubles the number of possible nodes from the previous level.
18. Question: Which collision resolution technique in hash tables uses a secondary data structure?
A) Linear Probing
B) Chaining
C) Quadratic Probing
D) Double Hashing
Answer: B
Explanation: Chaining resolves collisions by maintaining a linked list at each hash table index to store multiple elements that hash to the same slot.
19. Question: What is the difference between a stack and a queue?
A) Stack uses FIFO, queue uses LIFO
B) Stack uses LIFO, queue uses FIFO
C) Both use FIFO
D) Both use LIFO
Answer: B
Explanation: A stack follows LIFO, while a queue follows FIFO, making them suitable for different applications like function calls versus task scheduling.
20. Question: Which data structure is represented using adjacency lists or matrices?
A) Stack
B) Queue
C) Graph
D) Tree
Answer: C
Explanation: Graphs are commonly represented using adjacency lists or matrices to store connections between vertices efficiently.
or
Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate Questions for Any Topic
Automatically generate questions using AI