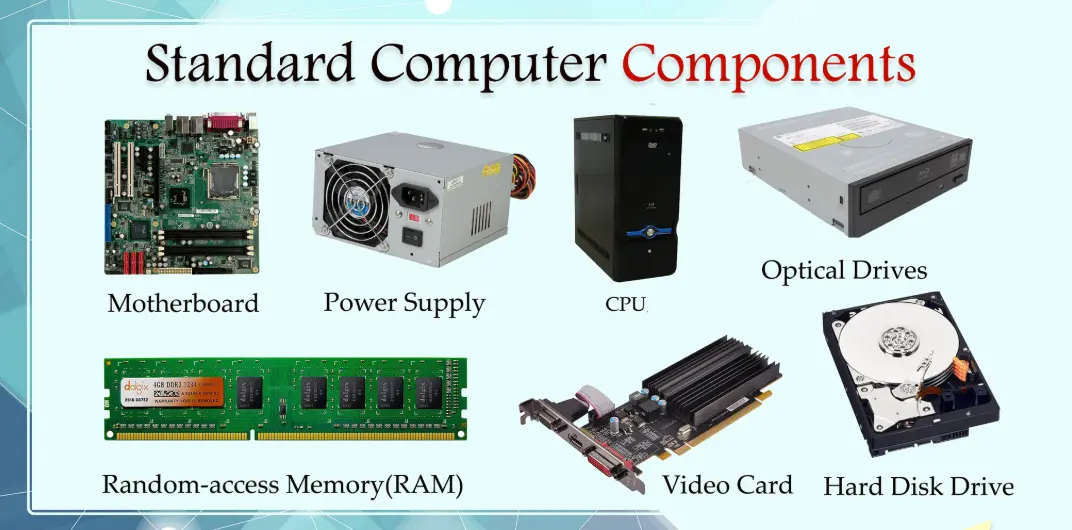
A computer is composed of several key hardware components that work together to process data and perform tasks.
– Central Processing Unit (CPU): Often called the brain of the computer, the CPU executes instructions from programs by performing calculations and managing data flow. It consists of cores, clock speed, and cache memory, which determine its performance.
– Random Access Memory (RAM): This is the temporary storage that holds data and instructions currently in use. RAM allows for quick access and multitasking, with capacity measured in gigabytes (GB). More RAM improves system speed but loses data when powered off.
– Motherboard: The main circuit board that connects all components. It houses the CPU, RAM slots, expansion ports, and other essential connectors, facilitating communication between hardware parts.
– Storage Devices: These include hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). HDDs use spinning disks for long-term data storage, while SSDs use flash memory for faster access. Storage capacity ranges from hundreds of gigabytes to terabytes.
– Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Specialized for rendering images, videos, and graphics-intensive tasks. Integrated GPUs are built into the CPU, while dedicated GPUs (e.g., from NVIDIA or AMD) handle complex computations for gaming and design.
– Power Supply Unit (PSU): Converts AC power from the outlet to DC power for the computer’s components. It must provide sufficient wattage and include safety features like overvoltage protection.
– Input and Output Devices: These include keyboards, mice, monitors, and printers. They allow users to interact with the computer—input devices send data in, while output devices display or produce results.
– Cooling System: Comprises fans, heatsinks, and liquid cooling to prevent overheating. Effective cooling ensures components operate efficiently and have a longer lifespan.
Understanding these components helps in building, upgrading, or troubleshooting a computer system.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: Create An Amazing Computer Component Quiz Using AI Instantly in OnlineExamMaker
- Part 2: 20 Computer Component Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate Questions for Any Topic
Part 1: Create An Amazing Computer Component Quiz Using AI Instantly in OnlineExamMaker
The quickest way to assess the Computer Component knowledge of candidates is using an AI assessment platform like OnlineExamMaker. With OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator, you are able to input content—like text, documents, or topics—and then automatically generate questions in various formats (multiple-choice, true/false, short answer). Its AI Exam Grader can automatically grade the exam and generate insightful reports after your candidate submit the assessment.
Overview of its key assessment-related features:
● Create up to 10 question types, including multiple-choice, true/false, fill-in-the-blank, matching, short answer, and essay questions.
● Automatically generates detailed reports—individual scores, question report, and group performance.
● Instantly scores objective questions and subjective answers use rubric-based scoring for consistency.
● API and SSO help trainers integrate OnlineExamMaker with Google Classroom, Microsoft Teams, CRM and more.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Computer Component Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is the primary function of the CPU in a computer?
Options:
A. To store data permanently
B. To process instructions and perform calculations
C. To provide power to the system
D. To display graphics on the screen
Answer: B
Explanation: The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, acts as the brain of the computer, executing instructions from programs by performing arithmetic, logical, control, and input/output operations.
2. Question: Which component is responsible for temporarily storing data that the CPU needs to access quickly?
Options:
A. Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
B. Random Access Memory (RAM)
C. Solid State Drive (SSD)
D. Read-Only Memory (ROM)
Answer: B
Explanation: RAM provides fast, temporary storage for data and instructions that the CPU is currently using, allowing for quick read and write access, which enhances overall system performance.
3. Question: What does the motherboard do in a computer system?
Options:
A. Generates heat to cool the system
B. Connects all major components and allows them to communicate
C. Stores the operating system permanently
D. Processes video signals
Answer: B
Explanation: The motherboard is the main circuit board that houses the CPU, RAM, and other essential components, providing the pathways for data transfer between them.
4. Question: Which type of memory is non-volatile and retains data even when the computer is turned off?
Options:
A. RAM
B. Cache Memory
C. ROM
D. Virtual Memory
Answer: C
Explanation: ROM (Read-Only Memory) is non-volatile, meaning it stores firmware like the BIOS that remains intact without power, unlike volatile memory such as RAM.
5. Question: What is the main purpose of a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)?
Options:
A. To manage network connections
B. To handle complex graphical computations and rendering
C. To store large amounts of data
D. To regulate the computer’s power supply
Answer: B
Explanation: The GPU is specialized for processing and rendering images, videos, and 3D graphics, offloading these tasks from the CPU to improve efficiency in visual applications.
6. Question: Which storage device uses spinning disks to read and write data?
Options:
A. SSD
B. HDD
C. USB Flash Drive
D. Optical Drive
Answer: B
Explanation: An HDD (Hard Disk Drive) employs magnetic spinning disks to store and retrieve data, making it a traditional, cost-effective option for large storage capacities.
7. Question: What component supplies electrical power to all other parts of the computer?
Options:
A. CPU
B. Power Supply Unit (PSU)
C. Motherboard
D. RAM
Answer: B
Explanation: The PSU converts AC power from the wall outlet to DC power required by the computer’s components, ensuring stable and regulated energy distribution.
8. Question: Which port is commonly used for connecting keyboards, mice, and other peripherals?
Options:
A. HDMI
B. USB
C. Ethernet
D. VGA
Answer: B
Explanation: USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports allow for easy connection of various devices, providing data transfer and power delivery in a plug-and-play manner.
9. Question: What is the function of a heat sink in a computer?
Options:
A. To increase processing speed
B. To absorb and dissipate heat from components like the CPU
C. To store additional data
D. To connect to the internet
Answer: B
Explanation: A heat sink is a passive cooling device that draws heat away from the CPU or GPU, preventing overheating and maintaining optimal performance.
10. Question: Which component allows for the expansion of features like additional graphics or sound capabilities?
Options:
A. RAM
B. Expansion Card (e.g., PCI card)
C. Hard Drive
D. Fan
Answer: B
Explanation: Expansion cards plug into slots on the motherboard, adding functionality such as better graphics or networking, by extending the system’s capabilities.
11. Question: What does BIOS stand for, and what is its role?
Options:
A. Basic Input Output System; it initializes hardware during boot-up
B. Binary Operating System; it runs applications
C. Built-In Operating Software; it manages files
D. Basic Interface for Systems; it handles user inputs
Answer: A
Explanation: BIOS (Basic Input Output System) is firmware that performs hardware checks and initializes components when the computer starts, before the operating system loads.
12. Question: Which type of RAM is commonly used in modern desktops and laptops?
Options:
A. DDR3
B. DDR4
C. SDRAM
D. EDO RAM
Answer: B
Explanation: DDR4 RAM offers higher speed, efficiency, and capacity compared to older types, making it the standard for current computer systems.
13. Question: What is the primary advantage of an SSD over an HDD?
Options:
A. Lower cost per gigabyte
B. Faster read and write speeds
C. Larger storage capacity
D. Better for mechanical durability
Answer: B
Explanation: SSDs use flash memory, providing quicker access times and no moving parts, which results in faster boot times and data transfer compared to HDDs.
14. Question: Which bus type is used for high-speed communication between the CPU and RAM?
Options:
A. USB Bus
B. PCI Express Bus
C. Front Side Bus
D. SATA Bus
Answer: C
Explanation: The Front Side Bus (FSB) connects the CPU to the northbridge, enabling rapid data exchange with RAM, which is crucial for system performance.
15. Question: What is the role of cache memory in a CPU?
Options:
A. To permanently store programs
B. To provide fast access to frequently used data
C. To connect external devices
D. To cool the processor
Answer: B
Explanation: Cache memory is a small, high-speed memory located on the CPU that stores copies of frequently accessed data from main memory, reducing access time.
16. Question: Which form factor is most common for desktop motherboards?
Options:
A. ATX
B. Micro-ATX
C. Mini-ITX
D. EATX
Answer: A
Explanation: ATX is a standard size that accommodates more expansion slots and ports, making it ideal for full-sized desktops with multiple components.
17. Question: What interface is typically used for modern high-speed SSDs?
Options:
A. SATA
B. NVMe
C. IDE
D. PATA
Answer: B
Explanation: NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is designed for SSDs connected via PCIe, offering much faster data transfer rates than traditional interfaces like SATA.
18. Question: Which component is primarily responsible for protecting internal parts from dust and physical damage?
Options:
A. CPU Cooler
B. Computer Case
C. Power Supply
D. Motherboard
Answer: B
Explanation: The computer case encloses and shields the internal components, also providing mounting points and airflow for cooling.
19. Question: What does overclocking a CPU involve?
Options:
A. Reducing the clock speed for energy savings
B. Increasing the clock speed beyond the manufacturer’s rating
C. Replacing the CPU with a newer model
D. Adding more RAM to the system
Answer: B
Explanation: Overclocking manually boosts the CPU’s clock speed to achieve higher performance, though it can lead to increased heat and potential instability.
20. Question: Which optical drive technology is used for reading and writing Blu-ray discs?
Options:
A. CD-ROM
B. DVD-RW
C. Blu-ray Drive
D. Floppy Drive
Answer: C
Explanation: A Blu-ray Drive uses laser technology to handle high-capacity Blu-ray discs, allowing for data storage, video playback, and more advanced media tasks.
or
Part 3: OnlineExamMaker AI Question Generator: Generate Questions for Any Topic
Automatically generate questions using AI