Bucket Sort is an efficient sorting algorithm designed for elements that are uniformly distributed across a range. It works by dividing the input array into a number of buckets, each representing a subrange of values. Elements from the array are then distributed into these buckets based on their values. Once distributed, each non-empty bucket is sorted individually, often using a simpler algorithm like insertion sort. After sorting the buckets, the elements are concatenated in order to produce the final sorted array. This method excels with data that is evenly spread, offering linear time complexity in the best cases, but it can be inefficient for data with a wide range or poor distribution.
Table of Contents
- Part 1: Best AI Quiz Making Software for Creating A Bucket Sort Quiz
- Part 2: 20 Bucket Sort Quiz Questions & Answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
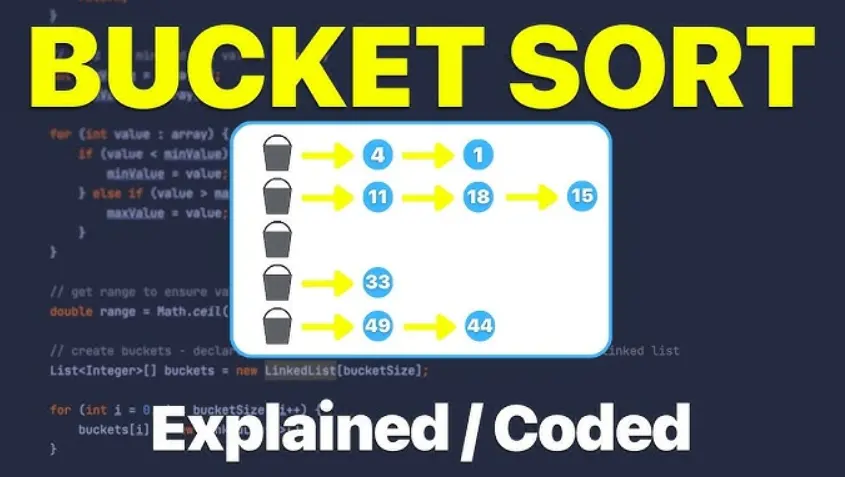
Part 1: Best AI Quiz Making Software for Creating A Bucket Sort Quiz
OnlineExamMaker is a powerful AI-powered assessment platform to create auto-grading Bucket Sort skills assessments. It’s designed for educators, trainers, businesses, and anyone looking to generate engaging quizzes without spending hours crafting questions manually. The AI Question Generator feature allows you to input a topic or specific details, and it generates a variety of question types automatically.
Top features for assessment organizers:
● Combines AI webcam monitoring to capture cheating activities during online exam.
● Enhances assessments with interactive experience by embedding video, audio, image into quizzes and multimedia feedback.
● Once the exam ends, the exam scores, question reports, ranking and other analytics data can be exported to your device in Excel file format.
● API and SSO help trainers integrate OnlineExamMaker with Google Classroom, Microsoft Teams, CRM and more.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 Bucket Sort Quiz Questions & Answers
or
1. Question: What is Bucket Sort?
Options:
A) A comparison-based sorting algorithm that uses a binary tree.
B) A sorting algorithm that divides elements into buckets and then sorts them individually.
C) A sorting algorithm that repeatedly swaps adjacent elements.
D) A sorting algorithm that uses recursion to divide the array.
Answer: B
Explanation: Bucket Sort works by distributing elements into a number of buckets and then sorting these buckets, which makes it efficient for uniformly distributed data.
2. Question: In which scenario is Bucket Sort most efficient?
Options:
A) When the input array is already sorted.
B) When elements are uniformly distributed across a range.
C) When dealing with a very small array.
D) When elements are in reverse order.
Answer: B
Explanation: Bucket Sort performs well with uniformly distributed elements because it can evenly divide them into buckets, leading to faster overall sorting.
3. Question: What is the best-case time complexity of Bucket Sort?
Options:
A) O(n log n)
B) O(n)
C) O(1)
D) O(n^2)
Answer: B
Explanation: In the best case, with uniformly distributed elements and a linear-time sort in each bucket, Bucket Sort achieves O(n) time complexity.
4. Question: What is the worst-case time complexity of Bucket Sort?
Options:
A) O(n)
B) O(n log n)
C) O(n^2)
D) O(1)
Answer: C
Explanation: If all elements fall into a single bucket, sorting that bucket could take O(n^2) time, especially if insertion sort is used.
5. Question: How are elements distributed in Bucket Sort?
Options:
A) Based on their binary representation.
B) Randomly across the array.
C) Into buckets based on their value range.
D) By swapping with the next element.
Answer: C
Explanation: Elements are placed into buckets according to their values, typically by dividing the range into intervals.
6. Question: Which sorting algorithm is commonly used to sort the elements within each bucket in Bucket Sort?
Options:
A) Quick Sort
B) Merge Sort
C) Insertion Sort
D) Heap Sort
Answer: C
Explanation: Insertion Sort is often used for sorting individual buckets because it is simple and efficient for small arrays.
7. Question: How does Bucket Sort differ from Radix Sort?
Options:
A) Bucket Sort uses keys, while Radix Sort does not.
B) Radix Sort processes digits, while Bucket Sort distributes based on value ranges.
C) They are identical algorithms.
D) Bucket Sort is always faster.
Answer: B
Explanation: Radix Sort sorts based on individual digits or places, whereas Bucket Sort groups elements into buckets based on their full values or ranges.
8. Question: Bucket Sort is particularly useful for data that is:
Options:
A) Already sorted.
B) Randomly ordered with no pattern.
C) Uniformly distributed over a range.
D) Consisting of negative numbers only.
Answer: C
Explanation: Uniformly distributed data allows for even bucket distribution, minimizing the time needed for sorting within buckets.
9. Question: What is the space complexity of Bucket Sort?
Options:
A) O(1)
B) O(n)
C) O(log n)
D) O(n^2)
Answer: B
Explanation: Bucket Sort requires additional space for the buckets, which is proportional to the number of elements, hence O(n).
10. Question: In Bucket Sort, if you have an array of numbers from 0 to 1, how many buckets might you use?
Options:
A) Exactly 1 bucket.
B) A fixed number based on the array size.
C) As many as the distinct values.
D) Typically 10 or a user-defined number.
Answer: D
Explanation: For numbers between 0 and 1, Bucket Sort often uses a predefined number of buckets, like 10, to distribute the elements evenly.
11. Question: Does Bucket Sort maintain the relative order of equal elements?
Options:
A) Yes, it is stable.
B) No, it is unstable.
C) It depends on the bucket size.
D) Only if insertion sort is not used.
Answer: A
Explanation: Bucket Sort is stable because the sorting algorithm used within buckets (like insertion sort) preserves the order of equal elements.
12. Question: What happens if the input array for Bucket Sort has elements that are not uniformly distributed?
Options:
A) It sorts faster.
B) It may become inefficient due to uneven bucket sizes.
C) It always fails.
D) No change in performance.
Answer: B
Explanation: Uneven distribution can lead to some buckets having many elements and others few, increasing the overall sorting time.
13. Question: In Bucket Sort, the process after distributing elements is:
Options:
A) Merging the buckets directly.
B) Sorting each bucket and then concatenating.
C) Recursively calling the sort.
D) Swapping elements across buckets.
Answer: B
Explanation: After distribution, each bucket is sorted individually, and then the sorted buckets are concatenated to form the final sorted array.
14. Question: Why might Bucket Sort be preferred over Quick Sort for certain datasets?
Options:
A) It has a lower space complexity.
B) It performs better on uniformly distributed data.
C) Quick Sort is always faster.
D) It doesn’t use comparisons.
Answer: B
Explanation: Bucket Sort excels with uniformly distributed data, avoiding the pivot selection issues that can make Quick Sort perform poorly in the worst case.
15. Question: A major disadvantage of Bucket Sort is:
Options:
A) It requires extra space.
B) It is very fast for all inputs.
C) It only works with integers.
D) It doesn’t handle duplicates.
Answer: A
Explanation: Bucket Sort uses additional memory for buckets, which can be a drawback for memory-constrained environments.
16. Question: For an array of n elements uniformly distributed, the average time complexity of Bucket Sort is:
Options:
A) O(n log n)
B) O(1)
C) O(n + k) where k is the number of buckets
D) O(n^2)
Answer: C
Explanation: With uniform distribution, the time is roughly O(n + k), as distributing elements is O(n) and sorting buckets is O(k) on average.
17. Question: If all elements in an array are the same, how does Bucket Sort perform?
Options:
A) It fails completely.
B) All elements go into one bucket and are sorted quickly.
C) It requires more buckets.
D) It becomes O(n log n).
Answer: B
Explanation: Identical elements would typically go into the same bucket, which can then be sorted efficiently if the bucket is small.
18. Question: What is the minimum number of buckets recommended in Bucket Sort?
Options:
A) 1
B) Equal to the array size
C) At least 2
D) It varies based on data range
Answer: D
Explanation: The number of buckets depends on the data range and distribution; there’s no fixed minimum, but it should suit the data for efficiency.
19. Question: In Bucket Sort, increasing the number of buckets generally:
Options:
A) Decreases sorting time for uniform data.
B) Makes it slower.
C) Has no effect.
D) Only works for large arrays.
Answer: A
Explanation: More buckets can lead to smaller subarrays to sort, reducing the time complexity for uniformly distributed data.
20. Question: A real-world application of Bucket Sort could be:
Options:
A) Sorting strings alphabetically.
B) Sorting exam scores that are percentages.
C) Encrypting data.
D) Searching in a binary tree.
Answer: B
Explanation: Bucket Sort is ideal for sorting data like percentages (e.g., 0-100), which can be evenly distributed into buckets for quick processing.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically Create Questions for Your Next Assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI