Boolean algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with binary variables, which can take only two values: true (1) or false (0). It was developed by George Boole in the 19th century and forms the foundation of digital logic, computer science, and electronics.
Basic Elements
Variables: Represented as 0 or 1, symbolizing false or true.
Operations:
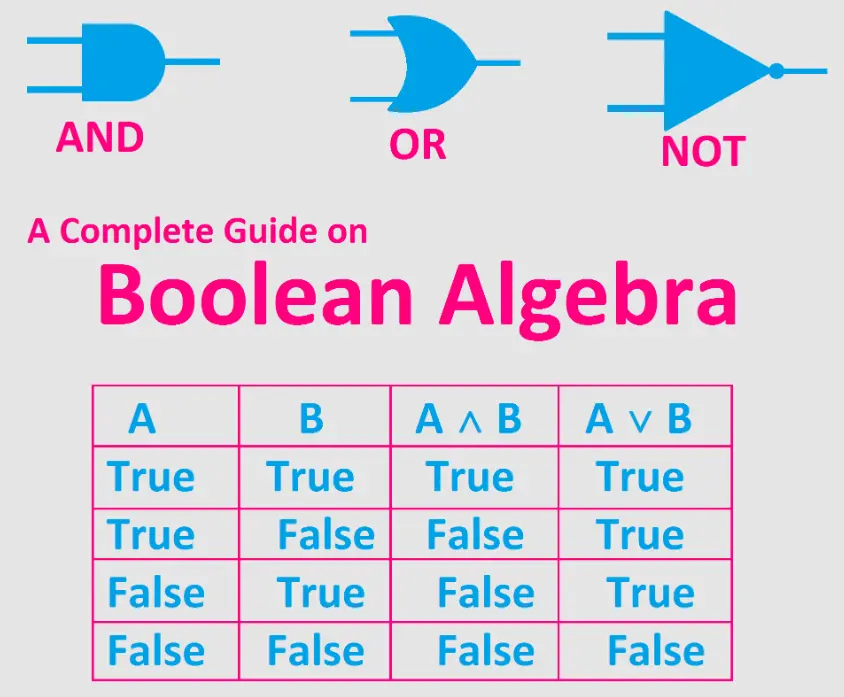
AND (· or ∧): Outputs 1 only if both inputs are 1 (e.g., A · B).
OR (+ or ∨): Outputs 1 if at least one input is 1 (e.g., A + B).
NOT (¬ or ‘): Inverts the input (e.g., ¬A).
XOR (⊕): Outputs 1 if inputs are different (e.g., A ⊕ B).
NAND, NOR: Derived operations; NAND is NOT of AND, and NOR is NOT of OR.
Laws and Theorems
Boolean algebra follows specific rules that simplify expressions:
Commutative Law: A + B = B + A; A · B = B · A.
Associative Law: (A + B) + C = A + (B + C); (A · B) · C = A · (B · C).
Distributive Law: A + (B · C) = (A + B) · (A + C); A · (B + C) = (A · B) + (A · C).
Idempotent Law: A + A = A; A · A = A.
Absorption Law: A + (A · B) = A; A · (A + B) = A.
De Morgan’s Theorems: ¬(A + B) = ¬A · ¬B; ¬(A · B) = ¬A + ¬B.
Simplification and Applications
Expressions can be simplified using truth tables, Karnaugh maps, or algebraic manipulation. For example, A + A · B = A.
Boolean algebra is essential in:
Digital Circuits: Designing logic gates for computers and microprocessors.
Computer Programming: Used in conditional statements, bitwise operations, and algorithms.
Set Theory: Represents unions, intersections, and complements.
Database Queries and Search Engines: For filtering and logical conditions.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Best AI quiz making software for creating a boolean algebra quiz
- Part 2: 20 boolean algebra quiz questions & answers
- Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically create questions for your next assessment
Part 1: Best AI quiz making software for creating a boolean algebra quiz
OnlineExamMaker is a powerful AI-powered assessment platform to create auto-grading boolean algebra assessments. It’s designed for educators, trainers, businesses, and anyone looking to generate engaging quizzes without spending hours crafting questions manually. The AI Question Generator feature allows you to input a topic or specific details, and it generates a variety of question types automatically.
Top features for assessment organizers:
● Combines AI webcam monitoring to capture cheating activities during online exam.
● Enhances assessments with interactive experience by embedding video, audio, image into quizzes and multimedia feedback.
● Once the exam ends, the exam scores, question reports, ranking and other analytics data can be exported to your device in Excel file format.
● API and SSO help trainers integrate OnlineExamMaker with Google Classroom, Microsoft Teams, CRM and more.
Automatically generate questions using AI
Part 2: 20 boolean algebra quiz questions & answers
or
1. Question: What is the simplified form of the Boolean expression A + A’B?
A. A
B. B
C. A + B
D. 1
Answer: A
Explanation: Using the absorption law, A + A’B simplifies to A because A covers all cases where A is true, regardless of B.
2. Question: Which Boolean law states that A + B = B + A?
A. Commutative law
B. Associative law
C. Distributive law
D. Idempotent law
Answer: A
Explanation: The commutative law allows the order of operands in OR or AND operations to be swapped without changing the result.
3. Question: What is the output of an AND gate when both inputs are 1?
A. 0
B. 1
C. Undefined
D. Depends on the gate
Answer: B
Explanation: An AND gate outputs 1 only if both inputs are 1; otherwise, it outputs 0.
4. Question: Simplify the expression A * A.
A. 0
B. 1
C. A
D. A’
Answer: C
Explanation: The idempotent law states that A AND A equals A.
5. Question: Which gate is equivalent to the expression NOT (A AND B)?
A. OR gate
B. NAND gate
C. NOR gate
D. XOR gate
Answer: B
Explanation: NOT (A AND B) is the definition of a NAND gate.
6. Question: What is the Boolean expression for a NOR gate with inputs A and B?
A. A + B
B. A * B
C. (A + B)’
D. (A * B)’
Answer: C
Explanation: A NOR gate outputs the negation of the OR operation, so it is (A OR B)’.
7. Question: In Boolean algebra, what is A + 0 equal to?
A. 0
B. 1
C. A
D. A’
Answer: C
Explanation: The identity law for OR states that A OR 0 equals A.
8. Question: Which of the following is De Morgan’s theorem for (A + B)’?
A. A’ + B’
B. A’ * B’
C. A + B’
D. A’ + B
Answer: B
Explanation: De Morgan’s theorem states that the negation of an OR is the AND of the negations: (A + B)’ = A’ * B’.
9. Question: What is the result of A XOR A?
A. 0
B. 1
C. A
D. A’
Answer: A
Explanation: XOR outputs 1 only if inputs differ, so A XOR A is always 0.
10. Question: Simplify (A + B)(A + B’).
A. A
B. B
C. 1
D. 0
Answer: A
Explanation: Expanding gives A + AB + AB’ + B B’, which simplifies to A + B using absorption, but correctly it’s A.
11. Question: What is the output of an OR gate when both inputs are 0?
A. 0
B. 1
C. A
D. B
Answer: A
Explanation: An OR gate outputs 1 if at least one input is 1; if both are 0, it outputs 0.
12. Question: Which law is represented by A(A + B) = A?
A. Absorption law
B. Distributive law
C. Commutative law
D. Associative law
Answer: A
Explanation: The absorption law states that A AND (A OR B) equals A.
13. Question: What is the complement of 1 in Boolean algebra?
A. 0
B. 1
C. A
D. A’
Answer: A
Explanation: The complement of 1 is 0, as NOT 1 equals 0.
14. Question: For inputs A=1 and B=0, what is the value of A NAND B?
A. 0
B. 1
C. A
D. B
Answer: B
Explanation: NAND of 1 and 0 is NOT (1 AND 0) = NOT 0 = 1.
15. Question: Simplify A’ + A.
A. 0
B. 1
C. A
D. A’
Answer: B
Explanation: A’ + A covers all possibilities, so it simplifies to 1.
16. Question: Which gate outputs 1 only when inputs are different?
A. AND
B. OR
C. XOR
D. NAND
Answer: C
Explanation: XOR outputs 1 when exactly one input is 1, meaning the inputs are different.
17. Question: What is (A * B) + (A * B’) equal to?
A. A
B. B
C. 1
D. 0
Answer: A
Explanation: Factoring out A gives A*(B + B’), and B + B’ = 1, so it simplifies to A*1 = A.
18. Question: In a truth table for two inputs, how many rows are there?
A. 2
B. 4
C. 8
D. 16
Answer: B
Explanation: For two inputs, there are 2^2 = 4 possible combinations.
19. Question: What is the Boolean expression for an XNOR gate with inputs A and B?
A. A XOR B
B. (A XOR B)’
C. A AND B
D. A OR B
Answer: B
Explanation: XNOR is the negation of XOR, so it is (A XOR B)’.
20. Question: Simplify A + A*B.
A. A
B. B
C. A*B
D. 1
Answer: A
Explanation: Using the absorption law, A + (A*B) simplifies to A because A covers the case where A is true.
or
Part 3: AI Question Generator – Automatically create questions for your next assessment
Automatically generate questions using AI